* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 1 Vocabulary
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
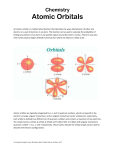
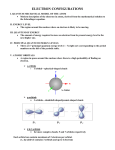
Chapter 1 Vocabulary 1. Antibonding MO – A molecular orbital that is higher in energy than the atomic orbitals from which it is formed. 2. Atomic Mass – The average mass number of the atoms of an element. 3. Bond Angle – The angle formed between two adjacent bonds. 4. Bond Length – The equilibrium distance between the nuclei of two atoms that are bonded to each other. 5. Bond Strength – An alternative name for bond dissociation energy. 6. Bonding MO – A molecular orbital that is lower in energy than the atomic orbitals from which it is formed. 7. Covalent Bond – A bond formed by sharing electrons between atoms. 8. Ground-State Electron Configuration – The most stable, lowestenergy electron configuration of a molecule or atom. 9. Isotope – Atoms of the same element that have different mass numbers. 10.Kekule Structure – A method of representing molecules in which a line between atoms indicates a bond. 11.Lewis Structure – A representative of a molecule showing valence electrons as dots. 12.Line-Bond Structure – A representation of a molecule showing covalent bonds as lines between atoms. 13.Lone-Pair Electrons – Nonbonding valence-shell electron pairs. Lonepair electrons are used by nucleophiles in their reactions with electrophiles. 14.Molecular Orbital (MO) Theory – A description of covalent bond formation as resulting from a mathematical combination of atomic orbitals (wave functions) to from molecular orbitals. 15.Molecule – A neutral collection of atoms held together by covalent bonds. 16.Node – A surface of zero electron density within an orbital. For example, a p orbital has a nodal plane passing through the center of the nucleus, perpendicular to the axis of the orbital. 17.Nonbonding Electrons – Valence electrons that are not used in forming covalent bonds. 18.Orbital – A wave function, which describes the volume of space around a nucleus in which an electron is most likely to be found. 19.Organic Chemistry – The study of carbon compounds. 20.Pi Bond – The covalent bond formed by sideways overlap of atomic orbitals. For example, carbon-carbon double bonds contain a pi bond formed by sideways overlap of two p orbitals. 21.Shell (Electron) – A group of an atom’s electrons with the same principal quantum number. 22.Sigma Bond – A covalent bond formed by head-on overlap of atomic orbitals. 23.sp Hybrid Orbital – A hybrid orbital derived from the combination of an s and a p atomic orbital. The two sp orbitals that result from hybridization are oriented at an angle of 180 degrees to each other. 24.sp2 Hybrid Orbital – A hybrid orbital derived by combination of an s atomic orbital with two p atomic plane at angles of 120 degrees to each other. 25.sp3 Hybrid Orbital – A hybrid orbital derived by combination of an s atomic orbital with three p atomic orbitals. The four sp3 hybrid orbitals that result are directed toward the corners of a regular tetrahedron at angles of 109 degrees to each other. 26.Valence Bond Theory – A bonding theory that describes a covalent bond as resulting from the overlap of two atomic orbitals. 27.Valence Shell – The outermost electron shell of an atom.