* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download lesson - Garnet Valley School District
Large numbers wikipedia , lookup
Big O notation wikipedia , lookup
Dirac delta function wikipedia , lookup
Non-standard calculus wikipedia , lookup
Continuous function wikipedia , lookup
History of the function concept wikipedia , lookup
Elementary mathematics wikipedia , lookup
History of logarithms wikipedia , lookup
Exponential family wikipedia , lookup
Function (mathematics) wikipedia , lookup
Name ___________________________________________ Date _____________________ Class ____________________
4.3: Introduction to Logarithmic Functions
Unit 4: Exponential & Logarithmic Functions
Big Idea #1: Exponential equations can also be written as logarithmic equations.
Big Idea #2: The logarithm is equal to the exponent in the exponential equation.
be = n
logb n = e
1. Complete the table.
Exponential
Equation
33 = 27
Logarithmic
Equation
log3 27 = 3
5-1 = 0.2
80 = 1
log4 16 = 2
2. Explain why the logarithm of 1 with base b is always 0.
_________________________________________________________________________________________________
Write each exponential equation in logarithmic form.
3. 37 = 2187
___________________________
4. 122 = 144
___________________________
5. 53 = 125
___________________________
Write each logarithmic equation in exponential form.
6. log10 100,000 = 5
___________________________
7. log4 1024 = 5
___________________________
8. log9 729 = 3
___________________________
Evaluate without a calculator.
9. log 1,000,000
___________________________
12. log4 16
___________________________
10. log 10
___________________________
13. log8 1
___________________________
11. log 1
___________________________
14. log5 625
___________________________
Solve for x in each without a calculator.
15. logx 16 = 2
___________________________
18. log x = –2
___________________________
16. logx 27 = 3
___________________________
19. log5 13 = log5 (19 – 2x)
___________________________
17. log7 x = 3
___________________________
20. log2 8x
___________________________
Name ___________________________________________ Date _____________________ Class ____________________
Big Idea #3: A logarithmic function is the inverse of an exponential function. You can identify
an inverse function by comparing its graph to the graph of the original function. The two
graphs are a reflection of each other across the line y = x.
Exponential function: f (x) = bx
The base b is any number greater than 1.
Example: g(x) = 3x
The domain is all real numbers.
The range is all positive numbers.
Logarithm function: f-1(x) = logb x
Use the same base to find the inverse function.
The inverse of g(x) is g-1 (x) = log3 x.
In the inverse function, the domain and range are
switched.
21. Find the inverse function of f (x) = 4x.
22. a. Find the inverse function of g(x) =
1x
5
_______________________
b. What are the domain and range of g(x) and g-1(x)?
Domain of g(x):
__________________
Range of g(x):
Domain of g -1(x):
__________________
Range of g-1(x): __________________
__________________
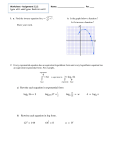
Without a calculator, use the given x-values to graph each function. Then graph its inverse.
Describe the domain and range of both functions. After, check the graphs using a calculator.
x
23. f (x) =
0.1x;
x = -1, 0, 1, 2
5
24. f ( x ) ; x = -3, -2, -1, 0, 1, 2, 3
2
Original: ____________________________________
Original: ____________________________________
Inverse: _____________________________________
Inverse: _____________________________________
Name ___________________________________________ Date _____________________ Class ____________________
4.3 INTRODUCTION TO LOGARITHMS
1.42 16; log5 0.2 1; log6 1 0
24. Domain: {x|x 0};range: all real
numbers
2. logb 1 0 is the same as b0 1 and any
number to the 0 power is 1.
3. log3 2187 7
4. log12 144 2
5. log5 125 3
6. 105 100,000
7. 45 1024
8. 93 729
9. 6
10. 1
11. 0
12. 2
13. 0
14. 4
15. x = 4
16. x = 3
17. x = 343
18. x = 0.01
19. x = 3
20. 3x
21. f 1(x) log4 x
22. a. g 1(x) log1/5 x
b. Domain of g(x) is all real numbers
Challenge
25. The hydrogen ion concentration in
moles per liter for a certainbrand of
tomato-vegetable juice is 0.000316.
a. Write a logarithmic equation for the pH
of the juice.
b. What is the pH of the juice?
range of g(x) is y 0
domain of g1(x) is x 0
range of g1(x) is all real numbers.
25. a. pH = -log(0.000316)
b. 3.5
23. Domain: {x|x 0}; range: all real
numbers
Original content Copyright © by Holt McDougal. Additions and changes to the original content are the responsibility of the instructor.
Holt McDougal Algebra 2