* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Study Island Test and Guide Gravity
Modified Newtonian dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Aquarius (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Astrobiology wikipedia , lookup
Lunar theory wikipedia , lookup
Geocentric model wikipedia , lookup
Rare Earth hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Equivalence principle wikipedia , lookup
Dialogue Concerning the Two Chief World Systems wikipedia , lookup
IAU definition of planet wikipedia , lookup
Late Heavy Bombardment wikipedia , lookup
History of Solar System formation and evolution hypotheses wikipedia , lookup
Solar System wikipedia , lookup
Planets beyond Neptune wikipedia , lookup
Comparative planetary science wikipedia , lookup
Extraterrestrial life wikipedia , lookup
Planetary habitability wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical unit wikipedia , lookup
Definition of planet wikipedia , lookup
Formation and evolution of the Solar System wikipedia , lookup
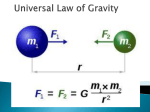
Copyright © 2012 Study Island - All rights reserved. Generation Date: 01/11/2012 Generated By: Garrison Hall Gravity 1. Which of the following is a result of gravitational forces in the Solar System? A. that Saturn is farther away from the Sun than Earth is B. the orbit of planets around the Sun in the Solar system C. the radiation given off by Jupiter D. the difference in surface temperature on each of the planets 2. What characteristics of a planet determine the strength of its gravitational force on other objects? A. the number of moons that the planet has B. diameter of the planet and its location in space C. the distance of the planet from the Earth D. mass of the planet and its distance from other objects 3. Which of the following is a result of gravitational forces in the Solar System? A. the orbit of moons around their planets in the Solar system B. the radiation given off by Jupiter C. Saturn is further away from the Sun than Earth D. the difference in surface temperature on each of the planets 4. Which of the following forces causes comets to regularly return to the inner solar system after being gone for many years? A. electromagnetic force B. magnetism C. gravity D. friction 5. Which of the following forces is responsible for keeping the planets in orbit around the Sun? A. gravity B. electromagnetic force C. friction D. magnetism 6. Gina's science teacher tells her that mass and weight are related, but have an important difference due to gravity. Gina's teacher says that Jupiter has a much greater gravitational force than Earth, while the Moon has a much smaller force. How would Gina's weight and mass change on these surfaces? A. Gina's weight would increase or decrease, while her mass remains the same. B. Gina's weight and mass would increase or decrease. C. Gina's weight and mass would stay the same. D. Gina's weight would stay the same, while her mass increased or decreased. 7. How would a rock's weight on the Moon or the Sun compare to its weight on Earth? Assume that the rock would not burn up. A. It would weigh more on the Moon and on the Sun. B. It would weigh less on the Moon and on the Sun. C. It would weigh more on the Moon and less on the Sun. D. It would weigh less on the Moon and more on the Sun. 8. The Sun's gravitational attraction, along with a planet's _______, keeps the planet moving in a(n) _______ orbit and determines the orbital speed. A. magnetic field; circular B. tectonic activity; irregular C. temperature; linear D. inertia; elliptical 9. Gina's science teacher tells her that mass and weight are related, but have an important difference due to gravity. Gina's teacher says that Jupiter has a much greater gravitational force than Earth, while the Moon has a much smaller force. How would Gina's weight and mass change on these surfaces? A. Gina's weight would increase or decrease, while her mass remains the same. B. Gina's weight would stay the same, while her mass increased or decreased. C. Gina's weight and mass would stay the same. D. Gina's weight and mass would increase or decrease. 10. Select the best definition for gravity. A. Gravity is responsible for keeping objects in orbit around one another; gravity is strongest on the moon and weakest on the Earth. B. Gravity is the force that is formed in the crust of the planet and it holds objects to the surface of the Earth. C. Gravity is the natural force that causes objects to move toward the center of the Earth. D. Gravity is a force that causes objects to move toward the center of the Earth. Gravity is caused by tectonic plate movement. 11. Planets in our solar system revolve around the Sun because A. the Sun is the most massive object in our solar system. B. the Sun is the hottest object in our solar system. C. the Sun is the brightest object in our solar system. D. the Sun is the slowest object in our solar system. 12. Two objects are placed a certain distance from each other. The amount of gravitational force between the two objects depends on their masses and the distance between them. As the masses of the objects increase, the force of gravity between them _____________. As the distance between the objects increases, the force of gravity between them ______________. A. increases; increases B. decreases; increases C. decreases; decreases D. increases; decreases 13. _______ is a force that keeps the Moon orbiting the Earth. A. Momentum B. Velocity C. Suspension D. Gravity 14. A satellite that is near the Earth is pulled into orbit by its gravity. The satellite is affected by Earth's gravity because of ___________. A. the distance from the Sun B. Earth's mass and distance from the satellite C. the large attraction to the Sun D. the lack of gravity by any other planet 15. A star is born when gas and dust from a nebula become so dense and hot that nuclear fusion starts. Which of the following forces is responsible for the formation of a star? A. friction B. electromagnetic energy C. gravitation D. magnetism 16. The farther a planet is from the Sun, the _______ the gravitational force between them and the _______ the planet's orbital speed. A. stronger; slower B. weaker; slower C. weaker; faster D. stronger; faster 17. What is the main difference between weight and mass? A. Weight is dependent on gravity, and mass is not. B. Weight can be measured, and mass cannot. C. There is no difference between weight and mass. D. Weight is measured in grams, and mass is measured in pounds. 18. Many planets are formed by a process called accretion, where chunks of material are drawn to bigger chunks of material and are slammed together until enough material has been gathered to produce a planet. Which of the following forces is responsible for accretion? A. nuclear B. magnetism C. gravitation D. electromagnetic energy 19. Which type of force holds galaxies together? A. gravity B. magnetic forces C. friction D. electrostatic forces 20. Which of the following is true? A. The Earth exerts a gravitational force on the Moon, but the Moon does not exert a gravitational force on the Earth. B. The Moon exerts a gravitational force on the Earth, but the Earth does not exert a gravitational force on the Moon. C. The Earth and Moon both exert a gravitational force on each other. D. The Earth and Moon do not exert gravitational forces. 21. The planet Mars has two moons, Deimos and Phobos. Phobos is about 9,000 km from Mars and is about six times more massive than Deimos. Deimos is about 23,000 km from Mars. Upon which moon does Mars exert a stronger gravitational force? A. Deimos and Phobos equally B. Deimos C. not enough information D. Phobos Answers 1. B 2. D 3. A 4. C 5. A 6. A 7. D 8. D 9. A 10. C 11. A 12. D 13. D 14. B 15. C 16. B 17. A 18. C 19. A 20. C 21. D Explanations 1. The gravitational force of the Sun pulls inward on the planets, forcing them to stay in orbit around the Sun. If not for the gravitational force of the Sun on the planets, they would quickly move away from it. 2. The size of a planet's gravitational force is determined by the mass of the planet and its distance from other objects. The more massive an object and the closer it is to an object, the greater its gravitational force is on the object. These large gravitational forces are why the planets orbit around the Sun and the moons and satellites orbit around planets. 3. The gravitational force of the planets pulls inward on their moons, forcing the moons to stay in orbit around the planets. If not for the gravitational force of the planets on their moons, the moons would quickly move away from their planets. 4. Gravity causes comets to regularly return to the inner solar system after being gone for many years. 5. Gravity causes the planets to stay in orbit around the Sun. Gravity is also responsible for keeping other objects in the solar system in orbital motion (e.g., moons orbit their planets; asteroids, meteoroids, and comets orbit the Sun). 6. Gina's weight, but not her mass would change on Jupiter and the Moon. Gina's weight would increase or decrease, while her mass remains the same. Mass does not change as gravity changes, but weight does. Weight is measured by gravitational forces of a planet or moon, which act upon an object. 7. The weight of an object is dependent upon the force of gravity. Because the Moon has less mass than the Earth, its gravitational force is also less, and so a rock would weigh less on the Moon than it does on the Earth. Similarly, because the Sun is so much more massive than the Earth, its gravitational force is a lot greater than the Earth's, and if a rock could be taken to the surface of the Sun, it would weigh a lot more than it does on the Earth. 8. What keeps a planet moving in orbit is a combination of the gravitational attraction between the planet and the Sun and the planet's inertia (its continual forward motion). Without the Sun's gravity, the planet's inertia would send it traveling in a straight line off into space. Without the planet's inertia, the Sun's gravity would pull the planet in to collide with the Sun. These two factors combine to form an elliptical planetary orbit and to determine the planet's orbital speed. 9. Gina's weight, but not her mass would change on Jupiter and the Moon. Gina's weight would increase or decrease, while her mass remains the same. Mass does not change as gravity changes, but weight does. Weight is measured by gravitational forces of a planet or moon, which act upon an object. 10. Gravity is the natural force of attraction that exists between planets (like Earth) and all objects with mass. Gravity pulls objects toward the center of the Earth; it seems as if gravity “holds” things to the surface. The further the object is from the center of the Earth, the less gravity acts on it. 11. All matter exerts a gravitational force. The more mass an object has, the stronger its gravitational pull. All the bodies in our solar system revolve around the Sun because the Sun is the most massive object in our solar system. 12. As the masses of the objects increase, the force of gravity between them increases. As the distance between the objects increases, the force of gravity between them decreases. The amount of gravitational forces between two objects depends on their masses and the distance between them. 13. The force of gravity is responsible for holding objects onto the surface of planets and, with Newton's law of inertia, is responsible for keeping objects in orbit around one another. 14. The satellite is affected by Earth's gravity because of Earth's mass and distance from the satellite. An object moves toward the Earth because of its mass and how close the Earth is to the object. Gravity on the Earth attracts the object and moves it nearer. 15. In the densest portion of the nebula, gravity exerts force on nearby particles of gas and dust. This area of the nebula becomes denser as the particles of gas and dust are pulled closer and closer together by the growing gravitational force. 16. The farther a planet is from the Sun, the weaker the gravitational force between them and the slower the planet's orbital speed. Planets that are farther from the Sun are less attracted to the Sun and have slower orbital speeds than planets that are closer to the Sun. Also, a given planet's speed will vary along its orbit as its distance from the Sun varies. 17. The mass of a body is a measure of how much matter it contains. Every object in the universe with mass attracts every other object with mass. The amount of attraction depends on the size of the masses and their distance apart. On any given planet, the force of attraction between an object and the planet is the object's weight on that planet. 18. Gravitation is the force that causes bodies of matter to be pulled together. 19. Gravity is the non-contact force that attracts objects to each other in space. 20. Since the Moon is in the Earth's gravitational field and vice versa, The Earth and Moon both exert a gravitational force on each other. However, the gravitational force exerted by the Moon is much smaller because the Moon has much less mass than the Earth. 21. The greater the distance between two objects and the less massive the objects, the weaker the gravitational force between them. Since Phobos is both closer to Mars and more massive than Deimos is, Mars has a stronger gravitational effect on Phobos than on Deimos. Copyright © 2012 Study Island - All rights reserved.