* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download BAŞKENT UNIVERSITY
Negative resistance wikipedia , lookup
Integrated circuit wikipedia , lookup
Radio transmitter design wikipedia , lookup
Integrating ADC wikipedia , lookup
Flexible electronics wikipedia , lookup
Transistor–transistor logic wikipedia , lookup
Immunity-aware programming wikipedia , lookup
Operational amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Josephson voltage standard wikipedia , lookup
Valve audio amplifier technical specification wikipedia , lookup
Valve RF amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Schmitt trigger wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Electrical ballast wikipedia , lookup
Voltage regulator wikipedia , lookup
Current mirror wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Power MOSFET wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
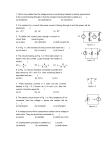
EXPERIMENT-3 POWER IN DC CIRCUITS BAŞKENT UNIVERSITY BIOMEDICAL ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT BME 211 CIRCUIT THEORY-I LAB. EXPERIMENT 3 POWER IN DC CIRCUITS Objective 1) To investigate the internal resistance of voltage sources. 2) To use variable resistors in applications. 3) Using delta-to-wye transformation to simplify circuits. 1. INTRODUCTION Measuring the internal resistance of voltage sources If a load R is connected to a voltage source, the output voltage generally falls. The reason for this is the internal resistance Ri of the voltage source which is connected in series with the external load. Voltage Source U0 Ri + U R If the unloaded voltage source possesses the open-circuit voltage U0, the voltage U at the terminal of the loaded voltage source is U=U0 - Ri*I Fig.1 In the event of a short-circuits, i. E. U = 0, the total voltage thus already drops across the internal resistance. Variable Resistor (Potentiometer) A 3 pinned variable resistor is like next figures, made of a carbon strip and a slipping pin. So if you have an “A” ohm variable resitor you have two different resistor between A-C and these resistor’s values are in range between 0-A ohm. Example: A=10 kohm R(A-B)=3 kohm => R(B-C)=A-3 = 7 kohm Fig.2 1 EXPERIMENT-3 POWER IN DC CIRCUITS 2. PRELIMINARY WORK Fig.3 2.1 If you want to take IS=2 mA from power supply, find the “x” value of variable resistor.(There is a 3 pinned variable resistor in the box.) Fig.4 2.2 Read Delta-to-Wye equıvalent circuits chapter in your text books. Find the IS value in Fig-4. ( Hint: Use - transformation ) 2 EXPERIMENT-3 POWER IN DC CIRCUITS 3. EXPERIMENTAL WORK 2.2 kohm 4.7kohm Fig.5 3.1 Set up the circuit in the figure 4.Find the “x” value of the variable resistor to take 2 mA from supply.(Hint: Connect an ampermeter to supply in series and change variable resistor to obtain 2 mA on the ampermeter. ) Write your x value. Rg Fig.6 3.2 Set up the circuit in figure 6. Measure necessary V L and IL values and calculate PL values for different RL values. Put a variable resistor with a range between 0-20 kohm for RL. (Hint: convert a 3 pinned variable resitor to 2 pinned variable resitor by connecting inner pin to one of outer pins.) Draw a PL-RL graph. 3.3 Find the inner resistance of the voltage source. Note the load resistance in your report.. 4. RESULTS AND CONCLUSION 4.1 What is the relation between Rg and RL ,which maximize the PL, in experiment 3.2 4.2 Where can you use the concept that you found in 4.1. 3 EXPERIMENT-3 POWER IN DC CIRCUITS Name : Lastname : Student id : Set No : Name : Lastname : Student id : Set No : 5. REPORT 3.1 x= 3.2 RL() 5000 6000 7000 8000 9000 10000 11000 12000 13000 14000 15000 VL IL PL Graph: 3.3 Rin = 4.1 4.2 4