* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Body Systems Notes:
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
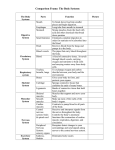
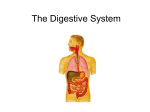
Body Systems Notes: Levels of organization: Cell Tissue Organ Organ Systems Organism Cell = the basic unit of structure and function of all living things. Tissue = a group of similar cells that perform the same function. 4 types of tissue: -muscle tissue = can contract or shorten, to make parts of your body move. -nerve tissue = carries messages back and forth between the brain and body to direct and control body movements. -connective tissue = provides support for the body and connects all its parts. -epithelial tissue = covers the surfaces of your body, inside and out, for protection and can also absorb or release chemicals. Organ = a structure that is composed of different types of tissue and performs a certain job in the body. Organ system = a group of organs that work together to perform major functions. 11 major organ systems. CIRCULATORY = carries needed materials (oxygen, glucose, nutrients) to the body cells; and carries wastes (carbon dioxide, nitrogen) away; helps fight disease (blood cells that kill microorganisms): consists of the heart, blood vessels and blood. (see below) -DIGESTIVE = takes food into one end of the body, breaks down food, and absorbs the digested materials, eliminates undigested wastes out the other end. (9 meters long). Mouth- teeth used for mechanical digestion (cutting, grinding etc), and saliva with enzymes to begin chemical digestion. Esophagus- a muscular tube that connects the mouth and stomach, pushes food down to stomach. Stomach – a j shaped muscular pouch located in the abdomen, mechanical digestion from muscles squeezing and churning, and chemical digestion through acids. Small intestine- where almost all chemical digestion and absorption of nutrients take place (6 meters long but only a few centimeters around). Liver- largest and heaviest organ inside the body, make bile to break up fats during digestion, helps breakdown and absorb medicines, and helps eliminate nitrogen from the body. Pancreas- a small organ that produces enzymes that help break down starches, proteins and fats, releases the enzymes into the small intestine. Large intestine- absorbs water, contains bacteria that feed on the undigested material and they produce Vit. K. Rectum- a short tube that compresses the waste material to a solid form. Anus – a muscular opening at the end of the rectum. -ENDOCRINE = controls many body processes (daily and long term) by means of chemicals such as saliva, sweat, hormones: made up of glands-sweat, saliva, ovaries, testes, hypothalamus, and pituitary (controls growth and development). -EXCRETORY = collects and removes wastes produced by the cells in the body: helps to maintain homeostasis: Kidneys- filter blood and remove urea(a nitrogen compound from the breakdown of proteins), excess water and other wastes to form of urine: Bladder- a saclike muscular organ that stores the urine. IMMUNE = white blood cells that destroy pathogens: Phagocyte-engulfs and destroys pathogens, lymphocytes(reside in the lymph system)-each type identifies a specific type of pathogen and has specific defenses targeted specifically for that pathogen. T-cells identify foreign proteins (antigens) on pathogens and initiate the attack on them, directing the other types of lymphocytes. B-cells produce antibodies against pathogens. MUSCLE = enables the body to move; moves food through the digestive system; keep the heart beating. Two categories of muscle tissue: -Voluntary muscles: muscles that are under your control: all skeletal muscles; work in pairs to move the bones; - Involuntary muscles: not under your conscious control, work automatically to control many types of movements inside the body such as those involved with breathing and digestion; cardiac muscle-in the heart, never gets tired; and smooth muscle- inside internal organs -NERVOUS = detects and interprets information from the environment outside the body and from within the body & directs the way your body responds to the information; controls most body functions esp. homeostasis: -consists of the central nervous system (brain & spinal cord), & peripheral nervous system (nerves) and sense organs all made up of nerve cells (neurons); (see pgs. 624 and 625) Brain= controls most function in the body and directs responses to all stimulus’, Spinal cord = a thick column of nerve tissue that links the brain to most of the nerves in the rest of the body. Nerves: a network of nerve cells from the body to the spinal cord; 2 types- somatic for voluntary actions, autonomic for involuntary reaction. -REPRODUCTIVE = produces sex cells that can unite with other sex cells to create offspring; controls development of male and female characteristics: male reproductive system specialized to produce sperm and the hormone testosterone (testes);female system specialized to produce eggs & estrogen (ovaries) and nourish the development of a baby until birth (uterus). -RESPIRATORY = takes oxygen into the body (for cellular respiration) and eliminates carbon dioxide: air travels first through the nose, pharynx (throat) and trachea (windpipe) -which filter, warm and moisten the air; then to the bronchial tubes and the lungs. Alveoli are tiny sacs of lung tissue where gases are exchanged between the air and blood. Cilia help to move mucus and trapped particles out of the respiratory system (so do coughing and sneezing). The epiglottis seals off the trachea when you swallow food so you don’t choke. Diaphragm muscle controls breathing: contraction of the diaphragm causes the muscle to drop and lungs to expand and fill with air, relaxation causes it to move up and air is forced out. -SKELETAL = helps shape and support the body, protects your internal organs, and works with the muscles to allow movement; makes blood cells and stores some materials: -it grows as the animal grows; supports the body against gravity, but allows easy movement. -made up of bone and cartilage; Cartilage is soft and flexible and cushions the joints; Bone is hard because it contains calcium and phosphorous: also has living cells (bone marrow) to make new bone and blood cells; see joint types pg 485. (206 bones in adult humans) -SKIN = protects the body from injury and infection, covers the body and prevents water loss; helps regulate body temperature: eliminate wastes (sweating); gather information (senses); and produce vitamin D. It is the largest organ. 2 layers: epidermis- outermost layer made up of dead cells, no nerves or blood vessels; dermis- contains live cells, nerves, blood vessels, sweat and oil glands, hair follicles. Special organs and tissues: Heart (see pg 539) = a hollow, muscular organ that pumps blood throughout the body; atria-two upper chambers-receive blood into the heart when heart muscles relax then they contract to force blood into the ventricles: ventricles-two lower chambers-pump blood out of the heart when heart muscles contract, separated by valves that prevent backflow of blood. Right side of the heart pumps blood to the lungs, left side to the body. Arteries then carry blood away from the heart and to a system of tiny capillaries, where substances are exchanged (by diffusion) with the cells, and then to the veins which carry the blood back to the heart. Blood (a special type of connective tissue): 4 components: (cells made in bone marrow) -plasma= the liquid part of the blood, 90% water and 10% dissolved nutrients and wastes. Proteins give it the yellow color. -red blood cells= disk shaped cells that take up oxygen in the lungs and deliver it to the cells elsewhere in the body. No nuclei-cannot reproduce and do not live long. -white blood cells= the body’s disease fighters, different kinds each with a different function. -platelets = cell fragment (no nuclei) that play an important part in blood clotting.