* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Geography 12
Terra Australis wikipedia , lookup
Provenance (geology) wikipedia , lookup
Composition of Mars wikipedia , lookup
History of geology wikipedia , lookup
History of Earth wikipedia , lookup
Geochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Geomorphology wikipedia , lookup
Great Lakes tectonic zone wikipedia , lookup
Plate tectonics wikipedia , lookup
Algoman orogeny wikipedia , lookup
Geology of Great Britain wikipedia , lookup
Large igneous province wikipedia , lookup
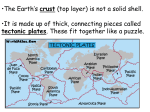
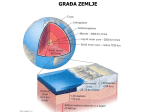
Chapter 6 Objectives: Geography 12 Worksheet 6.6 Plate Interiors: Zones of Inactivity Read pages 111 – 114 of Planet Earth: A Physical Geography. Answer the following questions: Vocabulary (1 mark each) /21 Cratons: The most stable part of a continent, often made up of ancient rocks, that experiences few earthquakes or volcanic eruptions; often know as shields Accretion: The process of growth through accumulation; often used to refer to the growth of the planets through the gravitational attraction of plantesimals, asteroids, and meteoroids: the growth of continents or cratons by the addition of new rocks along their edges through mountain-building activity or collisions with other blocks of continental crust. Supercontinent: A single, massive continent made up of all the world’s continents; Pangea is the last supercontinent that began to break up about 100 million years ago to form the smaller, more numerous continents we know today Appreciate the power and scope of tectonic processes and their effects Appreciate the slowness of tectonic processes based on a human time scale Understand that the lithosphere is an everchanging part of a dynamic planet Understand the general pattern of tectonic activity over geologic time and explain the location pattern of tectonic activity over the earth’s surface Explain the tectonic processes that shape the earth’s surface, including folding, faulting, and volcanic activity Describe and explain the pattern of major surface features created by tectonic processes Predict the nature and general patterns of occurrence of tectonic activities and processes, especially earthquakes and volcanic eruptions Describe the positive and negative aspects of tectonic activities Short Answer (2 marks each) 1. Scientists speculate ocean floor rock is much younger that continental rocks. Why would ocean floor rocks be younger? Because of the subduction. The rocks at subduction zones are consumed as they migrate to the ansthenosphere. Continental rocks on the other hand are lighter and are not consumed at subduction zones, allowing them to stick around much longer. 2. Cratons are described as the roots of mountains. Explain. They are actually what is left from millions of years of erosion, so they are called the roots of the mountains. 3. Briefly describe the process of accretion. The edges of continents are often plate boundaries and are active zones of mountain building. This is one way continents increase in size. Another way they increase in size is through erosion of the mountains, depositing eroded material at the edge of the continent. 4. How did Wegener explain his idea of a supercontinent splitting up and the pieces (continents) moving apart from each other? He looked at the shape of the continents and concluded that because they look like the fit together they must have drifted apart. Later, scientists theorized thatThe supercontinent acted as a thermal cap, allowing thermal activity to increase under the supercontinent. This caused hills which allowed the continents to split and slide away from each other. 5. Using an outline map of the present world, reassemble the continent of Pangea. Color each continent and then cut and paste them into Pangea. (5 marks for neatness, 5 for accuracy)