* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Ch. 4 Review Worksheet
Euler angles wikipedia , lookup
Euclidean geometry wikipedia , lookup
Pythagorean theorem wikipedia , lookup
System of polynomial equations wikipedia , lookup
Multilateration wikipedia , lookup
Rational trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Integer triangle wikipedia , lookup
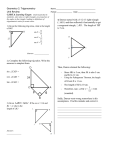
Honors Math 3 Unit 4: Trigonometry Name_______________________________ Ch 4 Review This week we will have a test on Trigonometry, Chapter 4. There are two sets of problems to help you prepare: the review problems in this packet, and the textbook chapter review on page 389. You can also do 4A, 4B, and 4C reflections if you haven’t yet already, but note that we did not cover section 4.14 (Heron’s Formula). Here is a list of some of the key skills and concepts from the chapter: Understand and apply the unit circle definitions of the trigonometric functions Find trigonometric function values using the unit circle, using special triangles (for 30°, 45°, 60°, and angles related to these), and in general using a calculator Prove and apply the Pythagorean identity (sin2 𝛼 + cos2 𝛼 = 1) Find trigonometric function values when given other values using quadrant relationships, the Pythagorean identity, and other identities Solve trigonometric equations by hand, using inverses on the calculator when needed Graph the functions sin 𝛼, cos 𝛼, and tan 𝛼, and identify the periods of the graphs Prove and apply the angle sum identities (formulas for sin(𝛼 + 𝛼) and cos(𝛼 + 𝛼) will be given on the test) Prove and apply the Law of Sines and Law of Cosines. Solve triangles (find unknown sides and angles) when given SSS, SAS, ASA, or AAS. Solve triangles in the potentially ambiguous case SSA. Review Problems –MUST BE SOLVED ON SEPARATE SHEET OF PAPER 1. Given that sin(39.05°) = 0.6300, answer the following without using the sin, cos, and tan keys on your calculator, a. Find cos(39.05°). b. Find tan(39.05°). c. Find an angle between 0° and 90° whose cosine equals 0.6300. d. Find an angle between 90° and 360° whose cosine equals 0.6300. e. Find all the solutions to the equation sin(x) = –0.6300. Directions for problems 2–6: For the triangles given below (each with labels arranged in the usual way): solve for the remaining angles and sides, and also find the triangle’s area. 2. In Δ𝛼𝛼𝛼, A = 20°, B = 60°, and c = 10. 3. In Δ𝛼𝛼𝛼, x = 17, z = 8, and Y = 52°. Hint: after finding the 3rd side, go after Z since you know it will be the smallest angle (no ambiguity in LOS) or use LOC 4. In Δ𝛼𝛼𝛼, a = 3, A = 120°, and B = 20°. 5. In Δ𝛼𝛼𝛼, x = 3, y = 7, and z = 11. 6. In Δ𝛼𝛼𝛼, a = 6, b = 12, and c = 16. 7. Two trains leave a station on different straight tracks. The tracks make an angle of 125° with the station as the vertex. The first train travels at an average speed of 100 kilometers per hour, and the second train travels at an average speed of 65 kilometers per hour. How far apart are the trains after 2 hours? B c 125° C station A 8. For each of the following sets of SSA measurements for Δ𝛼𝛼𝛼, find all unknown sides and angles. If there are two possible sets of measures, find both. a. 𝛼 = 7, 𝛼 = 5, ∠𝛼 = 25.8° b. 𝛼 = 6, 𝛼 = 10, ∠𝛼 = 31.2° c. 𝛼 = 3, 𝛼 = 10, ∠𝛼 = 31.2° 9. Prove using two different methods (1. with a unit circle diagram, 2. with an angle-sum identity) that sin270 cos 2 2 10. Solve this equation, finding solutions in the interval 0° ≤ 𝛼 ≤ 360° : sin sin cos 11. Find all solutions to the equation sin 𝛼 cos 𝛼 = 3 sin 𝛼. 12. Find all solutions to the equation 3 sin(3𝛼) + 8 = 10. Then find all solutions on the interval −270° ≤ 𝛼 ≤ 180°. 13. Find the exact values of sinq , cosq , and tanq if q = 315o 14. Which of the following angles does not have the same sin, cos, and tan values as 45°? (a) -315o (b) 225o (c) 405o (d) -675o 15. Answer the questions using the following information: sin 20° ≈ 0.342, cos 20° ≈ 0.940. a. What are the angles in Quadrants II, III, and IV whose sine and cosine values are either equal or opposite to those of 20°? b. Find sine and cosine for each of the angles you listed in part a. 16. What degree angle does the line y = 2x make with the x-axis? Hint: Draw this line on a unit-circle diagram, as on page 340. 17. Take it further. Applying the angle-sum identities, find a formula for cos(4𝛼) in terms of cos(𝛼) and sin(𝛼). Hint: 4𝛼 = 2𝛼 + 2𝛼. Answers 1. a. Use the Pythagorean Identity. Answer: 0.7766. b. Divide the sine by the cosine. Answer: 0.8112. c. 50.95° d. 309.05° e. 219.05° + 360° n and 320.95° + 360° n for any integer n 2. (ASA case) C = 100°, a = 3.47, b = 8.79; Area 15.04 3. (SAS case) X = 100.43°, Z = 27.57°, y = 13.62; Area 53.58 4. (AAS case) C = 40°, b = 1.18, c = 2.23; Area 1.14 5. No such triangle exists because 11 3 + 7. 6. (SSS case) A = 18.57°, B = 39.57°, C = 121.86°; Area 30.58 7. 294.5 kilometers 8. a. c 11.2, B 18.1 , C 136.1 b. or c. no triangle possible 9. sin(270 + q ) = sin270cosq + cos270sinq = -1× cosq + 0× sinq = -cosq 10. 90°, 210°, 330° 11. 180° n where n is any integer 12. All solutions: 𝛼 = 13.94° + 120𝛼 and 𝛼 = 46.06° + 120𝛼 where k is an integer. Solutions on given interval: 𝛼 = −226.063°, −193.94°, −106.063°, −73.94°, 13.937°, 46.06°, 133.937°, 166.06° -1 - 2 1 2 = , cosq = = , tanq = -1 2 2 2 2 14. Answer: (b). 45° and 225° do have equal tan values, but their sin’s and cos’s are opposite. cos160 = -0.940 cos70 = 0.342 15. sin160 = 0.342 sin70 = 0.940 13. sinq = sin200 = -0.342 cos200 = -0.940 sin340 = -0.342 cos340 = 0.940 cos110 = -0.342 cos250 = -0.342 cos290 = 0.342 sin110 = 0.940 sin250 = -0.940 sin290 = -0.940 16. tan–1(2) ≈ 63.435° 17. cos(4 𝛼) = cos(2 𝛼)cos(2 𝛼) – sin(2 𝛼)sin(2 𝛼) = (cos(𝛼 + 𝛼))2 – (sin(𝛼 + 𝛼))2 = (cos2 𝛼 – sin2 𝛼)2 – (2 sin 𝛼 cos 𝛼)2. If you expand in the first term and then collect like terms, this simplifies to sin4(𝛼) + cos4(𝛼) – 6 sin2(𝛼) cos2(𝛼).