* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Bio J Genetics Test Study Guide – Test Friday, March 10
Survey
Document related concepts
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Behavioural genetics wikipedia , lookup
Transgenerational epigenetic inheritance wikipedia , lookup
Genome-wide association study wikipedia , lookup
Medical genetics wikipedia , lookup
Dominance (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
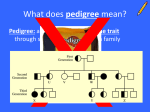
Genetics Test Study Guide – Be able to answer genetics problems with the following inheritance patterns: - Study suggestion: on a clean piece of paper, copy 1 example of each of the following types on problem. Title the problem with the correct inheritance pattern and then list some “clues” to look for in the problem to help you identify it as that pattern. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. complete dominance incomplete dominance co-dominance X-linked (sex-linked) Test Cross Know the difference between genotypes and phenotypes - be able to identify a person’s genotype or phenotype base on a verbal description Know how to find the possible allele combinations for dihybrid crosses. Be able to tell the phonotype and genotype of both traits. Know the meaning of the following words: Allele P1 generation Carrier Homozygous F1 generation complete dominance Heterozygous F2 generation incomplete dominance Hybrid Monohybrid co-dominance Pure Dihybrid Sex-linked pedigree progeny Know who Mendel was and what his contributions were - KNOW HIS THREE LAWS!!!!! Know what each part of the punnett square means - top is the possible eggs that mom can make - side is the possible sperm cells that dad can make - middle are the ZYGOTES (fertilized eggs) or possible progeny (offspring!) Know how many alleles we have for each trait, how many we pass down to each child Be able to interpret a pedigree chart - What shape represents female? - What shape represents male? - How do we represent someone with a particular trait? - How do we represent a carrier? - How do we show marriage? Children? Study Activities: I. Identify the type of inheritance describe in each problem. Then identify what the phenotype of each possible genotype would be. 1. The color of snapdragons is caused by a single gene (R). The flowers can be red, pink or white. a. What type of inheritance is this? b. List the 3 possible genotypes and their phenotypes 2. In fruit flies the white eye trait is much more common in males than females. Although it is recessive, if the males inherit even one copy, they will have white eyes. Otherwise the eyes will be red. a. What type of inheritance is this? b. List ALL the possible genotypes (hint there are 5) and their phenotypes. 3. In horses coat color is genetic (C). A horse can have all white hairs, all red hairs, or have both red and white hairs. This last type of horse is called Roan. a. What type of inheritance is this? b. List the 3 possible genotypes and their phenotype II. Test crosses: 1. What is the purpose of a test cross? 2. Would a test cross be needed for a trait that is incompletely or co-dominant? Why or why not? 3. Why genotype is the “unknown” individual ALWAYS crossed with? 4. What do you look for in your off-spring to answer your original question? III. Dihybrid Crosses: 1. How many traits are being examined in a dihybrid cross? 2. How many alleles FOR EACH TRAIT does an individual have? 3. How many alleles TOTAL will make up a genotype if you are examining 4 TRAITS? 4. Red flowers (R) are incompletely dominant to white flowers (r). Tall stems (T) are completely dominant to short stems (t). a. What is the genotype of a Pink flowered, short stemmed plant? b. What possible PAIRS of alleles can this plant pass to its offspring? i. Think: how many alleles for EACH TRAIT are passed from one parent? IV. Pedigrees 1. What is the purpose of a pedigree chart? 2. Draw a pedigree of a family that meets the rules below: a. Cystic fibrosis is a recessive trait. It is NOT on the x chromosome b. Mom and dad are carriers of the disease c. Mom’s mother is a carrier, her father is not d. Dad’s father is a carrier, his mother is not e. Mom and Dad are both the only children their parents had. f. Mom and Dad have 4 children: 2 sons and 2 daughters g. One of the daughters has the disease h. One of the sons is a carrier i. The son who is NOT a carrier is married to a woman j. They have two daughters. Neither daughter is a carrier V. Genetics problems: a. Go back to all your problems in your packets and see if you can solve them from scratch. b. AT LEAST practice setting up the genotypes again based on the problem.