* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Crustacea
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
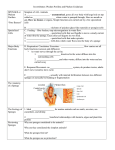
Zoologist Name: Prd: Interesting Examples of creatures in Phylum Porifera: Sounds like…. “por-IF-er-ah” Sponge Glass sponge Magic Sponges? If you were to take a living sponge and were to smash it through a screen and break apart all of the cells…. what would happen? _____________________________________ _____________________________________ _____________________________________ The Facts … Body symmetryReproductionMovement- Asymmetrical Asexually and Sexually stationary- using holdfast Food- gather food from water which passes through them _____________________________________ Sponges are examples of … Cell Aggregates . Porifera stands for the Greek words meaning “________having pores__________” The body of a sponge is covered in pores (tiny holes), which allows the sponge to take in ______Food__________ such as ______plankton_______________ as well as _______oxygen____________. Collar cells . aka Choanocytes wiggle their tails and water flows swish sea water through the sponge. As the water flows through, the Chonanocytes snag pieces of food. Sponges do not have bones, yet they are hard. Sponges have tiny _____spicules________ that act as skeletons. PHYLUM PORIFERA Choaocyte or ‘collar cell’ Water goes OUT through the Osculum Water goes IN through thepores Nemo is in Danger!! The coral reef is in danger! Although some parts of the coral reef is as hard as a rock, the ecosystem is very delicate. If things like _________scuba divers___________ or _______________boat anchors _______________ touch the coral it can damage to the reef and destroy many animals’ niches. Sounds like “ny-DARE-ee-ah” Examples of creatures in Phylum Cnidaria: Hydra Hydra (Chlorohydra viridissima): Jellyfish Hydra live in __________Fresh water____________ . They are the only Cnidarian not to live in salt water. Anemones Corals “Duuuuuude. Takin on the Jellies!” This hydra is in it’s ________polyp________________ stage. Hydra eat food like ______Daphnia________________ Picture of Hydra The Facts … Body symmetry- Radial Reproduction- Asexually and Sexually Movement- Polyps- Stationary Medusas- movement varies Food- carnivores- sting their prey . Members of this phylum all have stinging cells to capture their prey and defend themselves called __________cnidocytes______________. Draw the two body plans of Cnidarians: Polyp stage Medusa stage Cnidarians can move in very interesting ways Hydra- summersault Jellyfish- swim Anemones- stretch out and bend from side to side ____________Coral reef____________ is made up mostly of Cnidarians and Attached Free swimming Porifera. Cniarians in their polyp stage will attach to anything surface on the ocean floor. As they grow, they construct a hard inner structure and surround it with a soft body. When Cniarians die, the soft tentacles disintegrate but the hard structure is left behind. Nom nom nom… How Do Cnidaria Eat? Cnidarians feed by capturing their prey using the stinging cells in their tentacles and then pull the prey animals to its mouth. Tentacles pass food into the body cavity where it will be digested. They spit out undigested food.____2-way digestive system___________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ … PHYLUM CNIDARIA Examples of creatures in Phylum Nematoda: Ascaris ( Ascaris lumbricoides)1 billion people infected. Worms are between 15 & 49 cm long. T. Solium ( Taenia solium) Round worms look like tiny pieces of cooked spaghetti with a pointed head and tail. The Facts … Body symmetryReproductionMovementFood- Bilateral Sounds like “nem-ma-TOE-dah” Sexual thrashing from side to side Parasites. Worms are the simplest animals that have a _____Brain_________. Their brain is more of a cluster of nerve tissue. Worms have a 1 way digestive system. They are more advanced than sponges or cnidarians. Label the MOUTH & ANUS and draw arrows for the path of food. Worms do not have eyes, ears or noses. How can they tell what is around them? ___________________________________________ ___________________________________________ _They have sense organs that can detect light and touch. They can detect the vibrations from footsteps.___________________________________ ___________________________________________ ___________________________________________ - Nematodes are the most abundant animals on earth, with over _____20,000_________ species identified. They can live in almost any environment on earth. PHYLUM NEMATODA (round) Examples of creatures in Phylum Platyhelmenthes: Planaria (Dugesia dorotocephala) -non-parasitic -Planarians are scavengers who feed on dead or decaying material -Planarian live in ponds, slide over wet soil, or swirl around in the ocean. -They have two spots on their head. Called eyespots. Cannot see images but help differentiate between light and dark. -They also have a sense of smell on their head to help detect food. -Planarians feed by sticking a feeding tube into the food, and digesting the food. The extra undigested food comes back out the tube (no anus) -Planarians are notorious for being able to regenerate. Tapeworms The Facts … Body symmetryReproductionMovementFood- Bilateral Sexual and Asexual (or regeneration) Muscular or cilliary movement scavengers or parasites Sounds like “plat-ee-hell-MEN-thees” Platyhelminthes Flat Worms Tapeworms ! (ewwww) Tape worms are parasitic. Host- an organism which the parasite lives in. Parasite- absorb food from the host’s digestive system This part is called the ___Scolex__________ What is the longest tape worm ever found to date? ____________________ What do Planarian and Frankenstein have in common???? How do tape worms get so long? ____________________________ Regeneration ! ____________________________ Regeneration is…. ____________________________ ______The ability of an organism to regrow lost parts. __ ____________________________ ______________________________________________ ____________________________ ______________________________________________ ____________________________ ______________________________________________ ____________________________ . PHYLUM PLATYHELMINTHES (flat) Examples of creatures in Phylum Annelida: Earthworms (Dugesia dorotocephala) The Facts … Body symmetryReproductionMovement- Sounds like…. “a-NELL-i-dah” Bilateral Sexual muscular contraction Did You Know??? The scientific name for an earthworm poop is _______Casting________________________ Food- Scavengers (leaves, Did You Know??? The average earthworm has about ____100______ segments! A segment is one of the small divisions on the surface of the worm. Why are Annelids good for our soil? 1. Breaking down organic matter 2. aeration and drainage 3. release chemicals into soil Earthworm Anatomy Segmented worms have a ________1 way______ digestive Mouth Brain Heart Coelom Nerve cord Digestive tract Blood vessels system Anus Annelids blood moves through a “______closed_______” circulatory system. Which means blood is confined to blood vessels. Describe how each of these features help earthworms move through the dirt. 1) Bristles- small hairs on the skin of worms, which helps them crawl through the dirt. 2) Mucus – a slippery substance worms create on the outside of their skin which helps them slide through the dirt. Earthworms need to remain moist at all times because they _______________________________________ _______________________________________ _________will die if they dry out because they absorb oxygen through the air_______________ PHYLUM ANNELIDA (segmented) . Examples of creatures in Phylum Echniodermata: Star fish Sea Lillies Sand dollars Sea Urchins The sea urchin are dome shaped and have long spines they use for protection, which also have poisonous sacs at the ends of the spines that can deliver a painful sting. Sea Cucumbers The Facts … Body symmetryReproductionMovement- Radial (usually 5 part) Sexual and Asexual (or regeneration) tube feet or moving limbs Food- carnivores / scavengers Where- ocean floors Sounds like… “ee-ky-no-der-MAH-tah” Echinodermata- Spiny Skin Most echinoderms, like starfish have tiny suction cups on the bottom of their called ___________Tube feet_______________________. They use these feet to move, and also to grasp prey. (ex. _____Clam shells______________) __________________Brittle stars _________________ don’t move using tube feet, instead they carry themselves around using their long limbs or tentacles. Sand dollars don’t have limbs or tube feet…. But have very short _______Spines________ which help them ___________________bury into the sand_________________________. _______Sea Cucumbers________________live on the __________ocean floor______________. They don’t have spines, but have a very tough, leathery skin. They have a mouth at one end and an anus at the other end. Describe their interesting defense mechanism… ___________________________________________________________________________ In times of defense the sea cucumber actually ejects it’s internal organs, which secrete a sticky thread that entangle the enemy while the sea cucumber gets away. The organs regenerate within a short period of time. They move with tiny tube feet on their bottom. They are filter feeders; they sweep food into their mouths with tentacles and then can digest the food and expel the remains. ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ PHYLUM ECHINODERMATA Examples of creatures in Phylum Mollusca: Clams Mussels Oysters Octopuses squids The Facts … Body symmetryReproductionMovement- Bilateral There are three main classes within Phylum Mulusca… Sexual muscular foot- or propulsion Food- Sounds like… “mall-US-kah” 1) Gastropoda 2) Bivalvia 3) Cephalopoda All animals in phylum mullusca contain a think muscular ‘______________foot__________’ This features helps them to open and close their shell, eat, move, or to burry into the sand. The 3 Classes of Phylum Mollusca Class Gastropoda Class Bivalvia Class Cephalopoda “Stomach foot” “Two Shells” “Head foot” Examples: Examples: Clams Oysters Mussels Scallops Snails slugs How do they move? Tiny cilia on bottom of the stomach foot. Produce mucus to slide on. Pearls Examples: Squids Octopuses Nautiluses How do they move? How do they move? Opening and closing their shell to squirt water Tentacles & Jet propulsion are formed when a small grain of sand gets stuck between the muscular foot and the shell of an oyster. The oyster covers the foreign object with layers upon layer of a shiny secretion. PHYLUM MULLUSCA Sounds like…. “are-thro-POE-dah” The Facts … Body symmetryReproductionMovement- Bilateral Sexual varies Food- carnivores or herbivores Arthropoda - comes from the Greek word meaning “____________joined legs__________” All arthropods share 4 characteristics 1) Exoskeleton 2) Segmented body 3) Jointed appendages 4) An “open circulatory system Arthropods have an “_______Open_____________” circulatory (blood) system. o This means…. Arthropods have a “outer” skeleton called an _________Exoskeleton_____________. How do arthropods grow bigger, if their skeleton is on the outside of their body? _______________________________________Describe Molting____________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________ There are 4 Sub-phyla of Arthropoda Crustacea Myriapoda Crustacea is greek for “__________hard exoskeleton______________” Myriapoda is greek for “_______many__ legs___________.” Examples of Crustaceans: Examples of Myriapods: -Hermit crabs -Lobsters -Barnacles -Shrimp -crayfish -Daphnia Centipedes – Carnivorous (bugs and beetles) Millipedes- Herbivorious ( leaves and organic matter) Crustaceans have two pair of antennae and mouthparts Why are they found in damp places? that are used for crushing and grinding food. ____________Exoskeletons are not waterproof, so they try to live in damp places so they don’t loose water, and dry out.______________________________________ Crustaceans have a special respiratory organ called _____________________________________________ gills _____________________________________________ Arachinida Insecta Examples of Arachnids: -Insects have three body sections: 1. Head 2. Chest 3. Abdomen -Spiders -Scorpions - ticks -mites -______Six_________ legs attached to the chest. Two body sections: 1) Head/chest Metamorphosis means “to _______transform________” 1) Egg 2) Larva (eat eat eat eat eat) 3) Pupa (sometimes wrapped in cocoon) 4) Adult (reproduction) 2) Abdomen They all have either 4 or 8 legs The fear of animals in this phylum is called… ______________Arachiniphobia______________ Defense mechanisms: stingers & camouflage Extremely powerful chemicals released by insects to attract a mate are called pheromones. PHYLUM ARTHROPODA Invertebrate Tid-bits The five kingdoms are: The levels of classification are (from largest to smallest) 1) Moneran Kingdom 2) Protista Phylum 3) Fungi Class 4) Plantea Order 5) Animalia Family Genus Species Animal Kingdom can be broken down into two major divisions: 1. Invertebrates 2. Vertebrates : Vertebral column = Backbone : Have a Backbone Characteristics of the Animal Kingdom 1. All display the 8 functions of life 2. Animal cells DO NOT contain a cell wall 3. Animals have organized body plans Cells Tissues Organs Types of Symmetry 1) Bilateral 2) Radial 3) Asymmetry Types of Reproduction Sexual Reproduction- Requires 2 sex cells (sperm & egg) Asexual Reproduction- Requires only 1 to produce offspring Organ systems Organism