* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download chapter 15 * foot, ankle and lower leg
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
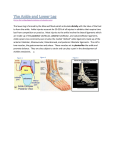
CHAPTER 15 – FOOT, ANKLE AND LOWER LEG FOOT ANATOMY FOOT ANATOMY It is complex! 26 bones 33 joints Over 100 muscles, tendons and ligaments ANATOMY - BONES PHALANGES (Toes) – 14 Big toe has two phalanges, the rest of the toes have three Proximal, middle, and distal FOOT ANATOMY - BONES METATARSALS – 5 1ST one is medial and 5th one is lateral FOOT ANATOMY – 26 BONES TARSAL BONES – 7 Calcaneus – heel bone Talus – forms the ankle Navicular – medial in respect to the talus Cuboid - lateral Cuneiforms (3) FOOT ANATOMY PLANTAR FASCIA Broad, flat tendonous structure that runs on the undersurface of the foot Starts on the calcaneus and inserts onto the heads of the metatarsals Supports the arch of the foot FOOT ANATOMY - ARCHES Support body weight and absorb shock There are four arches: MEDIAL LONGITUDINAL ARCH LATERAL LONGITUDINAL ARCH METATARSAL ARCH TRANSVERSE ARCH FOOT - MOTIONS Toes Flexion and Extension Foot Pronation – like fallen arch Supination – high arch ANKLE ANATOMY - BONES BONES Two bones in the lower leg Tibia – medial, larger, weight bearing Medial Malleolus Fibula Lateral Malleolus Two tarsal bone Talus Calcaneus ANKLE ANATOMY - JOINTS TRUE ANKLE JOINT Tibia, fibula and talus Mortise Definition: where the talus fits into the tibia and the fibula ANKLE ANATOMY - JOINTS Subtalar joint Between the Talus and the Calcaneus ANKLE ANATOMY - LIGAMENTS LATERAL – 3 ligaments named for bones Anterior talofibular (ATF) Calcaneofibular (CF) Posterior talofibular (PTF) ANKLE ANATOMY - LIGAMENTS MEDIAL Deltoid Strong ligament 4 parts that form one ligament ANKLE ANATOMY - LIGAMENTS TIBIOFIBULAR LIGAMENTS – holds tibia and fibula together Anterior tibiofibular Posterior tibiofibular ANKLE MOTIONS Dorsiflexion Plantarflexion Inversion Eversion LOWER LEG ANATOMY Bones Tibia Fibula LOWER LEG MUSCLES The muscles are in four compartments with 2-4 muscles in each compartment Compartments are held together by fascia LOWER LEG MUSCLE COMPARTMENTS 1. LATERAL – everts the ankle 2. ANTERIOR – dorsiflexes the ankle 3. DEEP POSTERIOR – plantarflexes the ankle (the calf muscle) 4. POSTERIOR MEDIAL – inverts and plantarflexes the ankle LOWER LEG - Major Muscles and Actions Anterior Tibialis - dorsiflexor Peroneals - evertors Gastrocnemius – plantarflexor Soleus – plantarflexor Posterior Tibialis – invertor PLANTAR FASCIITIS Common with athletes who are on toes and/or have high arches Causes: Not enough arch support in shoes, tight calf muscle Signs/Symptoms: Pain occurs in the heel to mid-foot, especially with dorsiflexion Hurts in the morning, feels better as they warm up Treatment: Gentle stretches, roll on tennis ball or frozen can, arch taping or orthodics. JONES FRACTURE Fracture of the base of the 5th metatarsal Causes: overuse; inversion; rotational forces S/S: Feels and hears a ‘pop’; pain in the lateral foot Tx: immobilization (cast) 6-8 weeks or longer, often requires surgery BUNIONS (HALLUX VALGUS) Deformity of the head of the 1st metatarsal Cause: extra bone is laid down on head of 1st metatarsal Great toe becomes malaligned S/S: Pain, swelling and deformity of big toe joint Treatment: Proper shoes; doughnut pad over the bunion; surgery? MORTON’S NEUROMA Neuroma is a mass about the nerve sheath S/S: burning, cramping, numb feeling in space between third and fourth toes. Cause: Hyperextension of toes and wearing shoes with narrow toe boxes can increase symptoms Tx: teardrop pad under the metatarsal heads, good shoe selection, possible surgery TURF TOE Great Toe sprain Cause: Hyperextension of the big toe at the metatarsal phalangeal joint; kicking something Common on artificial turf b/c turf shoes allow more motion S/S: swelling and pain in the joint Tx: RICE, rigid insoles or toe boxes, taping to prevent hyperextension of toe INGROWN TOENAILS Cause: leading side of toenail grows into skin, usually results in infection and pain May trim nails too short or ill-fitting shoes S/S: Inflammed nail bed, may have drainage/pus Tx: May need to refer to doctor; soak in betadine bath; pack cotton under toenail PUBLIC SERVICE ANNOUNCEMENT HIGH HEELS Loads 5 times your body weight onto your heel Overloads forefoot Deforms the arch Reduces shock absorption Plantar fasciitis Leads to inflamed nerves in your toes Morton’s Neuroma Shortens your calf Achilles tendinitis Changes your center of gravity – more forward Have to extend back to compensate ANKLE SPRAINS Inversion Most common type of ankle sprain Accounts for 80% of all sprains AKA ‘a lateral ankle sprain’ First degree sprain Only involves the anterior talofibular ligament Mild pain, tenderness, and swelling No instability ANKLE SPRAINS Inversion Second degree sprain Anterior talofibular ligament is torn and calcaneofibular ligament is injured as well Most painful Moderate swelling Mild Instability ANKLE SPRAINS Inversion Third degree sprain Complete tear of all three lateral ligaments Uncommon Lots of pain, but it can subside Very unstable Usually requires surgery ANKLE SPRAINS Eversion Not as common Can occur more on tartan surfaces and artificial turf Everything is worse (pain, swelling, etc) when compared to an inversion injury If the deltoid tears, the tibiofibular ligaments may tear also High Ankle Sprain Involves Anterior Inferior Tibiofibular (AITFL) Ligament Injury allows tibia and fibula to separate High Ankle Sprain Cause: Inversion with rotation; rotation of foot S/S: pain with external rotation of foot; tender over AITFL Treatment: RICE, may need to be immobilized; possible surgery if severe enough Ankle Fractures Always need to suspect a fracture when evaluating a potential sprained ankle Cause: Too much motion S/S: immediate swelling, point tender over the bone, does not want to weight bear Treatment: splint, ice, x-ray Cast 6-8 weeks MEDIAL TIBIAL STRESS SYNDROME ‘SHIN SPLINTS’ Occurs in distal 2/3 of posterior/medial tibia Causes: pronation, lack of flexibility in the lower legs, hard surfaces, hills, muscle weakness, poor shoes, increasing running distance too quickly S/S: resisted plantar flexion and inversion should hurt, pain is just off the tibia Treatment : prevention (shoes, arch support), strengthening, stretching, ice massage, contrast bath, tape arches Refer to MD if no improvement to rule out stress fracture COMPARTMENT SYNDROME Occurs when pressure increases in compartment and shuts off blood and nerve supply to the foot Most often occurs in the anterior and deep posterior compartment THREE TYPES Acute Acute Exertional Chronic ACUTE COMPARTMENT SYNDROME Medical emergency Causes: direct blow to the lower leg Usually in the anterior lower leg Symptoms come about several hours later S/S: compartment is tense, warm, red and shiny; complains of (c/o) deep aching pain; circulation and sensory problems in foot Tx: ice, elevation – refer to ER immediately ACHILLES TENDINITIS Chronic, overuse condition that comes about gradually Causes: running and jumping, repetitive stress, running up hills, poor flexibility S/S: achy type pain, Achilles is tender on palpation, pain with standing plantarflexion, may have crepitus, hurts to warm up and to cool down TREATMENT If there is crepitus, no running for 1-2 weeks Stretch! Heel lift in both shoes Orthodics Heat and/or ice ACHILLES TENDON RUPTURE Achilles in largest tendon in body For Gastronemius and Soleus muscles Most common tearing spot is 1” above its insertion on the calcaneus Causes: Sudden, forceful plantar flexion and extension of the knee, age, previous tendinitis S/S: Feel and hear a snap, “kicked in the leg”, very weak plantarflexion, no Achilles observed Tx: Immobilization to ER, surgery?