* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Bundle 1 - Humble ISD
Age of the Earth wikipedia , lookup
Algoman orogeny wikipedia , lookup
Sedimentary budget wikipedia , lookup
Geology of Great Britain wikipedia , lookup
Geology of the Death Valley area wikipedia , lookup
Geomorphology wikipedia , lookup
Marine geology of the Cape Peninsula and False Bay wikipedia , lookup
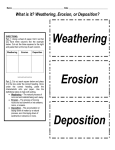
External Forces Formation of Sedimentary Rock HISD Elementary Science Unit Connections Water and wind can be used to create energy but are also the main agents in changing the Earth’s surface. How can water change the Earth’s surface? How can wind change the Earth’s surface? What landforms are created through changes from water or wind? Misconceptions Thinking that weathering and erosion are essentially the same thing and the words can be used interchangeably. Fact: Weathering is the physical or chemical break down of rocks and erosion is the process of transporting sediment. The processes can happen at nearly the same time but they are completely different processes. Erosion is always bad. Fact: Delta areas, like the Mississippi and the Nile, were created by the deposition of eroded sediment carried downriver. Without erosion, these rich, fertile farming areas would not exist. Not acknowledge a rock whose grains are actually smaller pieces of rock, is itself a rock made up of smaller rocks. Fact: In geology, a rock made up of other pieces of rock a sedimentary rock. If those pieces are made up of individual grains of sand, the bigger rock is sandstone. If those pieces are bigger, like pebbles or boulders, the huge rock with all the pieces together is a "conglomerate." Concept & Processes & Skills Rocks are broken down into sediments such as sand and silt by the slow process of weathering. Over time, erosion carries sediment to new places and deposits the sediment. The Earth’s landforms are created from the processes of weathering, erosion, and deposition. Landforms such as stalagmites, stalactites, deltas, and sand dunes, are created through the deposition of sediments. Landforms such as canyons, rivers, sea arches, and other smaller landforms are made by water weathering and erosion. U-valleys are created by glacier weathering and erosion. Formation of sedimentary rock is caused by layers of sediments cemented together by heat and pressure. Graphic Cues Student Outcomes Explain how landforms, such as rivers, canyons, and sea arches, are created through weathering and erosion from water. What does a canyon look like? How did it form? What evidence do you have? What does a sea arch look like? How did it form? What evidence do you have? How did weathering, erosion, and deposition help form these landforms? Did this process happen quickly or slowly? Why? Explain how landforms, such as U-valleys, are created through weathering and erosion from ice. What does a U-valley look like? How did it form? What evidence do you have? How did weathering, erosion, and deposition help form these landforms? Did this process happen quickly or slowly? Why? Explain how landforms, such as sand dunes and desert arches, are created through weathering and erosion from wind. What does a desert arch look like? How did it form? What evidence do you have? What evidence helped make the decision? How did weathering, erosion, and deposition help form these landforms? Explain how landforms, such as sand dunes, deltas, and stalagmites, are created through deposition. Was the landform here originally? How did the landform form? Where did the sediment in this landform come from? How did the sediment get here? Explain the process that leads to landslides. What external force can cause a landslide? What other forces are involved in landslides? (gravity) Are landslides a fast change or a slow change? What would happen to the area below a landslide? (homes, cities) Explain how rocks can be turned into sediment slowly What effect does water have on rocks? What effect does wind have on rocks? What effect does ice have on rocks? What process occurs to move sediment? Explain the processes that cause rocks to become smaller. Explain what had to happen to a rock to create sand. Demonstrate how sedimentary rocks consist of sediments, minerals, and organic materials that have been compacted and cemented together. What types of materials do you find in a sedimentary rock? What causes the sediments to be pressed together? Weathering Erosion Deposition Sediment Sand dune Glacier Vocabulary Focus Key Vocabulary for the Week Rock layer Sedimentary rock Canyon Delta Compaction Cementation Mountain Hill Valley Plain Landform