* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Modul 1. General aspects of diagnostic radiology
Proton therapy wikipedia , lookup
Positron emission tomography wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear medicine wikipedia , lookup
Radiation burn wikipedia , lookup
History of radiation therapy wikipedia , lookup
Radiosurgery wikipedia , lookup
Center for Radiological Research wikipedia , lookup
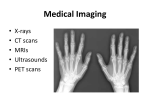
Medical imaging wikipedia , lookup
Image-guided radiation therapy wikipedia , lookup
Industrial radiography wikipedia , lookup
Modul 1. Physical and technological bases of radial diagnostic The text test questions 1. Which of the following techniques uses scintillation crystals? A. Thermography B. * Radionuclear C. X-ray diffraction D. NMR imaging E. Ultrasonography 2. Which of the following techniques uses X-ray tube? A. Thermography B. Dopplerography C. * X-ray D. NMR imaging E. Ultrasonography 3. Which of the following techniques uses fluorescent screen? A. Thermography B. Xeroradiography C. * Fluoroscopy D. NMR imaging E. Ultrasonography 4. Which of the following techniques uses films? A. Thermography B. Xeroradiography C. * X-ray graphy D. NMR imaging E. Ultrasonography 5. Which of the following techniques uses selenium plate A. Thermography B. * Xeroradiography C. X-ray diffraction D. NMR imaging E. Ultrasonography 6. Which of the following techniques uses magnet? A. Thermography B. Xeroradiography C. X-ray diffraction D. * NMR imaging E. Ultrasonography 7. Which of the following techniques uses radiofrequency generator A. Thermography B. Xeroradiography C. X-ray diffraction D. * MRI imaging E. Sonography 8. Which of the following techniques uses piezoelectric crystals? A. Thermography B. Xeroradiography C. X-ray diffraction D. NMR imaging E. * Ultrasonography 9. All of them use non-ionizing radiation, except: A. Dopplerography B. * Radiography 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. C. MRI D. Thermography E. Ultrasonography The most accurate investigation for assessing ventricular function is: A. Thermography B. * MRI C. Nuclear scan D. Echocardiography E. Multislice CT Which of the following is not penetration beam? A. * Infrared beam B. Proton beam C. 18 MEV photons D. 8 MEV photons E. Electron beam Which of the following is the most penetration beam? A. Infrared beam B. Proton beam C. * 18 MEV photons D. 8 MEV photons E. Electron beam All the following are features of radiation except: A. Actinic or chemical B. * Non ionizing C. Photographic D. Biological E. Fluorescein Calculus on USG is due to: A. Annihilation B. Destroy of waves C. Artefact D. Refraction E. * Reflection Acoustic shadow on USG is due to: A. Annihilation B. Absorption of waves C. Artifacts D. Refraction E. * Reflection Radiation exposure occurs in all of the following except: A. * MRI and Ultrasound B. Plain X-ray C. Fluoroscopy D. MRI and scintigraphy E. CT scan In MRI, strength of magnetic field is: A. 25 Tesla B. 11 Tesla C. 5 Tesla D. * 1.0 Tesla E. 0.2 Tesla Maximum penetration is seen with: A. Ultrasound waves 19. 20. 21. 22. 23. 24. 25. 26. B. Electron beam C. * γ-waves D. α-particles E. β-particles MRI detects all the following except. A. Cyst B. Hydatidi formmole C. Placenta praevia D. * Down syndrome E. Anencephaly CT detects all the following except. A. Cyst B. Hydatidi formmole C. Placenta praevia D. * Down syndrome E. Anencephaly Ultrasound detects all the following except. A. Cyst B. Hydatidi formmole C. Placenta praevia D. * Down syndrome E. Anencephaly A patient presents with ARF (arterial renal flow) with a normal ultrasound report. The next most useful investigation is : A. Dopplerography B. * DTPA scan C. Intravenous pyelography D. Retrograde pyelography E. Renal angiography Infrared waves occurs in: A. * Liquid-crystal contact thermography B. Ultrasound C. MRI D. Plain X-ray E. CT scan Infrared waves occurs in: A. Ultrasound B. MRI C. * Radiothermometry D. Plain X-ray E. CT scan Infrared waves occurs in: A. Ultrasound B. MRI C. * Thermography D. Plain X-ray E. CT scan Mechanical waves occurs in: A. * Dopplerography B. MRI C. Fluoroscopy D. Plain X-ray E. CT scan 27. 28. 29. 30. 31. 32. 33. 34. 35. Mechanical waves occurs in: A. * Duplex sonography B. MRI C. Fluoroscopy D. Plain X-ray E. CT scan Mechanical waves occurs in: A. * Ultrasound B. MRI C. Fluoroscopy D. Plain X-ray E. CT scan Magnetic exposure occurs in: A. Fluorography B. * MR spectroscopy C. Fluoroscopy D. Plain X-ray E. CT scan Magnetic exposure occurs in: A. Fluorography B. * MRI C. Fluoroscopy D. Plain X-ray E. CT scan Radiation exposure occurs in all except: A. Fluorography B. * Radiothermometry C. Fluoroscopy D. Plain X-ray E. CT scan Radiation exposure occurs in all except: A. Fluorography B. * Thermography C. Fluoroscopy D. Plain X-ray E. CT scan Radiation exposure occurs in all except: A. Fluorography B. * MR-spectroscopy C. Fluoroscopy D. Plain X-ray E. CT scan Deleterious effect of ultrasound on small organism is: A. Obliteration B. Disintegration C. * Cavitation D. Vacoulation E. Ionization Cell most sensitive to radiation: A. All of the above B. Platelets C. Basophil D. Neurotrophil 36. 37. 38. 39. 40. 41. 42. 43. 44. E. * Lymphocyte One Gray (Gy) of radiation is equal to: A. 100 Bk B. 1000 rad C. * 100 rad D. 10 rad E. 1 rad Radiation exposure occurs in all except: A. Fluorography B. * Ultrasound C. Fluoroscopy D. Plain X-ray E. CT scan Radiation exposure occurs in all except: A. Fluorography B. * MRI C. Fluoroscopy D. Plain X-ray E. CT scan Which is mutagenic? A. Magnetic field B. Radiofrequency waves C. Infrared waves D. Ultrasound waves E. * Gamma rays Which is mutagenic? A. Magnetic field B. Radiofrequency waves C. * X-rays D. Infrared waves E. Ultrasound waves Which is mutagenic? A. Magnetic field B. Radiofrequency waves C. * UV rays D. Infrared waves E. Ultrasound waves Which is mutagenic? A. * Beta rays B. Magnetic field C. Radiofrequency waves D. Infrared waves E. Ultrasound waves Which is mutagenic? A. * Alfa rays B. Magnetic field C. Radiofrequency waves D. Infrared waves E. Ultrasound waves Which is mutagenic? A. Alfa rays B. Beta rays C. * All of the above 45. 46. 47. 48. 49. 50. 51. 52. 53. D. UV rays E. X-rays Which is not mutagenic? A. Alfa rays B. Beta rays C. * Radiofrequency waves D. UV rays E. X-rays Which is not mutagenic? A. Alfa rays B. Beta rays C. * Magnetic field D. UV rays E. X-rays Which is not mutagenic? A. Alfa rays B. Beta rays C. * Infrared waves D. UV rays E. X-rays Which is not mutagenic? A. Alfa rays B. Beta rays C. * Ultrasound waves D. UV rays E. X-rays The tissue most resistant to ultrasound waves is: A. * Bone B. Vagina C. Cervix D. Colon E. Rectum The tissue most resistant to ultrasound waves is: A. * Goldblader stones B. Vagina C. Cervix D. Colon E. Rectum Most sensitive test for metastatic deposit is: A. Ultrasound B. Tomography C. Skeletal survey D. CT scan E. * Isotope scan Presence of cyst in an parenchymal organs is best made out by: A. Thermography B. Contrast study C. * Ultrasound D. MRI E. CT Presence of calcification in an intracranial lesion is best made out by: A. Thermography B. Contrast study 54. 55. 56. 57. 58. 59. 60. 61. 62. C. Ultrasound D. MRI E. * CT In radiothermography scanners, the principle is: A. None of the above B. * Infrared waves detection C. Microwaves D. Magnetic waves and radio waves generation E. Piezoelectric crystal excitation In thermography scanners, the principle is: A. None of the above B. * Infrared waves detection C. Microwaves D. Magnetic waves and radio waves generation E. Piezoelectric crystal excitation In MRI machines, the principle is: A. None of the above B. Infrared waves generation C. Microwaves D. * Magnetic waves and radio waves generation E. Piezoelectric crystal excitation In ultrasound machines, the principle is: A. None of the above B. Infrared waves C. Microwaves D. Very low frequency radio waves E. * Piezoelectric crystal excitation Radiation protection shields are made up of: A. Wood B. Tin C. * Lead D. Silver E. Copper Thermo emission of the body was discovered by: A. Henri Bequerel B. * M. Pitke C. Rutherford D. Pierre Curie E. Marie curie Radioactivity was discovered by: A. * Henri Becquerel B. Enrico Formi C. Rutherford D. Pierre Curie E. Marie curie Thermography was invented by: A. * Ray Lousson B. Takashita Koba C. John Snow D. Eric Storz E. Gedfrey Hounsfield NMR was invented by: A. F. Bloch, E. Pursell 63. 64. 65. 66. 67. 68. 69. 70. 71. B. Takashita Koba C. John Snow D. Eric Storz E. * Gedfrey Hounsfield USG was invented by: A. * R. Dussik B. Takashita Koba C. Paul Namen D. Eric Storz E. Gedfrey Hounsfield CT scan was invented by: A. Nina Zagurska B. Takashita Koba C. John Snow D. Eric Storz E. * Gedfrey Hounsfield Radioactivity was discovered by Becquerel in: A. 1956 B. 1946 C. 1901 D. * 1895 E. 1796 In USG the image not depends upon: A. Frequency of returning echo B. Type of doppler machine used C. Frequency of doppler used D. * Temperature E. Strength of returning echo In color doppler the color depends upon: A. Frequency of returning echo B. Type of doppler machine used C. Frequency of doppler used D. * Relation of transducer to blood flow E. Strength of returning echo CT is not useful in: A. Pyeloectasis B. Full bladder C. Ascites D. Breast cyst E. * Endocrine disorders MRI is not useful in: A. Pyeloectasis B. Full bladder C. Ascites D. Breast cyst E. * Metallic driftage Ultrasonogram is not useful in: A. Pyeloectasis B. Full bladder C. Ascites D. Breast cyst E. * CBD (common bile duct) stones at the distal end of the CBD Investigation of choice for a pregnant lady with upper abdominal mass: 72. 73. 74. 75. 76. 77. 78. 79. A. X-ray scopy B. DSA (Digital Subtraction Angiography) C. CT scan D. * MRI E. Barium meal The following is not an ionizing radiation: A. * USG and MRI B. Radionuclide scanning C. USG and xerorentgenography D. CT and thermography E. MRI and CT Radiation is used in: A. MRI spectroscopy B. * Scintigraphy C. Dopplerography D. NMR E. USG Infrared waves is used in: A. Radiography B. * Radiothermography C. Digital subtraction imaging D. NMR E. CAT (Computed Axial Tomography) scan Magnetic field is used in: A. Radiography B. Thyroid scan C. Digital subtraction imaging D. * NMR E. CT scan Radiation is not used in: A. Radiography B. Thyroid scan C. Digital substraction imaging D. * NMR E. CAT scan Frequency of sound waves used for thyroid ultrasonography is: A. 18MHz B. * 7.5-10 MHz C. 5.0-7.5 MHz D. 3.5-5.0 MHz E. 2.5-3.5 MHz Frequency of sound waves used for superficial ultrasonography is: A. 18 MHz B. * 7.5-10 MHz C. 5.0-7.5 MHz D. 3.5-5.0 MHz E. 2.5-3.5 MHz Frequency of sound waves used for trans vaginal ultrasonography is: A. 12 MHz B. 7.5-10 MHz C. * 5.0-7.5 MHz D. 3.5-5.0 MHz E. 2.5-3.5 MHz 80. 81. 82. 83. 84. 85. 86. 87. 88. Frequency of sound waves used for trans abdominal ultrasonography is: A. 12 MHz B. 7.5-10 MHz C. 5.0-7.5 MHz D. * 3.5-5.0 MHz E. 2.5-3.5 MHz Infrared asymmetry is best detected by: A. * Thermography B. MRI scan C. CT scan D. USG E. Plain X-ray Fluid formation is detected by: A. * All of the above B. MRI scan C. CT scan D. USG E. Plain X-ray Calcification is best detected by: A. Thermography B. MRI scan C. * CT scan D. USG E. Plain X-ray An obese patient has heavy, thick bones. A good X-ray is taken with: A. None of the above B. Increased developing time C. Increased exposure time D. * Increase in KV E. Increase in mA At t = 0 there are 6x1023 radioactive atoms of a substance, which decay with a disintegration constant (X) equal to 0.01/sec. What would be the initial decay rate? A. 7x1023 B. 6x1020 C. * 6x1021 D. 6x1022 E. 6x1023 Gamma camera in Nuclear Medicine is used for: A. IRMA B. RIA C. Monitoring the surface contamination D. * Measuring the radioactivity in human body E. Organ imaging Which one of the following has the maximum ionization potential? A. Mechanical waves B. Gamma (γ)-Photon C. * Helium ion D. Proton E. Electron Phosphorous-32 emits: A. Protons B. X- rays C. Neutrons 89. 90. 91. 92. 93. 94. 95. 96. 97. D. Alfa particles E. * Beta particles Which one of the following imaging techniques gives maximum radiation exposure to the patient? A. Abdomen scan B. * Bone scan C. CT scan D. MRI E. Chest X-ray All of the following radioisotopes are used as systemic radionucleide, except: A. All of the above B. * Samarium-153 C. Iridium-192 D. Strontium-89 E. Phosphorus-32 All of them use non- ionizing radiation, except: A. Dopplerography B. * Radiography C. MRI D. Thermography E. Ultrasonography Which of the following is the most penetration beam? A. Alpha beam B. Proton beam C. * 18 MEV photons D. 8 MEV photons E. Electron beam All the following are features of radiation except: A. Chemical B. * Non penetrating C. Photographic D. Biological E. Fluorescein Radiation exposure occurs in all of the following except: A. Xerography B. Plain X-ray C. Fluoroscopy D. * MRI E. CT scan Maximum penetration is seen with: A. n particles B. Electron beam C. * γ-rays D. p particles E. β-particles Most radiosensitive of the following is: A. Cancer of the cervix and Cancer of the pancreas B. Cancer of the pancreas C. * Cancer of the ovary D. Cancer of the kidney E. Cancer of the cervix The intracavitary radiation is given in: A. * All of the above 98. 99. 100. 101. 102. 103. 104. 105. B. Carcinoma of the oral cavity C. Carcinoma of the esophagus D. Carcinoma of the rectum E. Carcinoma of the cervix A patient presents with ARF (arterial renal flow) with a normal ultrasound report. The next most useful investigation is : A. None B. * DTPA (Diethylenetriaminepentaacetic Acid) scan C. Intravenous pyelography D. Retrograde pyelography E. Renal angiography Radiation exposure occurs in all except: A. Xerography B. * MRI C. Fluoroscopy D. Plain X-ray E. CT scan Half life of Technetium 99m is: A. one week B. 24 hours C. 12 hours D. * 6 hours E. 2 hours Which is not mutagenic? A. Y -rays B. Beta rays C. * Ultrasound D. UV (ultraviolet) rays E. X-rays Least sensitive structure to radiation is: A. Rectum B. * Vagina C. GIT (gastrointestinal tract) D. Cervix E. Uterus The tissue most resistant to radioactivity is: A. Ovary B. * Vagina C. Cervix D. Colon E. Rectum Acute radiation sickness is characterized by: A. Phallodynia B. * Gastrointestinal, CNS (central nervous system) and hematological symptoms C. Muscae volitantes symptoms D. Neris sign E. Gordons sign Isotope which is replacing radium is: A. Natrium B. Californium C. Gold D. * Iridium E. Cesium 106. 107. 108. 109. 110. 111. 112. 113. 114. Most radio-dense substance is: A. Bowel cells B. * Bone C. Brain D. Soft tissue E. Fluid Most sensitive test for metastatic deposit is: A. MRI scan B. Tomography C. Skeletal survey D. CT scan E. * Isotope scan Target material used for generating X-rays: A. Zinc B. Palladium C. Cadmium D. Cobalt E. * Tungsten Which of the following are most radioactive: A. H3 B. Yt 90 C. I 130 D. * Co 60 E. Co 59 Hot nodule is seen in: A. Mixed tiroiditis B. All of the above C. Adenocystic carcinoma D. Mixed parotid E. * Adenolymphoma X-ray machine is kept at a distance of 6 feet from the photographic plate to: A. Primary segregation the image B. None C. Enhance contrast D. * Primary (decrease) magnifications E. Increase the image Radioactive cobalt emits: A. Protons B. Neutrons C. Alpha rays D. Beta rays E. * Gamma rays Isotope used for liver scan is: A. Cobalt60 and Technetium99m B. Cobalt60 C. I 132 D. I131 E. * Technetium99m Isotope selectively concentrated in abscess cavities: A. Niobium B. Chromium C. Selenium D. Technetium 115. 116. 117. 118. 119. 120. 121. 122. 123. E. * Gallium Presence of calcification in an intracranial lesion is best made out by: A. Thermography B. Contrast study C. Ultrasound D. MRI E. * CT Unit of one dose of radiation absorbed is: A. Hounsfield B. Becquerel C. Curie D. Roentgen E. * Grey In a modern rotatory anode X-ray tube cooling of anode is done by: A. All of the above B. Inversion C. * Radiation D. Convection E. Conduction The photoelectric interaction occurs primarily in: A. Internal cell B. All shells equally C. Outer cell D. * 'K'cell E. 'L'cell X-ray films are least sensitive to which colored light: A. All of the above B. * Red C. Yellow D. Blue E. Violet The photosensitive material used in X-rays films consist of: A. Titanic bromide B. Cadmium tungstate C. Zinc sulphide D. * Silver bromide E. Cellulose Latest source of neutrons for radiotherapy is: A. Iodine-125 B. Radium-226 C. * Californium-256 D. Iodine-131 E. Strontium-90 "Target material" which produces X-rays in a diagnostic X-rays tube is made of: A. Zinc B. Copper C. Cobalt D. * Tungsten E. Lead Use of a cone results in films of: A. Middle motion B. Long scale contrast C. Less motion 124. 125. 126. 127. 128. 129. 130. 131. 132. D. Low contrast E. * Higher contrast Use of filters result in: A. All of the above B. * Beam of greater intensity C. Less penetrating beam D. Wider beam coverage E. Softer beam radiation Centenary year for X-ray is: A. 2007 B. 2001 C. 1997 D. 1999 E. * 1995 The longest half life is that of: A. Hydrogen B. Cesium C. * Uranium D. Radium E. Radon Cobalt 60 is radioactive source: A. * Artificial and Gamma ray B. Beta ray C. Gamma ray D. Natural E. Artificial The least radiosensitive tissue is: A. Stomach B. Thyroid C. Kidney D. Bone E. * Nervous tissue Mammography is useful in: A. * All of the above B. Detection C. Large fatty breast D. Lobular carcinoma of opposite breast E. Detection of early Cancer of these Xeroradiography is used in Cancer of the detection: A. Liver B. Pancreatic C. Colonic D. * Breast E. Stomach Isotope used in bone scans: A. Natrium B. Chromium C. Selenium D. Gallium E. * Technetium First sign after radiation is: A. Burns and deep ulser B. Deep ulcer 133. 134. 135. 136. 137. 138. 139. 140. 141. C. Burns D. Necrosis E. * Erythema Radiation protection shields are made up of: A. Water B. Tin C. * Lead D. Silver E. Copper Radioactivity was discovered by: A. * Henri Bequerel B. Enrico Formi C. Rutherford D. Pierre Curie E. Marie Curie In diagnosis of acute myocardial infarction hot spot is seen with: A. Co60 scan B. Cs127 scan C. Strontium 90 scan D. * Tc 99 scan E. Thallium 201 scan The first CT scan was manufactured by: A. Thochiba, Japan B. General Electric, USA C. * Electromusical instruments, England D. Mitsubishi, Japan E. Hitachi, Japan The half life of I131 is: A. 12 days B. * 8 days C. 5.2 days D. 2 days E. 8 hours CT scan was invented by: A. Jorg Maikl B. Takashita Koba C. John Snow D. Eric Storz E. * Gedfrey Hounsfield Deleterious effect of ultrasound on small organism is: A. All of the above B. Disintegration C. * Cavitation D. Vacoulation E. Ionization Cell most sensitive to radiation: A. All of the above B. Platelets C. Basophil D. Neurotrophil E. * Lymphocyte One gray of radiation is equal to: A. 0,1 rad 142. 143. 144. 145. 146. 147. 148. 149. 150. B. 1000 rad C. * 100 rad D. 10 rad E. 1 rad Radioactivity was discovered by Becquerel in: A. 1959 B. 1946 C. 1901 D. * 1896 E. 1796 Half life of Rn222 is: A. 1 month B. 5 days C. 4 days D. * 3-6 days E. 3 days Least affected by radiation: A. Epithelium B. Lymphocytes C. * Cartilage D. Gonads E. Marrow Radiation mediates its effect by: A. Hemorrhage B. Osmolysis of cells C. Protein coagulation D. Ionization of the molecules E. * Denaturation of DNA Contrast in X-rays is dependent on: A. All of the above B. Distance between source and object C. Duration of exposure D. mAmper E. * KVolt The atom which scatters X-rays more is: A. Air B. * Hydrogen C. Lead D. Mercury E. Carbon Speed of X-ray is equal to: A. Current strength B. All of the above C. Tube voltage D. Speed of electrons in X-ray tube E. * Speed of light Calcification is best detected by: A. Thermography B. MRI scan C. * CT scan D. USG E. Plain X-ray Best imaging modality in patients with breast implants is: 151. 152. 153. 154. 155. 156. 157. 158. A. Thermography and Radiocompetentiv analisis B. Radionuclide scan C. Mammography D. CT scan E. * MRI scan 60 Co- units: A. All of the above B. α, β and γ-radiation C. α and β-radiation D. β-radiation E. * γ-radiation Which of the following is not an artificial radioisotope element? A. * Co59 B. Tc99m C. Ra226 D. I125 E. Co 60 X-rays are produced by: A. Mesons B. Protons C. Positrons D. Neutrons E. * Electrons X-rays are formed when electrons hit: A. Cathode B. None of the above C. Radium source D. * Anode E. Water Bronchography may be dangerous if a patient with: A. Lung tumor B. All of the above C. * Iodine sensitivity D. Bronchiectasias E. Emphysema Source of gamma rays is: A. Phosphorus B. Xenon C. Cesium D. * Cobalt E. Radium The due used for CG (Cardiography) is: A. Radium B. Meglumine iodothalamate C. Biligraffin D. Sodium diatrozite E. * Iopanoic acid All of the following dyes are water soluble except: A. Urografin B. * Myodil C. Conray 420 D. Iodohexol E. Metrizamide 159. 160. 161. 162. 163. 164. 165. 166. 167. Atomic weight is equal to total number of: A. Electrons and protons B. Protons, neutrons and electrons C. Protons and electrons D. * Protons and neutrons E. Protons Isotopes have same atomic: A. Shadow B. Density C. Both weight and number D. Weight E. * Number Radium gives: A. β-rays, X-rays and γ-rays B. β-rays, X-rays C. X-rays D. β-rays and γ-rays E. * γ-rays Nucleus of an atom contains: A. Protons, electrons and p-mesons’ B. * Protons and neutrons C. Electrons and protons D. Only protons E. Electrons X-rays are: A. Mechanical wives B. * Electromagnetic waves C. Neutrons D. Protons E. Electrons Best diagnosis of tracheo-oesophageal fistula is by: A. Natrii sulfur B. Urografin C. * Dianosil D. Conray240 E. Barium sulphate In phlebography dye is injected into: A. Humeral artery B. Short saphenous vein C. Non of above D. Anterior tibial vein E. * Dorsal metatarsal vein Safest light used in darkroom in a X-ray department is: A. All of the above B. Dull white C. Yellow D. Blue E. * Red Curie is unit for: A. Excretion dose B. Quantity of radionuclide disintegrating per second C. Degree of potential danger to health D. Absorbed dose E. * Exposure 168. In phlebography dye is injected into: A. Humeral artery B. Short saphenous vein C. * Dorsal metatarsal vein D. Great saphenous vein E. Anterior tibia vein 169. X-ray was discovered by Roentgen in: A. 1905 B. 1907 C. * 1895 D. 1902 E. 1886 170. Safest light used in darkroom in a X-ray department is: A. All of the above B. * Red C. Green D. Blue E. Dull white 171. Curie is unit for: A. Excretion dose B. Quantity of radionuclide disintegrating per second C. Degree of potential danger to health D. Absorbed dose E. * Non of above Test questions to pictures 1. What radiological research is represented on Fig. 24? A. Photoroentgenography B. Roentgenography C. Roentgenoscopy D. Aiming roentgenography E. * Digital roentgenography 2. What radiological research is represented on Fig. 25? A. Photoroentgenography B. Roentgenography C. Roentgenoscopy D. * Ultrasonic research E. Aiming roentgenography 3. What radiological research is represented on Fig. 29? A. Photoroentgenography B. Roentgenography C. Roentgenoscopy D. Usual tomography E. * Magnetic-resonant tomography (MRI) 4. On Fig. 1 is represented A. Radionuclide detector B. * X-ray tube C. The dosimetric detector D. Piezokrystall E. X-ray film 5. On Fig 1 cathode is designated by numeral A. 1 B. *2 3 4 5 On Fig 1 anode is designated by numeral A. 1 B. 2 C. *3 D. 4 E. 5 On Fig 1 glass cylinder is designated by numeral A. *1 B. 2 C. 3 D. 4 E. 5 On Fig 2 is represented A. * The roentgenogram of organs a chest cavity B. The roentgenogram of a surface a chest cavity C. The roentgenogram of the mediastinum D. The roentgenogram of a vertebra E. The heart roentgenogram On Fig 3 is represented A. * A stomach full filled by suspension of barium sulphate B. The roentgenogram of a chest cavity C. The roentgenogram of the mediastinum D. The roentgenogram of chest part of the vertebra E. A stomach On Fig 4 is represented A. * A stomach filled by barium sulphate B. The roentgenogram of a chest cavity C. A stomach hardly filled by barium sulphate D. The roentgenogram of chest part of the vertebra E. A stomach On Fig 5 is represented A. * A stomach filled by barium sulphate B. Thin intestines filled by air C. The stomach is hardly filled by barium sulphate D. The thick intestines are filled by barium sulphate E. A stomach with air On Fig 6 is represented A. * Lymphography B. Angiography C. The stomach is filled by barium sulphate D. The thick intestines are filled by barium sulphate E. Fistulography On Fig 7 is represented A. * Urography B. Angiography C. Lymphography D. Thick intestines filled by barium sulphate E. Fistulography What contrast substance using for urography on Fig 7? A. * Urographyn C. D. E. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. Iodolipolum Echogen Barium sulphate Barium tamoxiphenum What contrast substance using for lymphography on Fig 6? A. Urographyn B. * Iodolipolum C. Echogen D. A barium sulphate E. A barium tamoxiphenum Name the most frequent complications characteristic for lymphography on Fig 6 A. Lungs oil embolization B. Chemical pneumonitis C. Inflammatory reactions D. * Inflammatory reactions, chemical pneumonitis, lungs oil embolization E. Inflammatory reactions, lungs oil embolization On Fig 8 source of radiation is represented A. 2 B. 3 C. 1 and 3 D. *1 E. 2 and 3 On Fig. 8 object of research is represented A. *2 B. 3 C. 1 and 3 D. 1 E. 2 and 3 On Fig. 8 perceiving device is represented A. 2 B. *3 C. 1 and 3 D. 1 E. 2 and 3 On Fig. 9 is represented A. Thick intestines B. * The thick intestines contrasted by barium sulphate C. A rectum D. Gallbladder E. A stomach What contrast substance using for the represent radiological research on Fig 9? A. Urographyn B. Iodolipolum C. Echogen D. * A barium sulphate E. Magnevist What diagnostic research is represented on Fig. 26? A. Photoroentgenography B. Roentgenography C. Roentgenoscopy D. Aiming roentgenography E. * A transthoracic puncture under control CТ The image on Fig. 10 is formed by using a method B. C. D. E. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. 22. 23. A. B. C. D. E. 24. 25. 26. 27. 28. 29. 30. 31. * Electroroentgenography X-ray graphy X-ray scopy A magnetic resonance imaging Ultrasound The image on Fig 11 is formed by using a method A. * Electroroentgenography B. X-ray graphy C. X-ray scopy D. A magnetic resonance imaging E. Ultrasound research The image on Fig. 12 is formed by using a method A. Electroroentgenography B. * X-ray graphy C. X-ray scopy D. A magnetic resonance imaging E. Ultrasound research What radiological research is see on Fig. 13? A. Electroroentgenography B. X-ray graphy C. * X-ray scopy D. A magnetic resonance imaging E. Ultrasound research What radiological research is represented on Fig. 14? A. Electroroentgenography B. X-ray graphy C. X-ray scopy D. * Aiming X-ray graphy E. Ultrasound research What radiological research is represented on Fig. 15? A. Electroroentgenography B. X-ray graphy C. X-ray scopy D. Aiming X-ray graphy E. * Coronarography What radiological research is represented on Fig. 16? A. Photoroentgenography B. X-ray graphy C. X-ray scopy D. Aiming roentgenography E. * Coronarography What contrast substance used for the given radiological research on Fig.16? A. Urographyn B. Iodolipolum C. Echogen D. * Angiographyn E. Barium sulphate What radiological research is represented on Fig. 17? A. Photoroentgenography B. Roentgenography C. Roentgenoscopy D. Aiming roentgenography E. * Ductography 32. 33. 34. 35. 36. 37. 38. 39. 40. What contrast substance used for the given radiological research on Fig. 17? A. Urographyn B. Iodolipolum C. Echogen D. * Tomogeksol E. Barium sulphate What radiological research is represented on Fig 18? A. A Photoroentgenography B. B. Roentgenography C. C. Roentgenoscopy D. D. Aiming roentgenography E. * Mammography What radiological research is represented on Fig. 19? A. Photoroentgenography B. Roentgenography C. * Angiography D. Aiming roentgenography E. Mammography What contrast substance used for the given radiological research on Fig. 19? A. Urographyn B. Iodolipolum C. Echogen D. * Tomogeksol E. Barium sulphate What radiological research is represented on Fig. 20? A. Photoroentgenography B. Roentgenography C. Roentgenoscopy D. Aiming roentgenography E. * A computer tomography On Fig. 21 is represented the 99Тс generator scheme. What numeral is designated eluent (a sterile solution 99Тс)? A. 1 B. 2 C. 3 D. 4 E. *5 On Fig. 21 is shown the 99Тс generator scheme. What numeral is designated eluent (a vacuum bottle)? A. *1 B. 2 C. 3 D. 4 E. 5 On Fig. 21 is represented the scheme A. * The generator 99Тс пертехнетата B. The device for roentgenoscopy C. A generator column 99Тс D. Gamma camera E. Radiograph What radiological research is shown on Fig. 22? A. Photoroentgenography B. Roentgenography Roentgenoscopy Aiming roentgenography * Ultrasonic research What radiological research is represented on Fig. 23? A. Photoroentgenography B. Roentgenography C. Roentgenoscopy D. Aiming roentgenography E. * Thermography What radiological research is represented on Fig. 27? A. Photoroentgenography B. Roentgenography C. * Angiography D. Ductography E. Bronchography What radiological research is represented on Fig. 28? A. Photoroentgenography B. Roentgenography C. Roentgenoscopy D. Usual tomography E. * Computer tomography (CT) What radiological research is represented on Fig. 30? A. Photoroentgenography B. Roentgenography C. Roentgenoscopy D. Usual tomography E. * Mammography What organ is designated by numeral 1 on Fig. 31? A. * A trachea B. The first left rib C. The right clavicle D. The left main bronchus E. The right main bronchus What organ is designated by numeral 4 on Fig. 31? A. A trachea B. The first left rib C. The right clavicle D. * The left main bronchus E. The right main bronchial tube What organ is designated by numeral 5 on Fig. 31? A. A trachea B. The first left rib C. The right clavicle D. The left main bronchial tube E. * The right main bronchial tube What organ is designated by numeral 1 on Fig.31? A. * A trachea B. The first left rib C. The right clavicle D. The left main bronchial tube E. The right main bronchial tube What organ is designated by numeral 4 on Fig. 31? A. A trachea C. D. E. 41. 42. 43. 44. 45. 46. 47. 48. 49. The first left rib The right clavicle * The left main bronchial tube The right main bronchial tube What organ is designated by numeral 5 on Fig. 31? A. A trachea B. The first left rib C. The right clavicle D. The left main bronchial tube E. * The right main bronchial tube B. C. D. E. 50.