* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 2008 Floriculture Problem Test - Key
Plant nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Plant secondary metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Plant stress measurement wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of plants wikipedia , lookup
History of botany wikipedia , lookup
Plant use of endophytic fungi in defense wikipedia , lookup
Plant breeding wikipedia , lookup
Plant defense against herbivory wikipedia , lookup
History of herbalism wikipedia , lookup
Venus flytrap wikipedia , lookup
Plant physiology wikipedia , lookup
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Plant ecology wikipedia , lookup
Ornamental bulbous plant wikipedia , lookup
Flowering plant wikipedia , lookup
Plant reproduction wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Sustainable landscaping wikipedia , lookup
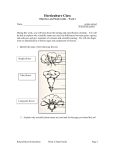
2008 STATE FFA FLORICULTURE KNOWLEDGE TEST Contestant Number: Name: Chapter Name: Score: Directions: Read each question carefully and choose the best possible answer. If provided with Scantron sheets, bubble in the answer. Otherwise, write the answer in the blank to the left of each number. Each correct answer is worth ten points. The maximum score is 500 points. 1. Geranium cuttings are best described as: a. Semi-hardwood. b. Herbaceous. c. Hardwood. d. Micropropagation. 2. When installing a flower bed, the taller, darker-colored flowers should be planted: a. Near the front of the bed. b. Mixed throughout the bed. c. On the outside edges of the bed. d. To the rear or center of the bed. 3. Flowers used to fill empty spaces and tie the floral arrangement together are called: a. Filler flowers. b. Line flowers. c. Form flowers. d. Massing flowers. 4. A number 9 florist ribbon is: a. 7/8” wide. b. 1 3/8” wide. c. 2” wide. d. 2 3/4” wide. 5. The first part of the new plant to emerge from the seed is the: a. Stem. b. Leaf. c. Root. d. Endosperm. 6. A pH of 6.0 is considered to be: a. Alkaline. b. Neutral. c. Acidic. d. Sweet. 2008 State FFA Floriculture Knowledge Test Page 2 7. The term that comes from a Latin word meaning “garden cultivation’ and includes vegetables, fruits, and ornamental plants is: a. Agronomy. b. Forestry. c. Zoology. d. Horticulture. 8. A 1-2-1 fertilizer ratio would be a fertilizer analysis of: a. 5-10-5. b. 20-10-10. c. 6-12-18. d. 3-9-9. 9. An insect can be described as having: a. 1 body section and 2 legs. b. 3 body sections and 6 legs. c. 2 body sections and 2 legs. d. 4 body sections and 8 legs. 10. The best gauge florist wire to use to make a bow is: a. 18 gauge. b. 22 gauge. c. 20 gauge. d. 14 gauge. 11. The parts of a poinsettia located beneath the flower that gives the white, pink, or red colors are the: a. Bracts. b. Stamens. c. Petals. d. Sepals. 12. Which plant is grown from a bulb? a. Poinsettia b. Chrysanthemum c. Petunia d. Easter lily 13. The one factor having the most impact on how quickly an area will be covered by ground cover plants is: a. Sunlight. b. Temperature. c. Spacing of plants. d. Moisture. 2008 State FFA Floriculture Knowledge Test Page 3 14. A structure made of wood poles and rolls of snow fence or other similar materials and used to shade plants in the summer is a: a. Cold frame. b. Lathhouse. c. Hotbed. d. Headhouse. 15. Which insect’s larvae feed on the roots of greenhouse plants? a. Spider mites b. Mealybugs c. Whiteflies d. Fungus gnats 16. When landscaping with bulbs, the most striking effect is achieved by placing them in a: a. Design pattern. b. Single row. c. Grouping of the same color. d. Grouping of mixed colors. 17. Foliage, such as Baker’s fern, is used in floral designs to: a. Fill empty spaces. b. Create the outline. c. Establish height. d. Establish width. 18. The ability of a plant to withstand the minimum temperature of an area is: a. Compatibility. b. Polarity. c. Hardiness. d. Topography. 19. The procedure used to break dormancy and to establish some growth before bulbs are brought into a warm room for flowering is called: a. Heating. b. Forcing. c. Bolting. d. Cooling. 20. The green part of the flower which covers and protects the flower bud before it opens is the: a. Ovary b. Sepal. c. Filament. d. Receptacle. 2008 State FFA Floriculture Knowledge Test Page 4 21. If poinsettia rooted cuttings are transplanted to 6-inch pots on September 10, the poinsettias should be ready for sale by: a. October 10. b. November 10. c. December 10. d. January 10. 22. The most widely used annual bedding plant that is pink, red, white, or blue is: a. Marigold. b. Coleus. c. Zinnia. d. Petunia. 23. A 6”-18” annual that may be pink, red, white, or multicolored and does best in shaded areas is: a. Impatiens. b. Snapdragon. c. Ageratum. d. Celosia. 24. Pests are a major problem for horticulturists. Insects with hard waxy shells and piercingsucking mouth parts which suck sap from plants are: a. Thrips. b. Scales. c. Mealybugs. d. Snails. 25. Assuming that all other factors for plant growth are present in an optimum supply, if the grower reduced the water supply, the photosynthesis rate would: a. Remain the same. b. Slow down. c. Stop. d. Speed up. 26. As a general rule, seedlings should be transplanted to a depth of: a. One inch above the first true leaves. b. Two inches above the first true leaves. c. One inch below the first true leaves. d. Two inches below the first true leaves. 27. When identifying horticultural plants, the term serrate would be referring to the leaf: a. Margin. b. Venation. c. Type. d. Arrangement. 2008 State FFA Floriculture Knowledge Test Page 5 28. Which horticulture or landscape tool is used to prune young, tender new growth on shrubs? a. Lopping shears b. Pruning saw c. Cutter mattock d. Hedge shears 29. What does the landscape symbol shown below represent? a. b. c. d. Stonework Loose aggregates and mulch Trailing ground cover Water 30. Total privacy for two landscapes which are side by side and at the same level requires an enclosure of: a. 5 feet. b. 6 feet. c. 7 feet. d. 8 feet. 31. Which small deciduous tree has scarlet leaves in the fall and is used as a specimen plant? a. Japanese maple b. Star magnolia c. Redbud d. Weeping cherry 32. Plantscaping has become popular in shopping malls, office buildings, and hotels. A popular interior landscape plant, often confused with philodendron, which requires indirect or filtered sunlight is: a. Jade plant. b. English ivy. c. Croton. d. Pothos. 2008 State FFA Floriculture Knowledge Test Page 6 33. Which annual bedding plant is characterized by its foliage being accented by splashed colored leaves? a. Begonia b. Hypoestes c. Verbena d. Dianthus 34. A sun loving perennial which blooms midsummer to fall and is commonly called cone flower is: a. Delphinium. b. Sweet William. c. Iris. d. Rudbeckia. 35. The best pH range for growing most horticultural plants is: a. 4.0-5.5. b. 5.6-7.0. c. 7.1-8.5. d. 8.6-10.0. 36. The science and practice of growing, storing, designing, and marketing flowering plants is: a. Arboriculture. b. Floriculture. c. Olericulture. d. Pomology. 37. Chrysanthemums are disbudded to: a. Produce smaller flowers. b. Increase resistance to insects. c. Produce fewer, but larger flowers. d. Slow down flowering. 38. Small hairlike worms that feed on plant roots are: a. Nematodes. b. Fungi. c. Mollusks. d. Caterpillars. 39. Which corsage construction method is most appropriate for flowers with composite (daisylike) florets, such as a daisy chrysanthemum? a. Clutchwire b. Hook c. Hairpin d. Piercing 2008 State FFA Floriculture Knowledge Test Page 7 40. The four main parts of a complete flower are: a. Stamen, sepal, pistil, and petal. b. Anther, filament, receptable, and stamen. c. Receptacle, ovary, stamen, and style. d. Stigma, ovule, style, and ovary. 41. Both chrysanthemums and poinsettias are: a. Long-day photoperiodic flowers. b. Short-night photoperiodic flowers. c. Medium-day photoperiodic flowers. d. Short-day photoperiodic flowers. 42. A crescent floral design is shaped like a: a. Inverted-T. b. Quarter moon. c. Fan. d. Circle. 43. Which environmental control device regulates the temperature in the greenhouse? a. Timer b. Humidifier c. Carbon dioxide meter d. Thermostat 44. The most common disease of Easter lilies is: a. Powdery mildew. b. Leaf rust. c. Root rot. d. Smut. 45. The suggested potting arrangement for mums in a 6” pot is: a. 1-3. b. 4-5. c. 6-7. d. 8-9. 46. If a container is 8 inches high, the height of the floral design should be at least: a. 9 inches. b. 10 inches. c. 11 inches. d. 12 inches. 47. Which horticultural plant was introduced into the United States from Mexico and was made popular by the work of Albert Ecke? a. Poinsettia b. Chrysanthemum c. Easter lily d. Carnation 2008 State FFA Floriculture Knowledge Test Page 8 48. Using the standard rule of thumb, how many plants should be used in a 10-inch basket? a. 5 b. 7 c. 9 d. 11 49. Which 8’-15’ broadleaf evergreen has white to pink flowers in the fall of the year? a. Ligustrum japonicum b. Camellia sasanqa c. Berberis darvinii d. Ilex cornuta 50. When planting Easter lily bulbs, each bulb should be placed so that the tip is covered with a potting medium of: a. One inch. b. Two inches. c. Three inches. d. Four inches. 2008 State FFA Floriculture Knowledge Test Page 9 2008 STATE FFA FLORICULTURE KNOWLEDGE TEST ANSWER SHEET # 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Answer b d a b c # 26. 27. 28. 29. 30. Answer c a d c b 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. c d a b b a d c b 31. 32. 33. 34. 35. 36. 37. 38. 39. a d b d b b c a b 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. 22. 23. 24. d c a c b b c d a b 40. 41. 42. 43. 44. 45. 46. 47. 48. 49. a d b d c b d a c b 25. b 50. b 2008 State FFA Floriculture Knowledge Test Page 10 2008 STATE FFA FLORICULTURE KNOWLEDGE TEST ANSWER SHEET # 1. Answer b Reference Introductory Horticulture, p. 78 # 26. Answer c Reference Working in Horticulture, p. 136 2. d Landscaping, p. 175-176 27. a Working in Horticulture, p. 61 3. a Introductory Horticulture, p 518 28. d Landscaping, p. 21 4. b Introductory Horticulture, p. 511 29. c Landscaping, p. 60 5. c Working in Horticulture, p. 115 30. b Landscaping, p. 203-204 6. c Working in Horticulture, p. 76 31. a Introductory Horticulture, p. 307 7. d Working in Horticulture, p. 4 32. d Introductory Horticulture, p. 235 8. a Working in Horticulture, p. 80 33. b Introductory Horticulture, p. 265 9. b Introductory Horticulture, p. 170 34. d Introductory Horticulture, p. 278 10. b Introductory Horticulture, p. 511 35. b Introductory Horticulture, p. 40 11. a Introductory Horticulture, p. 124 36. b Introductory Horticulture, p. 3 12. d Introductory Horticulture, p. 339 37. c Introductory Horticulture, p. 135 13. c Introductory Horticulture, p. 334 38. a Introductory Horticulture, p. 183 14. b Working in Horticulture, p. 230 39. b Introductory Horticulture, p. 525 15. d Working in Horticulture, p. 178 40. a Working in Horticulture, p. 38 16. c Introductory Horticulture, p. 338 41. d Introductory Horticulture, p. 124, 131 17. a Working in Horticulture, p. 291 42. b Introductory Horticulture, p. 519 18. c Working in Horticulture, p. 124 43. d Working in Horticulture, p. 223 19. b Introductory Horticulture, p. 340 44. c Introductory Horticulture, p. 142 20. b Introductory Horticulture, p. 27 45. b Introductory Horticulture, p. 133 21. c Introductory Horticulture, p. 125 46. d Introductory Horticulture, p. 518 22. d Introductory Horticulture, p. 266 47. a Introductory Horticulture, p. 123-124 23. a Introductory Horticulture, p. 265 48. c Introductory Horticulture, p. 263 24. b Working in Horticulture, p. 176-177; 181 49. b Introductory Horticulture, p. 298 25. b Working in Horticulture, p. 93 50. b Introductory Horticulture, p. 141