* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Integrated Science
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
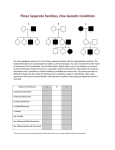
Integrated Science II Chapter 7 Elaborate Name _______________________________ Period _________ Date _________________ /20 Inheritance Patterns A pedigree is a family tree showing the phenotypes of individuals for an inherited disease or trait. Pedigrees are often used by geneticists to determine the inheritance patterns for a genetic disorder. Objective: to use pedigrees to identify patterns of inheritance and to make predictions. Part I: Interpreting a Pedigree 1. Read the background information about pedigrees and the symbols used, p. 379-381. 2 - 4. Study the pedigrees on p. 382. For each pedigree, look for patterns that indicate whether the type of inheritance is autosomal dominant, autosomal recessive, or sex-linked. Describe patterns you observed. Pedigree Type of Inheritance Describe patterns you observed A B C 5. Study the Pedigree Handout and describe the characteristics of each specific type of inheritance pattern. Type of Inheritance Characteristics of the Inheritance Pattern Autosomal Dominant Autosomal Recessive X-linked Recessive 6. Working with a partner, use the handout and what you already know about inheritance to complete the table below by placing a check mark in the column for the type of inheritance pattern that has the characteristic. Some characteristics might describe more than one pattern. Autosomal Autosomal Sex-Linked Characteristic Dominant Recessive Recessive a. Brothers and sisters are equally likely to have the trait b. Family members from all generations have the trait c. The trait can be inherited from either parent d. Men in the family are more likely to have the trait e. The trait might appear in offspring without appearing in the parents Analysis Questions 1. What are some differences between the inheritance of sex-linked traits and those of autosomal traits? ___________________________________________________________________________________________ 2. What are some differences between the inheritance of dominant and recessive traits? ___________________________________________________________________________________________ 3. Explain why a person with two dominant alleles cannot be a carrier. ___________________________________________________________________________________________ Part II: Making a pedigree (Please Be NEAT… complete a “rough draft” first before drawing the pedigree below) 1. Read the information about Ben and his family, p. 385. 2. Draw a pedigree for Ben’s family showing 3 generations. Ben and his cousin Chris will be the third generation and their grandparents will be the first generation. Use the information on p. 386, 381, and from the story to make your pedigree chart. Show the genotypes of as many family members in the pedigree as possible. 3. Draw a Punnett Square to determine the probably that Ben was going to inherit red-green color blindness. Assume that Ben’s father was not red-green color blind. The probability that Ben would be re-green color blind is ___________. Analysis Questions 1. Why are pedigrees useful tools to understand inheritance patterns for a trait?_____________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________________ 2. What inheritance pattern is shown in Ben and Chris’s family pedigree?___________________________________ Explain why you came to this conclusion. __________________________________________________________ 3. What inheritance pattern is shown in the pedigree on the front of this sheet? _____________________________ 4. Using clues from the pedigree, determine the genotypes of the following individuals: I-1 _____, I-2 _____, II-1 _____, II-2 _____, II-3 _____, II-4 _____, II-5 _____, II-6 _____, II-7 _____, II-8 _____, III-1 _____, III-2 _____, III-3 _____, III-4 _____, III-5 _____, III-6 _____, III-7 _____, III-8 _____, III-9 _____