* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Common Core Learning Standards GRADE 8 Mathematics
Schrödinger equation wikipedia , lookup
Two-body problem in general relativity wikipedia , lookup
BKL singularity wikipedia , lookup
Equation of state wikipedia , lookup
Derivation of the Navier–Stokes equations wikipedia , lookup
Maxwell's equations wikipedia , lookup
Euler equations (fluid dynamics) wikipedia , lookup
Calculus of variations wikipedia , lookup
Navier–Stokes equations wikipedia , lookup
Equations of motion wikipedia , lookup
Schwarzschild geodesics wikipedia , lookup
Differential equation wikipedia , lookup
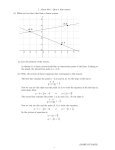
Common Core Learning Standards GRADE 8 Mathematics EXPRESSIONS & EQUATONS Common Core Learning Standards Work with radicals and integer exponents. Concepts Embedded Skills Properties of exponents Divide the numerical expressions with integer exponents with like bases by subtracting the exponents. Evaluate numerical expressions with integer exponents. Write a numerical expression with a negative exponent as an equivalent numerical expression with a positive exponent (write the base as a fraction). Multiply numerical expressions with integer exponents with like bases by adding the exponents. 8.EE.1. Know and apply the properties of integer exponents to generate equivalent numerical expressions. For example, = Vocabulary Base Exponent Integer Expression Monomial Coefficient Numerical expression Add and subtract and divide numerical expressions with integer exponents. SAMPLE TASKS I.) Explain why the given expressions are equivalent: ____________________________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________________________ Copyright (c) 2011 by Erie 1 BOCES- Deep Curriculum Project for Mathematics-- Permission to use (not alter) and reproduce for educational purposes only. II.) Using your knowledge of the laws of exponents, explain why each student is correct or incorrect Jose’s simplified expression) = x12 Charlotte’s simplified expression) = x12 ___________________________________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________________________ III.) Complete the following table of values: Column A Column B What effect does the sign of the exponent in column A have on the answer in column B? __________________________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________________ Copyright (c) 2011 by Erie 1 BOCES- Deep Curriculum Project for Mathematics-- Permission to use (not alter) and reproduce for educational purposes only. Common Core Learning Standards Work with radicals and integer exponents. 8.EE.2. Use square root and cube root symbols to represent solutions to equations of the form x2 = p and x3 = p, where p is a positive rational number. Evaluate square roots of small perfect squares and cube roots of small perfect cubes. Know that is irrational. Concepts Embedded Skills Square roots and cube roots Calculate the solution to x2 = p, where p is a positive rational number by taking the square root of both sides. Calculate the solution to x3 = p, where p is a positive rational number by taking the cube root of both sides. Evaluate a square root of a perfect square. Name numbers that are perfect squares and nonperfect squares. Evaluate a cube root of a perfect cube. Name numbers that are perfect cubes and nonperfect cubes. Vocabulary Square root Cube root Squared Cubed Solution Perfect square Perfect cube Exponent Inverse operation Index Rational Irrational Identify that non-perfect squares and non-perfect cubes are irrational numbers (focus on ). Copyright (c) 2011 by Erie 1 BOCES- Deep Curriculum Project for Mathematics-- Permission to use (not alter) and reproduce for educational purposes only. SAMPLE TASKS I.) Sally incorrectly solved the following equation on her last math test. Where is Sally’s mistake and on the lines below how should she correctly solve the equation? Step 1 Step 2 Step 3 Step 4 = x=8 _____________________________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________________________ II.) Classify each number below as a rational or irrational number: a) = __________________ d) = ____________________ b) = _________________ e) = ____________________ c) = _________________ III.) Solve for x in the following equation and justify your answer. Copyright (c) 2011 by Erie 1 BOCES- Deep Curriculum Project for Mathematics-- Permission to use (not alter) and reproduce for educational purposes only. Common Core Learning Standards Work with radicals and integer exponents. 8.EE.3. Use numbers expressed in the form of a single digit times a whole-number power of 10 to estimate very large or very small quantities, and to express how many times as much one is than the other. For example, estimate the population of the United States as 3 X and the population of the world as 7 X , and determine that the world population is more than 20 times larger. Concepts Scientific notation Embedded Skills Vocabulary Compare the magnitude (size) of 2 or more numbers written in scientific notation. Rewrite numbers in standard form in scientific notation. Expand numbers written in scientific notation into standard form. Divide numbers in scientific notation to compare their sizes. Scientific Notation Magnitude Standard Form Estimate Expand SAMPLE TASKS I.) The estimated circumference of the Earth is 300,000 miles. The estimated width of the United States is 3,000 miles. Convert each measurement into Scientific Notation and determine approximately how many times larger the circumference of the Earth is compared to the width of the United States. II.) A liter of organic lemon water has molecules in it. If Wegmans sells 2,500 liters of organic lemon water a day, how many molecules would be sold after one week? Give your answer using scientific notation. Copyright (c) 2011 by Erie 1 BOCES- Deep Curriculum Project for Mathematics-- Permission to use (not alter) and reproduce for educational purposes only. Common Core Learning Standards Work with radicals and integer exponents. Concepts Embedded Skills Add, subtract, multiply, and divide numbers written Operations with scientific in scientific notation, applying laws of exponents. Find appropriate units for very large and small notation quantities. Demonstrate on the calculator and identify that E on the calculator means x 10a. 8.EE.4. Perform operations with numbers expressed in scientific notation, including problems where both decimal and scientific notation are used. Use scientific notation and choose units of appropriate size for measurements of very large or very small quantities (e.g., use millimeters per year for seafloor spreading). Interpret scientific notation that has been generated by technology. Vocabulary Scientific notation Decimal notation Powers of 10 Standard form Exponents SAMPLE TASKS I.) The continent of North America consists of Canada, the United States, and Mexico. Find the approximate population of North America in scientific notation if the approximate population of Canada is 30 million, Mexico is 100 million, and the United States is 3 x 108 people. II.) The equation to find the density of an object is equal to grams and its volume is where m = mass and V = volume. The mass of one sample of a substance is liters. Find the density of the given substance in scientific notation. Copyright (c) 2011 by Erie 1 BOCES- Deep Curriculum Project for Mathematics-- Permission to use (not alter) and reproduce for educational purposes only. III.) Alex was using his scientific calculator to do his math homework and he got the number 1.34E28. Explain what this value means and write the answer in both scientific notation and standard form. IV.) A fern grows inches per second. How much will it have grown after three and one-half hours? Give your answer in scientific notation and label it appropriately. Copyright (c) 2011 by Erie 1 BOCES- Deep Curriculum Project for Mathematics-- Permission to use (not alter) and reproduce for educational purposes only. Common Core Learning Standards Understand the connections between proportional relationships, lines, and linear equations. 8.EE.5. Graph proportional relationships, interpreting the unit rate as the slope of the graph. Compare two different proportional relationships represented in different ways. For example, compare a distance-time graph to a distance time equation to determine which of two moving objects has greater speed. Concepts Graphing relationships Embedded Skills Identify the slope of a linear relationship from equations, tables, and graphs. Create and label an appropriate quadrant I graph. Describe unit rate as the slope of a graph. Vocabulary Proportions Unit rate Slope Direct variation Compare two different proportional relationships represented in different ways (graph vs. table vs. equation vs. verbal description). SAMPLE TASKS See Below Copyright (c) 2011 by Erie 1 BOCES- Deep Curriculum Project for Mathematics-- Permission to use (not alter) and reproduce for educational purposes only. I.) Part A: Given the following table of values, illustrate the relationships for each car on the graph provided. Time Elapsed (in hours) Car A Distance (in miles) Car B Distance (in miles) 0 0 0 2 100 104 4 200 208 6 300 312 8 400 416 Part B: Based on your graph, which of the following cars have the greater rate of speed? Explain how you determined your answer. ____________________________________________ ____________________________________________ ____________________________________________ ____________________________________________ Part C: Write the equation of a line that represents Car A if d is the distance and t is the time. _____________________________ Copyright (c) 2011 by Erie 1 BOCES- Deep Curriculum Project for Mathematics-- Permission to use (not alter) and reproduce for educational purposes only. II.) John is going on a trip driving his motorcycle to Albany. His friend, Jeff, is going and driving his motorcycle too. Which friend is using more gas per mile at a faster rate? Explain how you found your answer. John’s Trip Jeff’s Trip Miles Traveled 0 50 100 150 Gas in Tank (in gal.) 7 5 3 1 ______________________________________________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________________________________________ Copyright (c) 2011 by Erie 1 BOCES- Deep Curriculum Project for Mathematics-- Permission to use (not alter) and reproduce for educational purposes only. Common Core Learning Standards Understand the connections between proportional relationships, lines, and linear equations. 8.EE.6. Use similar triangles to explain why the slope m is the same between any two distinct points on a non-vertical line in the coordinate plane; derive the equation y = mx for a line through the origin and the equation y = mx + b for a line intercepting the vertical axis at b. Concepts Embedded Skills Linear equations Determine the slope of a line by counting the rise over the run of the given line. Explain why the slope of a line is the same for any two points on the graph using rise over run. Explain slope as a constant rate of change (rise over run). Given a line that passes through the origin, write the equation for the line in the form y = mx, where the slope is found using rise over run. Given a line that passes the vertical axis at point other than the origin, write the equation for the line in the form y = mx + b, where the slope is found using rise over run and b is where the line intercepts the vertical axis. Vocabulary Slope Y-intercept Slope intercept form Similar triangles Non-vertical line Origin Constant rate of change SAMPLE TASKS I.) Using any two points on the given line find the slope. Show your work. Does the slope of the line change depending on which two points you use? Show an example to justify your answer. __________________________________________ What is the equation of the line? ______________________________ Copyright (c) 2011 by Erie 1 BOCES- Deep Curriculum Project for Mathematics-- Permission to use (not alter) and reproduce for educational purposes only. II.) Given the following diagram, explain how the slope is found between the coordinates (-4, 4) and (8, -2). If you pick two different points on the same line, explain what happens to the slope. __________________________________________ __________________________________________ III.) The equation of the line in graph d. is y = 2x, what 2 characteristics about this line makes this equation true? __________________________________________ __________________________________________ __________________________________________ Copyright (c) 2011 by Erie 1 BOCES- Deep Curriculum Project for Mathematics-- Permission to use (not alter) and reproduce for educational purposes only. Common Core Learning Standards Analyze and solve linear equations and pairs of simultaneous linear equations. 8.EE.7a. Give examples of linear equations in one variable with one solution, infinitely many solutions, or no solutions. Show which of these possibilities is the case by successively transforming the given equation into simpler forms, until an equivalent equation of the form x = a, a = a, or a = b results (where a and b are different numbers). Concepts Solving linear equations Embedded Skills Solve a linear equation with one solution. Solve a linear equation with infinitely many solutions. Solve a linear equation with no solution. Check the solution to an equation. Explain the differences between one solution, no solution, and infinitely many. Vocabulary Equation Variable Infinite solution Linear No solution Inverse operation Distributive property Combine like terms SAMPLE TASKS I. Does this equation have no solution, one solution or infinitely many solutions? Explain your response. x+1=x+2 ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ II. Does this equation have no solution, one solution or infinitely many solutions? Explain your response. 2x + 3 = 7x + 13 ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ Copyright (c) 2011 by Erie 1 BOCES- Deep Curriculum Project for Mathematics-- Permission to use (not alter) and reproduce for educational purposes only. III. Does this equation have no solution, one solution or infinitely many solutions? Explain your response. 4 + 12x = 6 + 3x – 2 + 9x ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ IV. Solve for x in this equation. Check your solution. V. Write 3 equations that have a variable on both sides of the equal sign. Write the equations so that one equation will have no solution, one equation will have one solution, and one equation will have infinitely many solutions. Solve each equation to show each example. Copyright (c) 2011 by Erie 1 BOCES- Deep Curriculum Project for Mathematics-- Permission to use (not alter) and reproduce for educational purposes only. Common Core Learning Standards Analyze and solve linear equations and pairs of simultaneous linear equations. 8.EE.7b. Solve linear equations with rational number coefficients, including equations whose solutions require expanding expressions using the distributive property and collecting like terms. Concepts Multi-step equations Embedded Skills Simplify equations using the distributive property, combining like terms, and inverse operations. Solve multi-step linear equations with rational number coefficients. Add, subtract, multiply, and divide rational numbers. Vocabulary Distributive property Combine like terms Coefficient Inverse operations Equations Rational numbers SAMPLE TASKS I. Does this equation have no solution, one solution or infinitely many solutions? Explain your response. ____________________________________________ ____________________________________________ ____________________________________________ Copyright (c) 2011 by Erie 1 BOCES- Deep Curriculum Project for Mathematics-- Permission to use (not alter) and reproduce for educational purposes only. II. Solve and check the equation III. When Josh solved the following equation it did not check. Correct Josh’s mistake and explain his mistake using numbers and words. _________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________ + + _________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________ IV. A pizza delivery man earns $7.50 per hour and $2.00 per delivery. Each week the driver spends $28.00 on car maintenance and $86.00 on gas. If the driver works 40 hours per week, how many deliveries are needed each week to earn $300.00 after expenses? Set up an equation to solve the problem above. Copyright (c) 2011 by Erie 1 BOCES- Deep Curriculum Project for Mathematics-- Permission to use (not alter) and reproduce for educational purposes only. Common Core Learning Standards Analyze and solve linear equations and pairs of simultaneous linear equations. 8.EE.8a. Understand that solutions to a system of two linear equations in two variables correspond to points of intersection of their graphs, because points of intersection satisfy both equations simultaneously. Concepts Systems of linear equations Embedded Skills Define the solution to a linear system of equations as the intersection point on a graph. Graph a system of linear equations. Identify the point of intersection to a system of linear equations. Vocabulary System of equations Solution Point of intersection SAMPLE TASKS I. Graph the system of linear equations below. What is the solution of the system of equations? Copyright (c) 2011 by Erie 1 BOCES- Deep Curriculum Project for Mathematics-- Permission to use (not alter) and reproduce for educational purposes only. II. Solve the following system of equations graphically. III. Stacey believes the solution to this system of equations answer. and is (-5,5). Is Stacey correct? Justify your Copyright (c) 2011 by Erie 1 BOCES- Deep Curriculum Project for Mathematics-- Permission to use (not alter) and reproduce for educational purposes only. IV. What is the solution to the system of linear equations shown in the graph. ANSWER: ______________ Copyright (c) 2011 by Erie 1 BOCES- Deep Curriculum Project for Mathematics-- Permission to use (not alter) and reproduce for educational purposes only. Common Core Learning Standards Concepts Embedded Skills Analyze and solve linear equations and pairs of simultaneous linear equations. Systems of equations algebraically Solve a system of linear equations algebraically with one solution. Solve a system of linear equations algebraically with no solution. Solve a system of linear equations algebraically with infinitely many solutions. Estimate the solution of a system of linear equations by graphing. Solve simple systems of linear equations by inspection. 8.EE.8b. Solve systems of two linear equations in two variables algebraically, and estimate solutions by graphing the equations. Solve simple cases by inspection. For example, 3x + 2y = 5 and 3x + 2y = 6 have no solution because 3x + 2y cannot simultaneously be 5 and 6. Vocabulary Elimination Substitution Algebraically Graphically One solution No solution Infinitely many solutions Systems of equations SAMPLE TASKS I. Identify the number of solutions from each graph below. a.) b.) ________________________ ________________________ c.) ________________________ Copyright (c) 2011 by Erie 1 BOCES- Deep Curriculum Project for Mathematics-- Permission to use (not alter) and reproduce for educational purposes only. II. Adam graphs a system of equations. He notices that the lines of the graphs are parallel. Given that the lines are parallel, what does it mean for the system of equations? _______________________________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________________________ III. Solve the system of equations ALGEBRAICALLY. =x IV. Explain why it is more accurate to solve a system of equations containing decimals by using algebra than by graphing the equations. ________________________________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ Copyright (c) 2011 by Erie 1 BOCES- Deep Curriculum Project for Mathematics-- Permission to use (not alter) and reproduce for educational purposes only. Common Core Learning Standards Analyze and solve linear equations and pairs of simultaneous linear equations. 8.EE.8c. Solve real-world and mathematical problems leading to two linear equations in two variables. For example, given coordinates for two pairs of points, determine whether the line through the first pair of points intersects the line through the second pair. Concepts Real world situations Embedded Skills Write a system of linear equations from a word problem. Solve a system of linear equations created from a word problem. Graph points on a coordinate plane. Calculate the slope of a line using the slope formula. Create an appropriate coordinate plane based on the constraints of a word problem. Vocabulary Intersect Linear equation Solution Variable Slope/rate of change Y-intercept Constraints Coordinate plane SAMPLE TASKS I. Emily sells pretzels and lemonade at a concession stand. One morning she sells 10 pretzels and 5 lemonades and makes a total of $40.00. In the afternoon, she sells 25 pretzels and 20 lemonades and makes $115.00. How much does Emily charge for 1 pretzel and how much does she charge for lemonade? Copyright (c) 2011 by Erie 1 BOCES- Deep Curriculum Project for Mathematics-- Permission to use (not alter) and reproduce for educational purposes only. II. A line passes through points (-3, -1) and (2, 4). Another line passes through (-3, 2) and (-1, -2). Do the lines intersect? Explain how you arrived at your answer. ______________________________________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________________________________ III. The table shows the initial height and growth rate of an apple tree and a cherry tree. Write a system of equations the gardener could use to determine the time t when height h of the two trees will be the same. Initial Height (ft) Growth rate (ft/yr) Apple 2.75 1.2 Cherry 2.12 1.38 _________________________________________________________________________________________ IV. Two brothers decide to save money. One starts with $10, and saves $2 each day. The other starts with none, but saves $3 each day. Write two equations to represent both brothers’ savings plans. Will they ever have the same amount of money? If not explain why. If they will, after how many days they have the same Copyright (c) 2011 by Erie 1 BOCES- Deep Curriculum Project for Mathematics-- Permission to use (not alter) and reproduce for educational purposes only. amount? ____________________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________________________ Copyright (c) 2011 by Erie 1 BOCES- Deep Curriculum Project for Mathematics-- Permission to use (not alter) and reproduce for educational purposes only.