* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Jing 1 Mrs. Jing English I Mythology Table of the Gods KEY 7
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
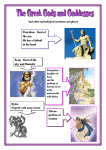
Jing 1 Mrs. Jing English I Mythology Table of the Gods KEY 7 January 2013 ZEUS Introduction king of the gods control the weather 'cloud-gatherer' 'thunderer' The ancient Greeks believed that when lightning struck earth, it was a sign of Zeus being present. Symbols spear-butt bronze helmet Places wife and sister of Zeus took terrible revenge on his illegitimate children a high crown Sceptre- a symbol of office Objects bronze axe silver pin cave on Mount Ida in Crete Heraion- one of oldest temples in Greece built in her honor Olympic Games Story Places Put potion in Kronos’s cup to cause him to vomit the children he had swallowed. Zeus and brothers and sisters won the battle against their father. Festivals HERA Symbols Introduction Objects thunderbolt seated on a throne Story She was so jealous of Hercules- son of Zeus that she delayed the day of his birth so that a different woman's child became king. Festivals Heraia (only women competed) Jing 2 ATHENA Introduction Goddess of war Goddess of cunning wisdom Invented chariot, bridle, and first ship Olive tree sacred to her Symbols Objects invented aulos- a pipe instrument god of the sun, truth, music, poetry, dance and healing Objects Music and stringed instruments Places Introduction associated with the owl Story Associated with Athens Parthenon built in her honor Festivals APOLLO Symbols bow in war lyre in peace Panathenaiasacrifices, competitions and a huge procession to present a new robe to the ancient statue of Athena on the Acropolis Story heartbroken. Even as a tree Daphne shuddered at his touch. Places oracle at Delphi Athena emerged from Zeus' skull, fully grown and dressed for battle. Festivals Pythian gamesmusic and poetry competitions Winner received wreath of laurel leaves Jing 3 DEMETER Introduction goddess of fertility and agriculture Symbols Objects fruit including pomegranates Introduction God of sea and horses caused earthquakes Objects offerings from sailors and fishermen mature woman sheaves of grain Story Places EleusisEleusinian Mysteries- secrets of agriculture and fertility POSEIDON Symbols trident white horses and golden chariot Places temple at Cape Sounion daughter Persephone how the seasons changed Festivals Thesmophoria was a festival for women only Story father of Polyphemoscreated storm to wreck Odysseus’ ship Festivals Isthmian Games Jing 4 APHRODITE Introduction Goddess of love and beauty wife of Hephaistos but in love with Ares Symbols Objects mirror god of travel, business, weights and measures and sports. messenger of the gods and guided the souls of the dead to the underworld patron of herdsmen, thieves, graves and messengers staff caused men to fall asleep instantly. Places Cyprus Traveller's hat. Herald's staff. Winged sandals. Objects Places Herm- a pillar like statue placed at the entrance of Greek homes. Borders and boundaries Adonia Story Judgment of Paris Festivals HERMES Symbols Introduction birds, doves, geese, sparrows Story On day of birth, stole Apollo’s cattle—then jumped back into bed When Apollo complained to Zeus, Zeus found this funny. Festivals Day of the Pots Jing 5 ARTEMIS Introduction Goddess of hunting, archery, and childbirth Goddess of wild animals Twin sister of Apollo Objects Pregnancy and childbirth were associated with her even though she had no children of her own. Symbols Bow and arrow Wild animals Places Ephesos- one of seven wonders of the world Story Actaeon turned into a stag for seeing her and nymphs bathing Festivals Brauronia- young girls 5-10 dressed up as bears ARES Introduction God of war but not cunning in battle Zeus believed he was the most hated of all his children. Objects Bronze armour Symbols Armour and helmet Places Thrace- homeland- a wild and barbarous place Story Was Aphrodite’s lover even though she was married to Hephaistos Festivals Before battle- soldiers offered a sacrifice to him Jing 6 HEPHAISTOS Introduction -God of fire, blacksmiths,volcanoes, and craftworkers -Thrown out of Olympus because he was lame -Married to Aphrodite Symbols Twisted foot tools Objects metalworkers Places Hephaisteion in Athenstemple dedicated to this god and Athena DIONYSOS Symbols Introduction Fun loving god of high spirits, strong emotions, and wine Story His mother Hera threw him out because he had a disfigured foot. However, she welcomed him back once she saw his talents as a blacksmith. Festivals Chalkeia was a special feast for bronze workers. Story Once turned pirates into dolphins vines Closely associated with drama and the theatre Objects Two-handled drinking cup Places Thebes Festivals Great Dionysia- annual theatre competition in Athens Jing 7 Mythology Notes: mythology- the study or collecting of myths myth“Myths are stories that are based on tradition. Some may have factual origins, while others are completely fictional. But myths are more than mere stories, and they serve a more profound purpose in ancient and modern cultures. Myths are sacred tales that explain the world and man's experience. The subjects of myths reflect the universal concerns of mankind throughout history: birth, death, the afterlife, the origin of man and the world, good and evil and the nature of man himself. A myth taps into a universal cultural narrative, the collective wisdom of man.” http://www.pbs.org/mythsandheroes/myths_what.html Function of a Myth: A myth can… -explain or interpret a natural phenomenon or occurrence. -explain the creation of the world. -teach people moral lessons. -explain some historical event. -explain some ancient cultural views or practices. -reveal the common emotions and experiences of mankind. Jing 8 Mythology Essential Questions: 1. What is the purpose of mythology? 2. What common themes run through the mythical stories themselves? 3. What vocabulary is derived from the characters and events in the literature? 4. What is the impact of mythology on modern culture? 5. What is the significance of anthropomorphism? 6. What common theme(s) does one notice between Greek mythology and elements of Shakespeare’s work (of Edgar Allan Poe’s short stories)?