* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download What is the theory of plate tectonics
Spherical Earth wikipedia , lookup
Post-glacial rebound wikipedia , lookup
History of geomagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Geochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Age of the Earth wikipedia , lookup
Oceanic trench wikipedia , lookup
Tectonic–climatic interaction wikipedia , lookup
History of geology wikipedia , lookup
Mantle plume wikipedia , lookup
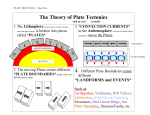
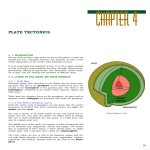
The Structure of the Earth & Plate Tectonics – Restless Planet What is the theory of plate tectonics? The Theory of Plate Tectonics states that _______________________ ________________________________________________________. In ________, Alfred Wegener introduced a hypothesis of continental drift, but he did not fully understand what caused the plates to move. As scientists amassed more data, Wegener’s hypothesis was amended to become the plate tectonic theory. A ____________ is an explanation of a scientific process that has been successfully tested. The _____________________________________ help scientists to understand why earthquakes, volcanoes, and mountain building occur. Scientists believe these plates have been moving for millions of years. Their research indicates that 250 millions years ago, the Earth's continents were all grouped together into one super-continent called _____________. About 200 million years ago, Pangaea covered approximately 30% of Earth’s surface. A large ocean, Panthalassa, covered the rest of the planet. Some clues leading scientists to accept the idea of Pangaea were: • ________: Fossils of the reptile Mesosaurus have been found in South America and Africa. Since the reptile couldn’t swim that distance, Wegener hypothesized that this reptile lived on both continents when they were joined. Additionally, plant fossils and matching rock layers have been found on both continents. • ________: Similar rocks were found in United States, Western Europe, and Greenland. • ________: Glacial deposits found in South America, Africa, India and Australia provide additional evidence that continents were connected. THE STRUCTURE OF THE EARTH The Earth is made up of three main layers: _______ __________ __________ Draw: The Crust: This is where we ____________. The crust is made up of: (describe) 1. ____________________ 2. _____________________ THE EARTH’S LAYERS The crust, mantle and core are labels for describing ________________ _______________________________________________________. Crust - The crust is Earth’s thin, outermost layer. __________________ is thick and made of low-density rock, such as granite. ________ crust is thin and made of denser rock, such as basalt. Mantle -The mantle is made of dense, _______________ minerals. Core - The Earth’s core is a hot, dense sphere of _________________. The lithosphere, asthenosphere, mesosphere, outer core & inner core distinguish between the 5 physical layers of the Earth. _________ the cool, outermost layer of the Earth. It consists of the crust and the rigid, uppermost part of the mantle. It is divided into huge pieces called tectonic plates, which move around on top of the asthenosphere. ____________- the solid, soft layer of the mantle below the lithosphere. It is made of mantle rock that flows very slowly, allowing the tectonic plates to move on top of it. __________ - or “middle sphere,” is the solid lower part of the mantle below the asthenosphere. __________ - the outer shell of Earth’s core. It is made of liquid iron and nickel. ___________ - a sphere of solid iron and nickel. Question: Describe the difference between the crust-mantle- core AND LAMOIC Question: What is plate tectonics in your own words: Why are there tectonic plate interactions? Earth is a _______ planet sailing through ______ space. Most of the _________ of our planet is hot enough to flow. The surface of Earth, however, is chilled as it loses heat into space. As a result, the rocks of Earth’s surface are hard and brittle. The cold outer layer of our planet, which holds together as a rigid shell, is not made of one solid piece. Instead this shell is broken into separate pieces, or _______________, that slide on top of the _________ interior. The tectonic plates are driven by the flowing part of the mantle, it sets them in motion. The movement of the plates causes a complex puzzle of plate collisions around the globe. Plate Tectonics (Label map with listed plates) The Earth’s crust is divided into __________ major plates, which are moved in various directions. Plate Examples include: _________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________ This plate motion causes them to ____________, ___________________ or ____________ against each other. What are tectonic plates made of? & what is below them? Plates are made of rigid _____________________. The lithosphere is made up of the ________ and the upper part of the ______. Below the lithosphere is the _____________________. Plate Movement “Plates” of lithosphere are moved around by the underlying hot mantle’s _____________________currents Describe how a convection current works and draw: There are three types of plate-plate interactions based upon relative motion: ________________ boundary - where plates collide ________________ boundary - where plates separate ________________ boundary - where plates slide past one another What happens at the convergent boundary? What forms around that boundary? Plates converge, which means __________________________________. Usually an oceanic plate converges with a continental plate. Since oceanic plates are more dense than continental plates, ocean plates are subducted or go down into the mantle in an area called the _____________zone. This type of boundary can also create a deep sea ____________. At the subduction zone the temperature of the rocks rises and causes them to melt, which forms magma that is forced upwards to create __________. Divergent boundary Plates separate, which means _________________________________. Usually an oceanic plate diverges from another oceanic plate. ____________________________ occurs at divergent oceanic plate boundaries and leads to the creation of new ocean floor. What happens at a divergent boundary? What forms along that boundary? As two tectonic plates slowly separate, ________________________ from within the mantle to fill the opening. As the ocean floor slowly separates, new rocks form at the ___________________ that is forming. The Mid-Atlantic Ridge is getting wider at a rate of 2.5 cm every year. Mid-ocean ridges Mid-ocean ridges are _____________________________________. Although named “mid-ocean”, there are not necessarily at the center of the ocean. Draw (slide 40) Sea floor spreading When the sea floor moves, magma moves upward and flows from cracks at the mid ocean ridge. The magma cools and forms __________________. This sea floor spreading idea is supported by the following observations: 1. When scientists tested rocks at the mid-ocean ridge and on both sides of the ridge, they found that the ________ rocks were closer to the ridge and ________ rocks were farther away from the ridge. 2. Earth has a magnetic field that from time to time reverses magnetic north and south poles. Volcanic rock provides a record of the magnetic poles at the time the rock cooled, thus past reversals are recorded in rocks forming along mid-ocean ridges. What happens at the transform boundary? What forms along that boundary? Plates ___________________________, and faults or breaks in the Earth’s crust can form there from stress. Stress- ________________________________________________ When one plate _____________ slips past another plate and releases the stress, ______________________________. The San Andreas fault is part of a transform boundary where the Pacific plate slides against the North American plate. Pacific Ring of Fire Most of the active volcanoes and earthquakes are located ___________ _____________________. The Pacific Ring of Fire is an area of almost _____________________ _________________________________. It circles the Pacific Ocean basin. Volcanos and Plate Tectonics: Volcanos are mostly focused at ________________________________. Volcanoes are formed by: Subduction - ______________ - Hotspots Draw slide 52: The volcanoes get ________________________ from one end to the other. Earthquakes and Plate Tectonics: At the boundaries between plates, _______ causes plates to ________ together. When built up energy causes them to “unstick”, ___________________ occur. Summary: 1. The Earth is made up of 3 main layers (core, mantle, crust) & 5 physical layers (LAMOIC) 2. On the surface of the Earth are tectonic plates that slowly move around the globe 3. Plates are made of crust and upper mantle (lithosphere) and move on the asthenosphere 4. There are 2 types of plates: oceanic and continental 5. There are 3 types of plate boundaries: convergent, divergent & transform 6. Volcanoes and Earthquakes are closely linked to the borders of the tectonic plates