* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Notes on the Civil War - Garrett Academy Of Technology
Lost Cause of the Confederacy wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Malvern Hill wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Lewis's Farm wikipedia , lookup
Second Battle of Corinth wikipedia , lookup
Blockade runners of the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Virginia in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Battle of New Bern wikipedia , lookup
Union blockade wikipedia , lookup
First Battle of Bull Run wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Harpers Ferry wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Chancellorsville wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Shiloh wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Island Number Ten wikipedia , lookup
Alabama in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Fredericksburg wikipedia , lookup
Border states (American Civil War) wikipedia , lookup
Hampton Roads Conference wikipedia , lookup
Economy of the Confederate States of America wikipedia , lookup
Opposition to the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Eastern Theater of the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Namozine Church wikipedia , lookup
Ulysses S. Grant and the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Antietam wikipedia , lookup
Western Theater of the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Seven Pines wikipedia , lookup
Military history of African Americans in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Capture of New Orleans wikipedia , lookup
Conclusion of the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Union (American Civil War) wikipedia , lookup
Northern Virginia Campaign wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Gaines's Mill wikipedia , lookup
United Kingdom and the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Siege of Vicksburg wikipedia , lookup
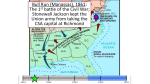
Notes on the Civil War Ft. Sumter: Bombardment started April 12, 1861 at 4:30 am – Edmund Ruffin fires 1st shot Union commander at Sumter was Maj. Robert Anderson Confederate commander was Gen. Pierre Gustave Toutant (PGT) Beauregard After 34 hours of bombardment, Anderson sends word that he will surrender On April 14, 1861, USA flag is lowered on Ft Sumter – two men killed when firing cannons in honor Advantages/ Disadvantages for both sides USA CSA 22 million people 9 million; 3.5 of them slaves 2/3 of the railroads – US built more during 1/3 of the RR – couldn’t build more war (trains were used to transport food, supplies and troops – very imp. to war effort) 4/5 of the factories 1/5 of the factories (both sides needed to switch over to war production, but after 1 year, US was producing all they needed) Better navy Not much of a navy Established government Financially stable needed to create a government needed to create economic system US had more generals, but not as good as CSA Union had only one military college – West Point; all others were in the south USA did not have a real cause for which to fight until Lincoln issued the Emancipation Proclamation which made freeing the slaves the goal of the war Had R E Lee and the better generals Had a military tradition and were better prepared for a military way of life Had a cause for which to fight – the CSA was fighting for their independence; their land, their families, and their way of life. Strategies for each Side USA Anaconda Plan – 1. US will create a naval blockade to keep European goods from getting to the CSA and keep CSA cash crops from being sold to make money for the war effort 2. US will take the Mississippi River to split the CSA in half and keep goods from Texas and Mexico from getting to the east (Europe was sending goods to CSA through Mexico) 3. seize Railroad centers to cut off flow of goods within the CSA 4. take New Orleans, Vicksburg, and Memphis to control Mississippi River **All this will slowly “choke” the CSA to death like an Anaconda Take Richmond – more of a symbolic strategy Later in the war, TOTAL WAR - this is Grant’s plan to bring the CSA to its knees. Put into effect most notably by Sherman on his March to the Sea. Destroy all that you cannot use so that the enemy can’t use it CSA Defend, defend, defend – hold out until the North gives up King Cotton Diplomacy – withhold cotton vital for Great Britian’s and France’s economy until they agreed to recognize the CSA, declare the Union blockade illegal, and assist the CSA in the war effort – ultimately a failure – GB and France went elsewhere for cotton Battles in the Eastern Campaign Army of Northern Virginia – CSA versus Army of the Potomac – USA First Manassas (Bull Run) US – Irwin McDowell CSA PGT Beauregard Peninsula Campaign US – George McClellan CSA Joseph Johnston Second Manassas (Bull Run) – US – John Pope CSA RE Lee Antietam (Sharpsburg) US – George McClellan CSA RE Lee bloodiest single day of fighting – preliminary Emancipation Proclamation is issued Fredericksburg US Ambrose Burnside CSA RE Lee Chancellorsville US Joseph Hooker CSA RE Lee “Stonewall” Jackson is killed by friendly fire Gettysburg US George Meade CSA RE Lee Wilderness Campaign US Ulysses Grant CSA RE Lee Cold Harbor US Ulysses Grant CSA RE Lee Appomattox Courthouse US Ulysses Grant CSA RE Lee Surrender on April 9, 2006 Grant gave Lee VERY generous terms of surrender Other battles of Importance Monitor v. Virginia (Merrimack) March 9, 1862 battle between two ironclad ships - new technology -CSA wanted to use it to destroy the Union Blockade - a draw New Orleans May 30, 1862 USA Admiral David Farragut and General Benjamin Butler CSA General Mansfield Lovell This give the USA control of the mouth of the Mississippi River Vicksburg May 18 - July 4, 1863 USA Ulysses S Grant CSA John C Pemberton Grant cannot take the town by any other means, so he lays siege to it and starves them out. The CSA holds out as long as they can but surrender on July 4, 1863 (the day after the end of the Battle of Gettysburg) . After Vicksburg, the only CSA hold on the Mississippi River is Port Hudson, LA. Port Hudson May 21 - July 9, 1863 USA Maj. Gen. Nathaniel P. Banks CSA Maj. Gen. Franklin Gardner The Union has also laid siege to this fort under Grant’s campaign and it falls on July 9, 1863. Also. Emancipation Proclamation - announced by Lincoln after Antietam; issued on January 1, 1863. The Emancipation Proclamation stated that all slaves in territory in a state of rebellion against the USA were freed. It did not include the slaves in the Border States (Maryland, Delaware, Kentucky, and Missouri) and does not include slaves in territory already in Union hands such as New Orleans and Port Royal, SC (Beaufort and Hilton Head). Because the states in rebellion considered themselves part of the Confederacy, they did not follow Lincoln’s orders, so the Emancipation Proclamation did not free any slaves when issued, but did free them as the Union troops took over Confederate territory. What it did do was make the abolition of slavery a goal of the war and give the Union a cause to fight for.