* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Class Notes Section 3.3 Analyzing Isosceles Triangles In an
Golden ratio wikipedia , lookup
Multilateration wikipedia , lookup
Reuleaux triangle wikipedia , lookup
History of trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Euler angles wikipedia , lookup
Perceived visual angle wikipedia , lookup
Rational trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Incircle and excircles of a triangle wikipedia , lookup
Trigonometric functions wikipedia , lookup
Pythagorean theorem wikipedia , lookup
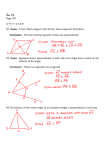
Class Notes Section 3.3 Analyzing Isosceles Triangles In an isosceles triangle, the two sides that are of equal length are called the legs and the third side is called the base. The point at which the legs meet is the vertex and the angle there is the vertex angle. The two angles that include the base are called the base angles. The angle formed by the congruent sides is called the VERTEX ANGLE. The two angles formed by the base and one of the congruent sides are called BASE ANGLES. The congruent sides are called LEGS LEG LEG Base angle Base angle The side opposite the vertex angle is called the BASE. Name the parts of this isosceles triangle: Other important triangle parts: Definitions: median - a segment that starts from an angle and goes to the midpoint of the opposite side. altitude - a segment that starts from an angle and is perpendicular to the opposite side. angle bisector - of a triangle…is a segment that bisects an angle and goes to the opposite side. perpendicular bisector - a segment that passes through the midpoint of a side AND is perpendicular to that side. Examples: E is a median of DEC is an altitude of DEC F D C H T is an angle bisector of RST Z is a perpendicular bisector of side V R S W Thm – Corresponding altitudes of congruent triangles are congruent. Thm – The bisector of the vertex angle of an isosceles triangle separates the triangle into two congruent triangles. B Proof – Given : Isosceles ABC , with AB BC BD bisects ABC Prove: ABD CBD 1 2 A D C Isosceles Triangle Theorem - if two sides of a triangle are congruent, then the angles opposite those sides are congruent. . . . . . B If Then A C A C AND (converse) if two angles of a triangle are congruent, then the sides opposite those angles are congruent. B If Then A C C A Example 1: DEF is isosceles. D is the vertex angle. The mE = 2x + 40 and the mF = 3x + 22. Find the measures of each angle. D F E Example 2: Given: Prove: XYZ is equilateral The measure of each angle of XYZ is 60 Y X Z 1) First, we have three congruent sides (given); so, their opposite angles are congruent. 2) Now we have three congruent angles. So, the triangle is equiangular. 3) So, we have an equilateral AND equiangular triangle. 5) How can we prove the three angles are each 60? (hint: what does the sum of the angles of a triangle add up to?) SO……. - a triangle is equilateral if and only if it is equiangular. - each angle of an equilateral triangle measures 60. Defn – The perimeter of a triangle is the sum of the lengths of all of its sides. Study the chart on page 145. Example 3: a. In the figure below, PQ PR , and PS and ST are medians. Find QT and QR. Q y T y+ S P 10 R b. KL is an altitude of HJK. Find “x”. H L J (9x – 27) (3x + 21) K c. PO is the perpendicular bisector of MN . Find “x”. M 2x + 5 P 15 – 3x 5x + 1 O N d. In JKL, JK JL , and JM is both a median, and altitude, and an angle bisector. Find the following. 1. mKMJ K 4 M L 56 2. KL 6 3. mKJM 4. mKJL 5. mK J Example 4: a. x = __________ b. x = __________ (2x +20) x c. (3x+8) x = __________ (2x – 25) d. (x + 5) Use the figure below to find the angle measures if m1 = 30. m2 = __________ m3 = __________ 8 3 m4 = __________ 5 m5 = __________ m6 = __________ m7 = __________ m8 = __________ 1 2 4 6 7