* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download C_Energy Momentum 2008
Specific impulse wikipedia , lookup
Hooke's law wikipedia , lookup
Newton's theorem of revolving orbits wikipedia , lookup
Eigenstate thermalization hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Classical mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Relativistic quantum mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Equations of motion wikipedia , lookup
Center of mass wikipedia , lookup
Matter wave wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnetic mass wikipedia , lookup
Rigid body dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Work (thermodynamics) wikipedia , lookup
Newton's laws of motion wikipedia , lookup
Hunting oscillation wikipedia , lookup
Mass versus weight wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical and experimental justification for the Schrödinger equation wikipedia , lookup
Centripetal force wikipedia , lookup
N-body problem wikipedia , lookup
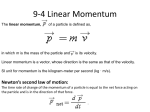
Physics C Energy and Momentum When does a force do positive work? Name:___________________ b) The work done by the rope on the sled When does a force do zero work? c) The work done by friction on the sled. When does a force do negative work? Units of Work SI System: Dot product equation for work: British System: cgs System: How to evaluate the dot product for work if given magnitudes and directions of vectors: Atomic Level: Problem: A droplet of water of mass 50 mg falls at constant speed under the influence of gravity and air resistance. After the drop has fallen 1.0 km, what is the work done by a) gravity and b) air resistance? How to evaluate the dot product for work if given unit vector representation of vectors: Applications of the dot product: Problem: A sled loaded with bricks has a mass of 20.0 kg. It is pulled at constant speed by a rope inclined at 25o above the horizontal, and it moves a distance of 100 m on a horizontal surface. If the coefficient of kinetic friction between the sled and the ground is 0.40, calculate: a) The tension in the rope. When is the dot product biggest? 6/24/2017 1 Bertrand • Problem: Determine the work done by the force as the particle moves from x = 2 m to x = 8 m. Problem: Vector A has a magnitude of 8.0 and vector B has a magnitude of 12.0. The two vectors make an angle of 40o with each other. Find A•B. F (N) 40 20 0 2 4 6 8 10 12 x (m) -20 -40 Problem: A force F = (5.0i + 6.0j – 2.0k)N acts on an object that undergoes a displacement of r = (4.0i – 9.0j + 3.0k)m. How much work was done on the object by the force? Problem: A force acting on a particle is Fx = (4x – x2)N. Find the work done by the force on the particle when the particle moves along the x-axis from x= 0 to x = 2.0 m. Problem: A force F = (5.0i – 3.0j) N acts upon a body which undergoes a displacement d = (2.0i – j) m. How much work is performed, and what is the angle between the vectors? Problem: Derive an expression for the work done by a spring as it is stretched from its equilibrium position Formula for calculating work for infinitesimal displacement: Problem: How much work does an applied force do when it stretches a nonlinear spring where the force varies according to the expressions F = (300 N/m) x – (25 N/m2) x2 from its equilibrium length to 20 cm? Integral expression for work when force is variable with position: 6/24/2017 2 Bertrand Define what is meant by “net work” What is the power expended by the probe’s engines? The acceleration due to gravity of Zombie is ½ that of earth’s. State the work-energy theorem in equation form: Problem: Develop an expression for the power output of an airplane cruising at constant speed v in level flight. Assume that the aerodynamic drag force is given by FD = bv2. Give an equation for kinetic energy: Problem: A force of F1 = (4.0 i + j) N and another of F2 = -4.0 j N act upon a 1 kg object at rest at the origin. What is the speed of the object after it has moved a distance of 3.0 m? By what factor must the power be increased to increase airspeed by 25%? Problem: Using what you know about units, calculate how many Joules is in a kilowatt-hour. Define power: Give several equations for calculating power: Give the SI unit of power: Conservative forces: Work in moving an object is path independent. Work in moving an object along a closed path is zero. Work is directly related to a negative change in potential energy Ex: gravity, electrostatic, magnetostatic, springs Problem: A 1000-kg space probe lifts straight upward off the planet Zombie, which is without an atmosphere, at a constant speed of 3.0 m/s. Non-conservative forces: Work is path dependent. Work along a closed path is NOT zero. Work may be related to a change in mechanical energy, or thermal energy Ex: friction, drag, magnetodynamic 6/24/2017 3 Bertrand Define potential energy: Problem: Gravitational potential energy for a body a large distance r from the center of the earth is defined as shown below. Derive this equation from the Universal Law of Gravity. Give examples of potential energy: How does potential energy relate to work? Law of Conservation of Mechanical Energy Gravitational potential energy: Problem: A single conservative force of F = (3i + 5j) N acts on a 4.0 kg particle. Calculate the work done if the particle if the moves from the origin to r = (2i - 3j) m. Does the result depend on path? Spring potential energy: What is the speed of the particle at r if the speed at the origin was 4.0 m/s? Problem: Three identical springs (X, Y, and Z) are hung as shown. When a 5.0-kg mass is hung on X, the mass descends 4.0 cm from its initial point. When a 7.0-kg mass is hung on Z, how far does the mass descend? What is the change in potential energy of the system? 6/24/2017 4 Bertrand Sample Problem: A bead slides on the loop-theloop shown. If it is released from height h = 3.5 R, what is the speed at point A? How great is the normal force at A if the mass is 5.0 g? What relationship exists between force and potential energy? Stable Equilibrium: General statement of the Law of Conservation of Energy (including dissipative forces). Unstable Equilibrium Sample Problem: A 2,000 kg car starts from rest and coasts down from the top of a 5.00 m long driveway that is sloped at an angel of 20o with the horizontal. If an average friction force of 4,000 N impedes the motion of the car, find the speed of the car at the bottom of the driveway. Neutral Equilibrium Equation that relates force and potential energy: Problem: A parachutist of mass 50 kg jumps out of a hot air balloon 1,000 meters above the ground and lands on the ground with a speed of 5.00 m/s. How much energy was lost to friction during the descent? Stable equilibrium equations: Unstable equilibrium equations: Neutral equilibrium equations: 6/24/2017 5 Bertrand Problem: The potential energy of a two-particle system separated by a distance r is given by U(r) = A/r, where A is a constant. Find the radial force F that each particle exerts on the other. What is the momentum of the system of football players? Define Impulse: Problem: A potential energy function for a twodimensional force is of the form U = 3x3y – 7x. Find the force acting at a point (x,y). Equations for impulse: Problem: Restate Newton’s 2nd Law in terms of impulse. Define linear momentum: Problem: A 150-g baseball moving at 40 m/s 15o below the horizontal is struck by a bat. It leaves the bat at 55 m/s 35o above the horizontal. What is the impulse exerted by the bat on the ball? Equations for linear momentum: Problem: How fast must an electron move to have the same momentum as a proton moving at 300 m/s? If the collision took 2.3 ms, what was the average force? Problem: A 90-kg tackle runs north at 5.0 m/s and a 75-kg quarterback runs east at 8.0 m/s. 6/24/2017 6 Bertrand State the Law of Conservation of Linear Momentum What kinds of energy and momentum changes characterize each type of collision? Elastic: Inelastic: Problem: An 85-kg lumberjack stands at one end of a floating 400-kg log that is at rest relative to the shore of a lake. If the lumberjack jogs to the other end of the log at 2.5 m/s relative to the shore, what happens to the log while he is moving? Explosion: Problem: A 1.5 kg cart traveling at 1.5 m/s collides with a stationary 0.5 kg cart and sticks to it. At what speed are the carts moving after the collision? Problem: Two blocks of mass 0.5 kg and 1.5 kg are placed on a horizontal, frictionless surface. A light spring is compressed between them. A cord initially holding the blocks together is burned; after this, the block of mass 1.5 kg moves to the right with a speed of 2.0 m/s. A) What is the speed and direction of the other block? B) What was the original elastic energy in the spring? Problem: A 1.5 kg cart traveling at 1.5 m/s collides elastically with a stationary 0.5 kg cart. At what speed are each of the carts moving after the collision? Describe an elastic collision: Problem: What is the recoil velocity of a 120-kg cannon that fires a 30-kg cannonball at 320 m/s? Describe an inelastic collision: Describe an explosion: 6/24/2017 7 Bertrand Sample problem: A pool player hits a cue ball in the x-direction at 0.80 m/s. The cue ball knocks into the 8-ball, which moves at a 35o angle above the x-axis. Assuming the collision is elastic, determine the angle of deflection of the cue ball. Center of Mass Problem y 2R x How do you calculate the center of mass for a system of point masses? Sample Problem y Problem: Find the x-coordinate of the center of mass of a rod of length L whose mass per unit length varies according to the expression = x. Determine the Center of Mass. 2 kg Problem: A thin strip of material of mass M is bent into a semicircle of radius R. Find its center of mass. x 0 1 kg -2 -2 0 Determine the center of mass of this shape. For more complicated problems, how do you determine the center of mass? Define center of mass 2 3 kg 2 4 Equation of motion of a System of Particles 6/24/2017 8 Bertrand