* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Comparative Practice 2012 WHAP Name: E. Napp Date: The
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
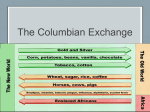
Comparative Practice 2012 Name: _______________________ Date: _______________________ WHAP E. Napp The Question: 2012 Comparative Essay from the World History AP Compare demographic and environmental effects of the Columbian Exchange on the Americas with the Columbian Exchange’s demographic and environmental effects on ONE of the following regions between 1492 and 1750. Africa OR Asia OR Europe Do Now: “The peoples of the eastern and western hemisphere had no sustained contact for thousands of years. Columbus’ voyages therefore ushered in a new era of interaction. This ‘Columbian Exchange’ brought in its wake both catastrophe and new opportunities. The catastrophe befell the Amerindians, who had no resistance to the diseases carried by the Europeans. The new opportunities came with the intercontinental exchange of new plants and animals. Historian Alfred Crosby, a pioneer in the study of the exchange of microbes, cites the lowest currently accepted estimate of the Amerindian population in 1492 as 33 million, the highest as perhaps 50 million. By comparison, Europe at the time had a population of 80 million. The death of millions of Amerindians followed almost immediately after Europeans began to arrive. At their lowest point after the coming of the Europeans, the populations of the western hemisphere dropped to 4.5 million. The biggest killers in this demographic catastrophe were not guns, but diseases: smallpox, measles, whooping cough, chicken pox, bubonic plague, malaria, diphtheria, amoebic dysentery, and influenza. The populations of the New World, separated by thousands of years and thousands of miles from those of the Old, had little resistance to its diseases. Up to 90 percent of the population died. Ironically, but more happily, links between the hemispheres also brought an exchange of food sources, which later facilitated the multiplication of human lives. From South America, the cassava spread to Africa and Asia and the white potato to northern Europe. Sweet potatoes traveled to China, as did maize (corn), of which China is today the second largest producer after the United States. Today, the former Soviet Union produces ten times more potatoes by weight than does South America; Africa produces almost twice as much cassava as does South America. Migration of flora and fauna went from east to west as well. Wheat was the leading Old World crop to come to the New World, but perhaps an even greater contribution came in domesticated animals: cattle, sheep, pigs, and goats. Domesticated horses, too, were imported from the Old World. In the long run, these exchanges of food sources did much to increase the population of the world more than ten times.” ~ The World’s History Identify environmental and demographic effects of the Columbian Exchange: ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ The Basic Core Rubric: 1. Has an Acceptable Thesis. [1 Point] 2. Addresses all parts of the question, though not necessarily evenly or thoroughly. [2 Points but Partial Credit May Be Given] 3. Substantiates thesis with appropriate historical evidence. [2 Points but Partial Credit May Be Given] 4. Makes at least one relevant, direct comparison between/among societies. [1 Point] 5. Analyzes at least one reason for a similarity or difference identified in a direct comparison. [1 Point] Remember the Expanded Core Points: Expands beyond the basic core of 1 – 7 points Questions: 1- What must an acceptable thesis for a Comparative essay contain? ________________________________________________________________________ 2- What does it mean that all parts of the question must be addressed although not necessarily evenly or thoroughly? ________________________________________________________________________ 3- What is historical evidence? ________________________________________________________________________ 4- How many direct comparisons must the student make? ________________________________________________________________________ 5- What must the student analyze? ________________________________________________________________________ 6- How might a student “expand” beyond the basic core? ________________________________________________________________________ 7- Make a list of all of the facts you remember regarding the Columbian Exchange: ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ 8- Make a list of all of the facts you remember regarding the Columbian Exchange’s demographic and environmental effects on the Americas. ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ 9- Make a list of all of the facts you remember regarding the Columbian Exchange’s demographic and environmental effects on the Americas. ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ 10- Make a list of all of the facts you remember regarding the Columbian Exchange’s demographic and environmental effects on Africa. ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ 11- Make a list of all of the facts you remember regarding the Columbian Exchange’s demographic and environmental effects on Asia. ________________________________________________________________________ 12- Make a list of all of the facts you remember regarding the Columbian Exchange’s demographic and environmental effects on Europe. _______________________________________________________________________ Identify Similarities and Differences in Two of the Regions: Similarities in demographic and Differences in the Demographic and environmental effects of the Columbian environmental effects of the Columbian Exchange: Exchange: The Essay’s Prompt: 2012 Comparative Essay from the World History AP Compare demographic and environmental effects of the Columbian Exchange on the Americas with the Columbian Exchange’s demographic and environmental effects on ONE of the following regions between 1492 and 1750. Africa Asia Europe The Thesis Statement: ______________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ My specific similarity was: ______________________________________________________ My specific difference was: ______________________________________________________ Write one body paragraph of the essay [Now, it is time to analyze the similarity or the difference – to explain how and why this similarity or difference occurred and how and why it impacted people in the empires]: ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ Checklist for the Essay: An acceptable thesis statements needs to be comparative, stating at least one similarity and at least one difference. Acceptable thesis statements also need to be explicit, not simply restatements of the question or vague statements such as “there were more similarities than differences.” They also need to be relevant to the time period. A good response provides valid similarities and differences, substantiated by specific pieces of evidence from within the time period. Good essays do not include evidence that is outside the time period or any of the stipulated regions. Students should be told to make their connections clear, because readers will not infer that a particular essay demonstrates content knowledge that is not present in the plain language of the student response. Every paragraph must be comparative. A good response provides analysis and uses this analysis as an explanation of a reason for a similarity or difference. A good essay could consistently analyze cause and effect for the noted similarities and differences. Questions: 1- What must an acceptable thesis statement for a comparative essay have? ________________________________________________________________________ 2- What makes a thesis statement explicit? ________________________________________________________________________ 3- What is not included in a good essay? ________________________________________________________________________ 4- Why must students make their connections clear? ________________________________________________________________________ 5- What must every paragraph be? ________________________________________________________________________ 6- Why must students analyze? ________________________________________________________________________ Rate Thesis Statement A: “Between 1492 and 1750, Africa and the Americas experienced similarities in the introduction of new crops, movement of natives, and disease, while having differences in shift of gender population, amount of death, ethnicity change, and environment.” My Grade for this Thesis Statement: ___________________ Why? ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ Rate Thesis Statement B: “The Columbian Exchange had its positive and negative effects on regions such as the Americas and Africa. Demographic and environmental changes emerged with the Columbian Exchange. Being large continents, Africa and the Americas faced the effects of the Columbian Exchange? ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ 1. The largest decline in percentage of global population in history occurred as a result of (A) Black Death in Europe (B) Global flu pandemic of 1918 – 1919 (C) Spread of AIDS in sub-Saharan Africa in the twentieth century (D) Spread of syphilis in Renaissance Europe (E) Epidemics in sixteenth-century Mesoamerica 5. Which of the following is most likely to have influenced eighteenth-century population trends in both Europe and China? (A) A sharp decline in average global temperatures (B) Introduction of Western Hemisphere crops (C) Innovation in birth control measures (D) Improvement in surgical procedures 2. In the period 1450–1750, which of the following, produced on large plantations by slave labor, were significant commodities in the growing world market? (A) Grains such as wheat and barley (B) Tropical fruits such as bananas and oranges (C) Animal products such as wool and beef (D) Cash crops such as sugar and tobacco 6. Between 1450 and 1750, which of the following were produced on large plantations by slave labor for the world market? (A) Wheat and barley (B) Corn and beans (C) Bananas and oranges (D) Wool and beef (E) Sugar and tobacco 3. How were trends in New Spain and Brazil similar during colonization? (A) Neither used slaves. (B) Both European conquerors decimated native American populations. (C) The societies both became ethnically homogeneous. (D) Copper mining was a critical part of the economy in both colonies. (E) all of the above 7. Which of the following best characterizes world trade in the period 1450 to 1750? (A) Commodities from Africa dominated trade with China and India. (B) The demand for Asian commodities was financed by New World silver. (C) International conflict declined because of growing cooperation among international traders. (D) European dominance of China began. (E) The African slave trade declined 4. In the period 1450–1750, which of the following, produced on large plantations by slave labor, were significant commodities in the growing world market? (A) Grains such as wheat and barley (B) Tropical fruits such as bananas and oranges (C) Animal products such as wool and beef (D) Cash crops such as sugar and tobacco 8. Which of the following characterized economic systems in Latin America and in Southeast Asia during the sixteenth century? (A) Both focused on porcelain manufacturing. (B) Both incorporated forced labor. (C) Both redistributed land to peasants. (D) Both produced grain for the European market. (E) Both focused on small farm-tomarket agriculture. A major consequence of Columbus’ voyages was the eventual exchange of goods between the Old World (Europe) and the New World (the Americas). Listed below are some of the goods that were shared in this “Columbian Exchange” between the continents: From Europe to the Americas Bananas Barley Cabbages Carnations Chickens Coffee Cows Crabgrass Daffodils Daisies Dandelions Horses Lemons Lettuce Lilacs Olives Oranges Peaches Pears Pigs Sugarcane Tulips Rice Sheep Turnips Wheat From the Americas to Europe Avocados Beans (kidney, navy, lima) Bell peppers Black-eyed Susans Cacao (for chocolate) Chili peppers Corn Cotton Marigolds Papayas Peanuts Petunias Pineapples Poinsettias Potatoes Pumpkins Quinine Rubber Squashes Sunflowers Sweet potatoes Tobacco Tomatoes Turkeys Vanilla beans Zinnias ~ Scholastic Magazine