* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 8_Notes Guide_HONORS
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
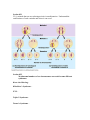
Chapter 8 Notes Guide (p. 126-152) Honors Biology- Castone Section 8.1 1) What does the phrase “Like begets like” mean? What does it refer to in this chapter? Section 8.2 2) What is a synonym for “cell division”? Section 8.3 3) Prokayotes (bacteria and archae) reproduce using a process called “binary fission”. Draw a picture of this and label important structures. Summarize what is happening in binary fission. (see Figure 8.3A) 4) What type of reproduction is this? Why? Section 8.4 5) Some important terms that you must understand and be able to differentiate amongst are: chromatin, sister chromatids, chromosome, and centromere. Illustrate all of them and state the differences. 6) How many chromosomes are in the human body? How does this compare to other organisms? Section 8.5 7) Cells asexually reproduce every day (this includes your cells!!). To do this, they go through a cycle called THE CELL CYCLE. Draw a diagram of this and label its parts. (see Figure 8.5) Section 8.6 8) What is the definition of mitosis? Draw the process below. MITOSIS Section 8.7 9) How is cytokinesis different for animal cells and plant cells? Section 8.8 10) This is an interesting section but will not be a major topic in the teaching of this chapter. Section 8.9 11) Go back to the Cell Cycle. Refresh your memory of it. Now, there are three “checkpoints” in the cell cycle. Explain the purpose of each. G1 checkpoint: G2 checkpoint: M checkpoint: Section 8.10 12) This is an interesting section but will not be a major topic in the teaching of this chapter. Know the definition of a cancer cell. Section 8.11 13) This section is a review of mitosis. It has interesting pictures. Section 8.12 14) Draw a homologous pair of chromosomes, illustrating what genes would look like on each. (Figure 8.12) 15) What is the difference between a somatic cell and a gamete? 16) What is the difference between an autosome and a sex chromosome? Section 8.13 17) Cells that contain homologous pairs (2 sets) of chromosomes are called ____________. This is symbolized by 2n, where n equals the number of different chromosomes in an organism. What cells are like this? 18) Cells that contain a single chromosome set are called ____________. What cells are like this? This is symbolized by n, where n is number of different chromosomes in an organism. What cells are like this? 19) What is fertilization and what is a zygote? 20) What is the definition of meiosis? Section 8.14 MEIOSIS I MEIOSIS II Section 8.15 21) This section compares and contrasts mitosis with meiosis. This comparison is in an Exercise in your Study Packet, so make sure you do that Exercise and understand it. Section 8.16 22) During meiosis, a special event called “crossing over” happens. It causes genetic recombination and is the reason you do not look like your siblings or your biological parents. Review and understand Figure 8.16 in the textbook. Section 8.17 We will not cover this here. Section 8.18 23) Draw two homologous chromosomes. Draw 2 genes on each chromosome. After crossing over occurs in meiosis, what are the possible combinations that could occur in the gametes that are created? Section 8.19 24) What is this picture of? Explain its purpose and label it accordingly. Section 8.20 This section is about Down Syndrome – an interesting section but not the major focus of the chapter. 25) Section 8.21 25) A mistake that can occur during meiosis is nondisjunction. Understand the ramifications of such a mistake and where it can occur. EXTRA INFORMATION PAGE Section 8.22 26)Abnormal numbers of sex chromosomes can result in some different syndromes. Know the following: Klinefelter’s Syndrome – XXY – Triple X Syndrome– Turner’s Syndrome – Section 8.23 26) Chromosomes can be accidentally altered (mutated). Understand the following alterations and their ramifications.