* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Cardiovascular System
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Artificial heart valve wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
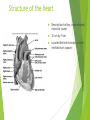
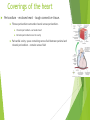
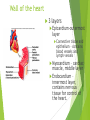
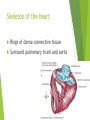
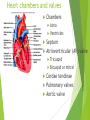
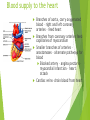
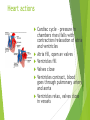
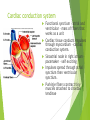
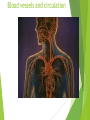
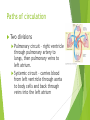
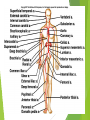
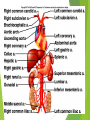
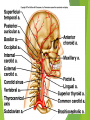
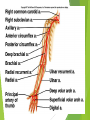
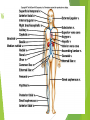
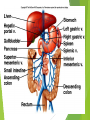
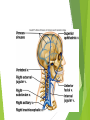
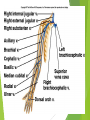
The Cardiovascular System Ch. 18,19 Introduction Cardiovascular system Heart Blood vessels Arteries Capillaries Veins Heart anatomy Structure of the heart Description-hollow, cone-shaped, muscular pump 12 cm by 9 cm Located behind sternum, within mediastinum (space) Coverings of the heart Pericardium – encloses heart – tough connective tissue. Fibrous pericardium surrounds visceral serous pericardium. Visceral pericardium- surrounds heart Parietal pericardium-lines the cavity Paricardial cavity- space containing serous fluid between parietal and visceral pericardium – contains serous fluid Wall of the heart 3 layers Epicardium-outermost layer Connective tissue and epithelium – contains blood vessels and lymph vessels Myocardium – cardiac muscle, middle layer Endocardium – innermost layer, contains nervous tissue for control of the heart. Skeleton of the heart Rings of dense connective tissue Surround pulmonary trunk and aorta Heart chambers and valves Chambers Atria Ventricles Septum Atrioventricular (AV) valve Tricuspid Bicuspid or mitral Cordae tendinae Pulmonary valves Aortic valve Path of blood through heart Inferior or superior vena cava Pulmonary vein Left atrium Right atrium Left AV valve Right AV valve Left ventricle Right ventricle Aorta Pulmonary artery Aortic valve Pulmonary valve Body Lungs When you come in: Prepare for quiz You will be asked to trace the path of blood through the heart in written bullet form, listing the vessels, structures, chambers, etc. 4/30/201 7 Quiz In bullet form, list the path of a blood cell from the foot. Include vessels, structures, chambers, valves. There are 14 – 7pts apiece Blood supply to the heart Branches of aorta, carry oxygenated blood – right and left coronary arteries – feed heart Branches from coronary arteries feed capillaries of myocardium Smaller branches of arteries – anastomoses – alternate pathways for blood Blocked artery – angina pectoris – myocardial infarction – heart attack Cardiac veins- drain blood from heart Heart beating Heart actions Cardiac cycle – pressure in chambers rises/falls with contraction/relaxation of atria and ventricles Atria fill, open av valves Ventricles fill Valves close Ventricles contract, blood goes through pulmonary artery and aorta Ventricles relax, valves close in vessels Heart sounds Heart sounds caused by valve closure First sound (lubb) – ventricles contract and AV valves close Second sound (dupp) ventricles relax and aortic and pulmonary valves close. Cardiac conduction system Functional synctium – atrial and ventricular – mass of fibers that works as a unit Cardiac tissue conducts impulses through myocardium – cardiac conduction system. Sinoatrial node in right atrium – pacemaker – self exciting Impulses spread through atrial synctium then ventricular synctium. Purkinje fibers contract tiny muscles attached to chordae tendinae Electrocardiogram ECG – electrical recording of changes that occur in cardiac cycle P wave – depolarization of atria QRS complex – depolarization of ventricles T wave – ventricular repolarization Regulation of the cardiac cycle Amount of blood pumped must adjust according to body needs SA node innervated by sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous system divisions so CNS controls heart rate. Cardiac control center in medulla oblongata – adjusts heart rate based on blood pressure measurements from baro receptors. Cerebrum/hypothalamus influence heart rate as well Reflection 1. Why does the heart need its own blood supply? 2. What do the heart sounds signify? 3. Describe the cardiac conduction system. 4/30/201 7 Warm up 1. 2. 3. What would happen to your cardiac conduction system if you had a left bundle branch block? The natural pacemaker is the ___________________. What might be malfunctioning if you constantly have a heart rate of 100 beats per minute? 4/30/201 7 Blood vessels Blood vessels include:Arteries , arterioles, capillaries, venules, veins Create closed system – carries blood away from heart to cells in body then back to the heart. Arteries and veins Arteries –strong, elastic Divide into arterioles Wall of artery - smooth muscles and connective tissue Capable of vasoconstriction/vasodilation – increases/decreases blood flow/pressure Clogged vessels – artherosclerosis – diets high in fat Diets high in fruits/vegetables=add phyto sterols to blood – scour out plaque deposits capillaries Smallest vessels – layer of endothelium Allows substances to be exchanged with cells More permeability in capillaries of liver, intestines, glands More metabolic activity – higher number of capillaries Precapillary sphincters – regulate amount of blood entering capillary bed Capillary beds can close down if more is needed elsewhere. Exchanges in the capillaries Blood in capillaries – high oxygen/nutrients Diffuse through wall to tissue Plasma proteins stay in capillary Hydrostatic pressure – drives passage of fluids/small molecules. Osmosis causes tissue fluid to return to blood Lymphatic vessels collect extra fluid and return it to circulation Venules and veins Venules – lead from capillaries – merge to form veins – veins return blood to heart. 3 layers with valves to prevent backflow Thinner, less muscular than arteries No high pressure blood Function as blood reservoirs Blood vessels and circulation Paths of circulation Two divisions Pulmonary circuit – right ventricle through pulmonary artery to lungs, then pulmonary veins to left atrium. Systemic circuit – carries blood from left ventricle through aorta to body cells and back through veins into the left atrium Reflection Compare and contrast arteries, veins and capillaries 4/30/201 7 Arterial system Venous system Blood pressure Blood pressure is the resistance against the walls of a blood vessel Factors that affect blood pressure Heart action Blood volume Peripheral Blood resistance viscosity Control of blood pressure adjusting Cardiac output and Peripheral resistance If blood pressure increases, heart rate slows and blood vessels dilate If BP drops, heart rate increases and blood vessels constrict. Vasomotor center of medulla oblongata controls Fetal circulation Two umbilical arteries – carry blood to placenta Placenta – structure attached to uterine wall – substances exchanged between blood of mother and baby Umbilical vein – returns blood from placenta to baby. Ductus venosus – returns blood from placenta to inferior vena cava, bypassing liver Foramen ovale – opening in septum between right and left atria -allows most of blood to bypass fetal lungs Ductus arteriosus-small vessel connects pulmonary artery with aorta, allows more blood to bypass fetal lungs After birth: Ovale closes, Ductus arteriosus contracts