* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download STEMi Lesson Plan Template Teachers Name: Sharmela
Survey
Document related concepts
History of botany wikipedia , lookup
Ecology of Banksia wikipedia , lookup
Plant ecology wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of plants wikipedia , lookup
Plant physiology wikipedia , lookup
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Ornamental bulbous plant wikipedia , lookup
Pollination wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Plant reproduction wikipedia , lookup
Perovskia atriplicifolia wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
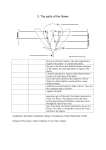
STEMi Lesson Plan Template Teachers Name: Sharmela Chandrashekhar School: P.S. 62 Q STEMi PD Attended: Queens Botanical Garden Lesson Title Flower Parts and Their Functions Grade Level 6th NYS Standards Or Common Core State Standards STANDARD 4: The Living Environment 1.1a Living things are composed of cells. Cells provide structure and carry on major functions to sustain life. Cells are usually microscopic in size. 1.1f Many plants have roots, stems, leaves, and reproductive structures. These organized groups of tissues are responsible for a plant’s life activities. Objective(s) Materials and Websites Students will be able to: Identify parts of a flowering plant and describe their functions. Identify selected parts of a flowering plant and explain the function of each. Identify and explain the parts of a flower and their role in the life cycle of flowering plants, including pollination, seed dispersal and germination. ~ Transparency and learner copies of Parts of a Flower ~ Magnifying glass ~ Microscope ~Flowers ~Computer with internet access ~http://urbanext.illinois.edu/gpe/case4/c4m1.html Smart Start Discuss with students the structure of flowers. Begin by making a list of all the flower parts they know. Then show students a diagram of a flower and discuss the locations of the parts of the plants and their functions. The following parts should be included in this discussion: pistil, stigma, ovary, ovule, stamen, anther, petal, and sepal. Mini-Lesson Explain that reproduction is a process that all living things do. Reproduction of flowering plants is made possible through the processes of pollination, seed production, seed dispersal and germination. If possible, present this in the context of a story of the life of a flower. Mention the key points and functions of the Petal, Sepal, Style, Stigma, Ovary, Ovule, Anther, Filament, Receptacle. As you mention each part, add the appropriate label to the display. As a class, brainstorm ways that plants are pollinated. Discuss how the structure of plants contributes to pollination. Ask students to consider whether they think insects, other animals, or the wind are involved in pollination. Then, on the basis of their observations and the class discussion, ask students to develop their own hypothesis about the mechanism of flower pollination. Have them write their hypothesis on their observation sheets. Application (Group Work) Conclusion Have students dissect the flower they chose. Although each student has his or her own flower, students can dissect their flowers in small groups so that they can share ideas and problem solve together. Each student should dissect his or her flower by carefully removing each part, starting from outside the flower and working inward, counting how many of each part is present on the flower. If a dissecting microscope is available, have students look at each part under the microscope. The flower consists of many different parts. Some of the most important parts being separated into both male and female parts. Stamen This is the male part of the flower. It is made up of the filament and anther, it is the pollen producing part of the plant. The number of stamen is usually the same as the number of petals. Anther This is the part of the stamen that produces and contains pollen. It is usually on top of a long stalk that looks like a fine hair. Filament This is the fine hair-like stalk that the anther sits on top of. Pistil This is the female part of the flower. It is made up of the stigma, style, and ovary. Each pistil is constructed of one to many rolled leaflike structures. Stigma One of the female parts of the flower. It is the sticky bulb that you see in the center of the flowers, it is the part of the pistil of a flower which receives the pollen grains and on which they germinate. Style Another female part of the flower. This is the long stalk that the stigma sits on top of. Ovary The part of the plant, usually at the bottom of the flower, that has the seeds inside and turns into the fruit that we eat. The ovary contains ovules. Ovule The part of the ovary that becomes the seeds. Petal The colorful, often bright part of the flower. They attract pollinators and are usually the reason why we buy and enjoy flowers. Sepal The parts that look like little green leaves that cover the outside of a flower bud to protect the flower before it opens. Extensions: Homework: Draw a flower from close observation at home. Label the main reproductive parts and their functions. Label the parts of a flower and describe their functions.