* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Switched Capacitor DC-DC Converters: Topologies and Applications
Electrical ballast wikipedia , lookup
Pulse-width modulation wikipedia , lookup
History of electric power transmission wikipedia , lookup
Power inverter wikipedia , lookup
Variable-frequency drive wikipedia , lookup
Three-phase electric power wikipedia , lookup
Electrical substation wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
History of the transistor wikipedia , lookup
Distribution management system wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
Schmitt trigger wikipedia , lookup
Integrating ADC wikipedia , lookup
Power MOSFET wikipedia , lookup
Voltage regulator wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
Current mirror wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
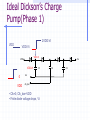
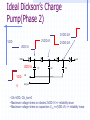
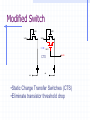
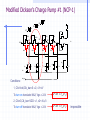
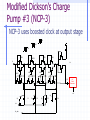
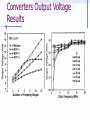
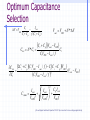
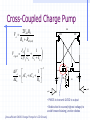
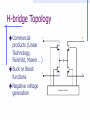
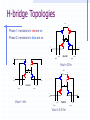
Switched Capacitor DC-DC Converters: Topologies and Applications Bill Tsang and Eddie Ng Outline Motivations Dickson’s Charge Pump Other Various Charge Pumps Applications Conclusion Motivations Inductorless On-chip integration Low cost High switching frequency Easy to implement (open-loop system) Fast transient but large ripple High efficiency but limited output power Ideal Dickson’s Charge Pump(Phase 1) 2VDD-Vt VDD VDD-Vt VDD-Vt VDD Vo VDD-Vt 0 VDD C1 clk clk_bar • Clk=0, Clk_bar=VDD • Finite diode voltage drops, Vt C2 C3 Ideal Dickson’s Charge Pump(Phase 2) 3VDD-2Vt 2VDD-Vt VDD 2VDD-2Vt VDD-Vt VDD Vo VDD-Vt VDD clk 0 clk_bar C1 C2 C3 • Clk=VDD, Clk_bar=0 • Maximum voltage stress on diodes 2VDD-Vt => reliability issue • Maximum voltage stress on capacitors VCn =n(VDD-Vt) => reliability issue Dickson’s Charge Pump V2+dV2 V1+dV1 V2 V V1 v1 Vth v2 VDD Vo Cp C1 Cp C2 Cp C3 C1=C2=C3=C clk clk_bar V V V Vth Io C C C p f (C C p ) (Body effect can be significant at later stages) Vout VDD N * (V Vt ) Vt Non-idealities Threshold voltage drop [Mos charge pumps for low-voltage operation] Vth Vtho γ VBS 2φF 2φF Parasitic capacitor divider voltage drop Low conversion efficiency and pumping gain G V V V V (V ) V2 2 1 tn 2 Limited maximum number of stages 2 VDD Vtho Vout,max 2φF 2φF γ [An on-chip High-voltage generator circuit for EEPROMs with a power supply voltage below 2V] Modified Switch MD1 VDD MD1 VDD MS1 CTS clk 2VDD clk •Static Charge Transfer Switches (CTS) •Eliminate transistor threshold drop Modified Dickson’s Charge Pump #1 (NCP-1) dV v3 dV V2 dV v1 MD1 MD3 MD2 v2 v1 MD4 v3 Vo VDD MS1 MS3 MS2 MS4 Cp Cp Cp C1 Cp C2 Cp C3 C4 C5 clk clk_bar Conditions: 1, Clk=Vdd,Clk_bar=0: v2, v3+V To turn on transistor Ms2; Vgs = 2V 2 * V Vtn (V2 ) 2, Clk=0,Clk_bar=VDD: v1, v2+V,v3 To turn off transistor Ms2; Vgs = 2V 2 * V Vtn (V1 ) impossible Modified Dickson’s Charge Pump #1 (NCP-1) Static Charge Transfer Switches (CTS) Better voltage pumping gain than diodes GV 2 V2 V1 V Lower voltage equals upper voltage of pervious stage Utilizing higher voltage from following stage to drive CTS Reverse charge sharing since CTS cannot turn off completely Modified Switch #2 MD1 MS1 MN1 used to turn off MS1 MP1 used to turn on MS1 MN1 MP1 Next stage clk • Eliminate transistor threshold drop • Complete turn-off of switch, MS1 Modified Dickson’s Charge Pump #2 (NCP-2) dV dV dV MD1 MS1 v2 C1 v3 MS3 MS2 MN2 Cp MD3 MD2 v1 MP2 Cp C2 Cp C3 clk clk_bar Conditions: 1, Clk=Vdd,Clk_bar=0: v2, v3+V To turn on transistor MP2 and MS2; Vgs = 2V 2 * V Vtp 2 * V Vtn (V2 ) 2, Clk=0,Clk_bar=VDD: v1, v2+V,v3 To turn on transistor MN2 and turn off MS2; Vgs = 2V 2 * V Vtn (V1 ) Complete Circuit(NCP-2) dV dV dV MD1 v2 v1 MS1 MD3 MD2 MD4 v3 Vo MS3 MS2 MS4 q MN2 MP2 Cp Cp Cp C1 Cp C2 Cp C3 clk clk_bar •Careful PMOS well connection to prevent latch-up •Diode-connected output stage used C4 C5 Modified Dickson’s Charge Pump #3 (NCP-3) NCP-3 uses boosted clock at output stage dV dV dV MD1 MD3 MD2 MD4 Vi Vo MS1 MS3 MS2 MS4 q C5 HV Clock Generator clk Cp Cp clk clk_bar C1 Cp C2 Cp C3 C4 Converters Output Voltage Results Optimum Capacitance Selection V VDD Ci I out Ci C p f (Ci C p ) Ctot N * Ci Vout VDD N * V C C V i p out VDD CiVDD I out / f Ci Ctot 2Ci C p CiVDD I out / f Ci Ci C p VDD (Vout VDD ) 2 Ci CiVDD I out / f Ci ,min I out I out VDD f VDD f 2 C p I out VDD f [A Low-Ripple Switched-Capacitor DC-DC Up converter for Low-voltage applications] Efficiency and Output Impedance Power loss due to: Vth, Rds(on), ESR, Cp, etc Efficiency estimation [Performance limits of switched-capacitor DC-DC Converter] Vout M *Vin M=ideal conversion ratio Output impedance (slow switching) [Performance limits of switched-capacitor DC-DC Converter] i Ts Vout 1 Ro q / Ts fC Ts=switching period i= parasitic time constant q=charge supplied to the source Vout Cross-Coupled Charge Pump VDD 2Vdd RL Vo RL Rds( on) I Vripple L 2f M10 M9 1 1 CL C1 CL Vo 1 sC1 sC L I L RL Vo 1 C1 RL CL1 C2 phi2 phi1 • PMOS to transmit 2VDD to output • Bodies tied to source(highest voltage) to avoid forward biasing junction diodes [Area-efficient CMOS Charge Pumps for LCD Drivers] H-bridge Topology 1 Commercial products (Linear Technology, Fairchild, Maxim …) Buck or Boost 3 functions Negative voltage generation 2 4 Oscillator and Control H-bridge Topologies Vin 1 2 Phase 1: transistors in red are on Phase 2: transistors in blue are on Vin 3 4 Vout 1 doubler phi1 2 phi2 phi1 phi2 Vout = 2Vin Vout Vin 1 3 4 Vin Vout phi1 inverter phi2 2 phi1 phi2 3 4 Vin Vout = -Vin phi1 Splitter phi2 Vout = 0.5 Vin phi1 phi2 Application (1): Flash Memory Floating gate programming Control gate voltage >> Vdd [ee141 lecture] Application (1): Flash Memory Nominal VDD= 5V Application (2): Sample Switches vicm vicm phi1 phi2d Ci Vi+ S/H circuit– constant vgs sampling with all input level Reduces distortion Reduces Rds(on) M10 CL phi1d phi2 Cs - + Vo+ OTA + - Cs phi1d Vo- phi2 Vi- CL phi2d phi1 vicm Ci vicm VDD M9 Phi_bar A M4 M5 M8 M3 M7 Voltage doubler C1 C2 C3 M2 Phi M1 M9 M6 M11 Vo VSS Phi_bar Vin Application (3): Low voltage Amplifier Positive zero in Miller compensation 1/gm pole-zero cancellation VDD [charge-pump assisted low-power/low-voltage CMOS Opamp Design] V- Charge pump V+ >2VGS Conclusion Different Dickson’s SC converters discussed Optimal Capacitor size selection Discussion of cross-coupled doublers Commercial product: Full H-bridge Applications: Flash, ADC, Amplifier, LCD driver