* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Earth
Astrobiology wikipedia , lookup
Rare Earth hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Late Heavy Bombardment wikipedia , lookup
Extraterrestrial skies wikipedia , lookup
Aquarius (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Geocentric model wikipedia , lookup
Dialogue Concerning the Two Chief World Systems wikipedia , lookup
Tropical year wikipedia , lookup
Extraterrestrial life wikipedia , lookup
History of Solar System formation and evolution hypotheses wikipedia , lookup
Planetary habitability wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical unit wikipedia , lookup
Solar System wikipedia , lookup
Comparative planetary science wikipedia , lookup
Hebrew astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Standard solar model wikipedia , lookup
Formation and evolution of the Solar System wikipedia , lookup
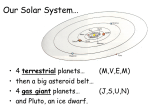
Earth is the only planetary body in the solar system that has conditions suitable for life ( at least as known to modern science). It is the third planet in distance outward from the Sun. The mean distance of the Earth from the Sun is about 149,573,000 km. The planet orbits the Sun at a speed of 29.8 km per second, making one complete revolution in 365.25 days. As it revolves around the Sun, the Earth spins on its axis and rotates completely once every 23 hours 56 minutes and 4 seconds. The Earth is the fifth largest planet of the solar system. The planet‘s total surface area is roughly 509,600,000 sq km, of which about 29 percent is land. It has a single natural satellite, the Moon. The Earth has a shape of an oblate spheroid, being flatter near the poles than near the Equator. The Earth´s gravity is not fixed, but rather varies from place to place on the surface (it is higher at the poles). The Earth´s atmosphere consists of a mixture of gases, chiefly nitrogen (78 %) and oxygen (21%). The rest are argon, water vapour, carbon dioxide and various other gases. The Earth is the only planet known to have liquid water. Together with ice, the liquid water constitutes the hydrosphere. Sea water makes up more than 98 % of the total mass of the hydrosphere and covers about 71 % of the Earth´s surface. The Earth´s surface is divided into seven continents: Europe, Asia, Africa, North America, South America, Australia and Antarctica. The World Ocean is broken down into three major oceans: the Atlantic, Pacific and Indian oceans. The Earth is surrounded by a magnetosphere, a region of strong magnetic forces that extends upward from about 140 km in the upper atmosphere. In the magnetosphere, the magnetic field of the Earth traps rapidly moving charged particles, the majority of which appear to be emitted by the Sun during periods of intense activity. If it were not for this shielding effect, such particles would bombard the terrestrial surface and destroy life. The Solar System is made up of all the planets that orbit our Sun. In addition to planets, the Solar System also consists of moons, comets, asteroids, minor planets, and dust and gas. Everything in the Solar System orbits or revolves around the Sun. The Sun contains around 98% of all the material in the Solar System. The larger an object is, the more gravity it has. Because the Sun is so large, its powerful gravity attracts all the other objects in the Solar System towards it. At the same time, these objects, which are moving very rapidly, try to fly away from the Sun, outward into the emptiness of outer space. The result of the planets trying to fly away, at the same time that the Sun is trying to pull them inward is that they become trapped half-way in between. Balanced between flying towards the Sun, and escaping into space, they spend eternity orbiting around their parent star. How Did The Solar System form? Scientists believe that the Solar System evolved from a giant cloud of dust and gas. They believe that this dust and gas began to collapse under the weight of its own gravity. As it did so, the matter contained within this could begin moving in a giant circle, much like the water in a drain moves around the center of the drain in a circle. At the center of this spinning cloud, a small star began to form. This star grew larger and larger as it collected more and more of the dust and gas that collapsed into it. Further away from the center of this mass where the star was forming, there were smaller clumps of dust and gas that were also collapsing. The star in the center eventually ignited forming our Sun, while the smaller clumps became the planets, minor planets, moons, comets, and asteroids. Photosynthesis is the process of converting light energy to chemical energy and storing it in the bonds of sugar. This process occurs in plants and some algae. Plants need only light energy, CO2, and H2O to make sugar. The process of photosynthesis takes place in the chloroplasts, specifically using chlorophyll, the green pigment involved in photosynthesis. Photosynthesis takes place primarily in plant leaves. Chlorophyll looks green because it absorbs red and blue light, making these colours unavailable to be seen by our eyes. It is the green light which is NOT absorbed that finally reaches our eyes, making chlorophyll appear green. However, it is the energy from the red and blue light that are absorbed that is, thereby, able to be used to do photosynthesis. The green light we can see is not/cannot be absorbed by the plant, and thus cannot be used to do photosynthesis. The overall chemical reaction involved in photosynthesis is: 6CO 2 + 6H2O (+ light energy) C6H12O6 + 6O2. This is the source of the O2 we breathe, and thus, a significant factor in the concerns about deforestation. The Water Cycle (also known as the hydrologic cycle) is the journey water takes as it circulates from the land to the sky and back again. The Sun's heat provides energy to evaporate water from the Earth's surface (oceans, lakes, etc.). Plants also lose water to the air (this is called transpiration). The water vapor eventually condenses, forming tiny droplets in clouds. When the clouds meet cool air over land, precipitation (rain, sleet, or snow) is triggered, and water returns to the land (or sea). Some of the precipitation soaks into the ground. Some of the underground water is trapped between rock or clay layers; this is called groundwater. But most of the water flows downhill as runoff (above ground or underground), eventually returning to the seas as slightly salty water. As water flows through rivers, it picks up small amounts of mineral salts from the rocks and soil of the river beds. This very-slightly salty water flows into the oceans and seas. The water in the oceans only leaves by evaporating (and the freezing of polar ice), but the salt remains dissolved in the ocean - it does not evaporate. So the remaining water gets saltier and saltier as time passes. Oceans cover about 70% of the Earth's surface. The oceans contain roughly 97% of the Earth's water supply Climate is defined as the weather conditions in a certain geographical area averaged over a long period of time, typically 30 years. The climate's determination is carried out using annual and monthly statistical measurements of local atmospheric data such as : temperature, precipitations, sun exposure, humidity, wind's speed . The earth can be divided into several major climatic zones and bands: Tropical / Subtropical / Arid / Equatorial / Semiarid / Mediterranean / Temperate / Oceanic / Continental / Subarctic / Polar / climates and Climate of Antarctica NATURAL DISASTERS Earthquake is a tectonic or volcanic disturbance within the Earth. The passage of seismic waves through the Earth often causes violent shaking of its surface. The origin of most major earthquakes can be explained in terms of the plate tectonics theory. The location of the earthquake is determined with a seismograph. The magnitude of an earthquake is usually expressed in terms of the Richter scale. The scale is so arranged that each increase in magnitude of one unit represents a tenfold increase in earthquake size, i.e. an earthquake of Richter magnitude 8 is 10,000 times as large as one of magnitude 4. Large earthquakes have caused some of the worst disasters in history. No other natural phenomenon is as destructive over so large an area in so a short time. People are crushed and buried under the collapsing structures or are burned to death in fires. Destructive, too, are the landslides and mudslides that occasionally accompany an earthquake. Much research has been devoted to earthquake prediction since the mid 1960s, but no method has yet been deviced to predict the time, place or magnitude of quakes. Seismologists have found that major earthquakes are often preceded by certain measurable physical changes in the environment around their epicentres.) Flood is a high-water stage in which water overflows its natural or artificial banks. Floods commonly results from excessive rainfall over short periods of time, and also from ice jams during the spring rise and from tsunamis (the mountainous sea waves caused by earthquakes) Famine is an extreme shortage of food, causing widespread and persistent hunger. The causes of famine are numerous, but they are usually divided into natural (drought, heavy rain and flooding, typhoons, plant disease and insect infestations; drought being the most common natural cause) and human categories (mainly warfare = destroying crops and food supplies and blockade tactics, overpopulation) Famine continues to be a problem in parts of Latin America, Central Africa and Southeast Asia. The effects of modern famines have been lessened by international relief organizations. Volcanic eruption, hurricane, forest fire, tsunami, avalanche, tornado Our Sun is not unique in the universe. It is a common middle-sized yellow star which scientists have named Sol, after the ancient Roman name. This is why our system of planets is called the Solar System. There are trillions of other stars in the universe just like it. Many of these stars have their own systems of planets, moons, asteroids, and comets. The Sun was born in a vast cloud of gas and dust around 5 billion years ago. Over a period of many millions of years, this gas and dust began to fall into a common center under the force of its own gravity. At the center, an ever growing body of mass was forming. As the matter fell inward, it generated a tremendous amount of heat and pressure. As it grew, the baby Sun became hotter and hotter. Eventually, when it reached a temperature of around 1 million degrees, its core ignited, causing it to begin nuclear fusion. When this happened, the Sun began producing its own light, heat, and energy. We don't often think of the Sun as having cooler areas on its surface. The Sun is far too hot for an astronaut to ever visit, but there are areas which are slightly cooler than others. These areas are known as sun spots. Sun spots are still very hot. However, because they are slightly cooler than the rest of the surface of the Sun, they appear slightly darker in color. The gravitational forces in Sun spots are also stronger than the other hotter areas. Of course, you cannot look directly at the Sun to see these spots because you would damage your eyes. Astronomers have to use special telescopes with filters and other instruments to be able to see the cooler spots on the surface of the Sun. During periods of high solar activity, the Sun commonly releases massive amounts of gas and plasma into its atmosphere. These ejections are known as solar flares. Some solar flares can be truly massive, and contain impressive power. On occasion, these more powerful flares can even cause satellites orbiting the Earth to malfunction. They can also interact with Earth's magnetic field to create impressive and beautiful light shows known as the Northern and Southern lights. As the Sun burns hydrogen at its core, it releases vast amounts of atomic particles, or pieces of atoms, into outer space. These atomic particles along with the Sun's radiation create a sort of wind, known as the solar wind. This wind blows particles outward in all directions from the Sun. Even as you read this, there are atomic particles which are traveling from the Sun towards you. Often, particles pass right through your body without you ever realizing it. The Sun is by far the largest object in the Solar System. 98% of all matter within the Solar System is found within the Sun. This means that all the planets, moons, asteroids, minor planets, comets, gas, and dust would all combine to make up only 2% of all the matter in the Solar System. The Sun is so large that the Earth could easily fit inside the Sun a million times. Because the Sun is so large compared to everything else, it is easily able to hold on to the rest of the matter, causing everything else to orbit around it. Light from the Sun can reach the Earth in only 8 minutes! This is called the speed of light. The Sun is nearly 93 million miles (approx 145 million km) from Earth.