* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Becoming Human Viewers Guide
Human genetic variation wikipedia , lookup
Multiregional origin of modern humans wikipedia , lookup
Homo floresiensis wikipedia , lookup
Origins of society wikipedia , lookup
History of anthropometry wikipedia , lookup
Before the Dawn (book) wikipedia , lookup
Discovery of human antiquity wikipedia , lookup
Homo heidelbergensis wikipedia , lookup
Human evolutionary genetics wikipedia , lookup
Homo erectus wikipedia , lookup
Homo naledi wikipedia , lookup
Anatomically modern human wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary origin of religions wikipedia , lookup
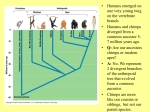
Name: Date: Becoming Human Viewers Guide Please read the following sections and answer all questions. Video can be seen at. www.becominghuman.org. A. Things to know before you see the video: Glossary paleoanthropology (n) the branch of anthropology concerned with fossil hominids Hadar (n) An archeological site in East Africa founded in 1968 australophithecus afarensis (n) an extinct hominid which lived between 3.9 and 2.9 millions years ago; Lucy was this type of hominid Meioscene Age (n) Miocene period: the fourth epoch of the world when the Himalayas and Alps were forming and there was diversification in primates; 23.3 to 5.3 millions years ago Laeotoli Footprints (n) Discovered by Mary Leaky in Tanzania, early human footprints Bipedalism (n) word used to describe an animal who uses two legs to walk Aboriginal (adj) word used to describe people, animals or plants native to an area for a very long time before any colonists arrived Terms Donald Johanson A paleontologist who found the australophithecus afarensis hominid known as Lucy Hominid A primate- humans and their ancestors can be described as a hominid Lucy Name for hominid found in the Afar region by Donald Johanson Mary Leakey Premiere archeologist, discovered very important artifacts Turkana Boy Name of a nearly complete skeleton of a hominid boy found in Kenya Homo Erectus An ancestor of humans; a primate who “stood up” Homo neanderthalensisA now extinct species of humans who lived in Europe between 120,000-350,000 years ago with a receding forehead and prominent brow ridges Homo sapiens a primate species to which humans belong Koonalda A limestone cave located in South Australia where Rock Art was founded in the 1950’s. Timeline 4000 million years ago First signs of life appear according to scientists 3.7 million years ago Footprints found in Kenya serve as strong evidence for the beginnings of bipedalism 3 million years ago Lucy the fossil died in the modern-day Afar region of Ethiopia 1.8 million years ago Homo erectus evolves in Africa 19,000 years ago Koonalda Cave Art is believed to have have been created 1954 Koonalda Cave Art is rediscovered in South Australia 1974 Lucy is discovered by Don Johanson B. Things to note while you see the video: 1. Why is northern Ethiopia such a good place for fossil hunting? 2. What is so significant about Lucy? What does she tell us about human origins? 3. What was the environment of Hadar like 3.2 million years ago? 4. What do many of the bones found at Hadar tell us about the way hominids lived and died? 5. What changes took place in Africa during the Meioscene Age (6 million years ago) that led to the development of hominids? 6. What are the Laeotoli footprints and what do they tell us about hominids? 7. Why is bipedalism as an anatomical (or bodily) adaptation so important? 8. Which two anatomical features distinguish h. erectus from a. afarensis? 9. How did bigger bodies and bigger brains affect the behavior of h. erectus? 10. Which physical features identified Neanderthals as human? Which physical features separated Neanderthals from modern humans? 11. What was found on the walls of the caves in Koonalda and why are they significant? What do they tell us about the evolution of human beings? C. Things to think about after you’ve seen the video: Interpreting what you heard - quotes: Read the three quotes and answer the following questions using the quotes, images and the notes you have taken as evidence. 1. “She was the ape that stood up.” 2. “Hominds such as Lucy serve as a touchstone for discussing human origins.” 3. “In some ways, homo erectus was the evolutionary parent of our own species.” 1. Which physical characteristics make human beings human? List them. Why is this list an incomplete definition of what makes human being uniquely human? 1. “These engravings are simple yet they represent the profound change in the way our ancestors viewed their world. They mark the birth of their ability to understand abstract concepts, both about their world and about themselves. This was the dawn of consciousness.” 2. “When you look at the rock art it was painted by the hands and the emotions and the mind of the artist that created it. To witness what the ancestors left behind is an incredible gift.” 2. The scholars in the film argue that the emergence of culture is what truly makes human beings uniquely human. Do you agree? Why or why not? Use the quotes listed above and the information you acquired from the film to answer this question in a persuasive paragraph? Big idea question: While Don Johanson tells a compelling story about the evolution of human beings, why is the human record so incomplete? What types of evidence could bridge these gaps? Do you think this type of evidence actually exists? Why or why not? Write a Persuasive Paragraph in which you cite specific evidence from the documentary to support your argument.