* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 02. DRC2010-10-01 03:482.4 MB
Survey
Document related concepts
Compounding wikipedia , lookup
Psychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Pharmaceutical industry wikipedia , lookup
Prescription costs wikipedia , lookup
Prescription drug prices in the United States wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacognosy wikipedia , lookup
Drug design wikipedia , lookup
Drug interaction wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Drug discovery wikipedia , lookup
Neuropharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
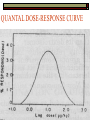
QUANTITATIVE ASPECTS OF DRUG ACTIONS DR. SHABANA ALI QUANTITATIVE ASPECTS OF DRUG ACTIONS Quantitative aspects are important for mode of use e.g. dose-response relationship Dose-Response Relationship of agonists Relationship between amount of drug administered in plasma and magnitude of desired response cont. A given dose of drug produces measurable degree of action in a biological system (sm.muscle or whole animal) Types of DRC Two types 1) 2) Graded Dose-Response Quantal Dose-Response 1) GRADED DOSE-RESPONSE When dose of drug response also e.g., contraction or relaxation of muscles, ∆ BP, ∆ blood sugar etc. Studied in vitro on a piece of small intestine Relationship b/w dose & response can be plotted on curve (x-axis=dose; y-axis=response) Conc./dose on arithmetic scale, curve is hyperbolic (not linear relationship) Conc./dose on log scale, curve is sigmoid-shaped (semi log dose-response curve) Effect of various conc. of ACh on isolated small intestine of rabbit showing graded response GRADED DOSE-RESPONSE CURVE Advantages of semi log Dose-Response Curve Wide range of drug doses is depicted Easy comparison between agonists Easy study of antagonists The middle portion (25-75%) of curve is linear; direct relationship between dose and response can be obtained GRADED DOSE-RESPONSE CURVE Following valuable data can be drawn Threshold dose: dose which produces first noticeable response ED50/EC50 (median effective dose or concentration): Dose or conc. which produces 50% of maximal response Cont. Drugs with same action at a receptor but with d/f potency show parallel DRC Potencies of two drugs can be compared by ED50 ED100/EDmax (ceiling effect): Conc. which produces maximal response 2) QUANTAL DOSE-RESPONSE Response follow all or none phenomenon (e.g., analgesics, convulsants, anticonvulsant activity, death etc) Dose of drug evokes a fixed pharmacological response Studied in whole animal (in vivo); data derived from group of animals or population Results can be plotted as Log dosepercentage curve Gaussian Distribution Curve (sigmoid > graded response) is obtained by keeping log doses on horizontal-axis and % response on vertical-axis QUANTAL DOSE-RESPONSE CURVE Following valuable data can be drawn from Quantal Dose Response curve A) Median Effective Dose (ED50) Dose of a drug required to produce 50% of maximum response B) Median lethal dose (LD50) Dose of a drug required to kill 50% of experimental animals; measurement of toxicity C) Median toxic dose (TD50) Dose producing toxicity in 50% animals or humans D) Therapeutic Index Ratio of the median lethal dose to median effective dose CONT. Therapeutic Index (TI) =LD50 / ED50 e.g. digoxin & warfarin have TI; Penicillin = TI Based on median doses; not about slope of DRC for therapeutic or toxic doses Approximate assessment of safety of the drug TI safer is drug &vice versa THERAPEUTIC INDEX E) Margin of safety Ratio of LD 0.1 / ED 99.9 LD0.1=min. lethal dose for 0.1 % of population; ED99.9%=minimum effective dose for 99.9 % of population STRUCTURE-ACTIVITY RELATIONSHIP Study of chemical structure of drug and its relationship with its pharmacological action Both affinity & efficacy of drug r determined by its chemical structure Minor change in drug molecule major change in pharmacological property cont. Significance of structure-activity relationship Synthesis of 1. Valuable therapeutic agent from parent compound Drug with wide margin of safety Drug with selectivity for tissues 2. 3. Useful therapeutic antagonist of hormone or neurotransmitter Improvement of PK property Drug designing, identification of receptors, size, shape, position, orientation of charged groups or H+ bond donors Improved affinity and selectivity for receptors E.g., Chlorpromazine (antipsychotic) trifluoperazine Procaine (antiarrhythmic) procainamide (resistant to hydrolysis) Benzyl pencillin (antibiotic) phenoxymthylpencillin, ampicillin, amoxycillin (resistant to HCl) Atropine (mydriatic) Homatropine (less lasting effect)