* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Interval Notation and Review of Inequalities
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
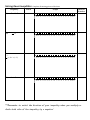
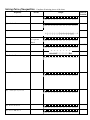
Algebra II Notes Name: _______________________ Date: ________ First Degree Inequalities and Interval Notation Interval Notation is another way for denoting the solution for an inequality by describing the interval containing the numbers that satisfy that inequality. The numbers at the end of the interval are enclosed in brackets [ or ] (the boundary is a solution/ filled in circle) or parentheses ( or ) (the boundary point is not a solution/open circle). If an interval extends forever to the right then the right endpoint is heading towards positive infinity or If an interval extends forever to the left then the left endpoint is heading towards negative infinity or Read the graph (number line) _____________to ____________to help write the solution. When graphing on a number line, an_________________ circle indicates that it is not a solution but is a boundary and a ______________________ circle indicates that it is a solution as well as a boundary. Examples and Practice: Complete all missing pieces of the chart. Inequality Words Graph A) x 3 x is less than 3 Interval Notation (,3) -10 –9 –8 –7 –6 –5 –4 –3 –2 –1 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 B) x 3 -10 –9 –8 –7 –6 –5 –4 –3 –2 –1 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 C) x 3 D) x is less than or equal to 3 x is greater than or equal to 3 (,3] -10 –9 –8 –7 –6 –5 –4 –3 –2 –1 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 -10 –9 –8 –7 –6 –5 –4 –3 –2 –1 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 E) a 2 -10 –9 –8 –7 –6 –5 –4 –3 –2 –1 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 F) m 5 2 -10 –9 –8 –7 –6 –5 –4 –3 –2 –1 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 G) H) (, 1] c is greater than 6 -10 –9 –8 –7 –6 –5 –4 –3 –2 –1 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 I) -10 –9 –8 –7 –6 –5 –4 –3 –2 –1 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 J) K) b is less than or equal to 0 -10 –9 –8 –7 –6 –5 –4 –3 –2 –1 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 3 ( , ) 2 Solving linear ineqalities. Inequality L) Words Complete all missing pieces of the chart. Graph 2x 5 3 Interval Notation -10 –9 –8 –7 –6 –5 –4 –3 –2 –1 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 M) x 2 5 N) 3 x 6 ( x 1) 4 O) -10 –9 –8 –7 –6 –5 –4 –3 –2 –1 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 -10 –9 –8 –7 –6 –5 –4 –3 –2 –1 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 b 2 -10 –9 –8 –7 –6 –5 –4 –3 –2 –1 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 ***Remember to switch the direction of your inequality when you multiply or divide both sides of the inequality by a negative! Solving Pairs of Inequalities. Inequality Complete all missing pieces of the chart. Words Graph Interval Notation P) a 1 and a 5 -10 –9 –8 –7 –6 –5 –4 –3 –2 –1 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 Q) 9 b 0 -10 –9 –8 –7 –6 –5 –4 –3 –2 –1 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 R) S) t is less than 4 or is greater than 6 -10 –9 –8 –7 –6 –5 –4 –3 –2 –1 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 ( 5,3] T) -10 –9 –8 –7 –6 –5 –4 –3 –2 –1 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 U) V) 3x 1 2 and 2(5 x) 16 -10 –9 –8 –7 –6 –5 –4 –3 –2 –1 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 W) 3(2 x 4) 1 7 or 7 x 7 -10 –9 –8 –7 –6 –5 –4 –3 –2 –1 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 X) 14 5( x 3) 1 11 -10 –9 –8 –7 –6 –5 –4 –3 –2 –1 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 Y) b 0 or b 2 -10 –9 –8 –7 –6 –5 –4 –3 –2 –1 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 Z) b 0 and b 2 -10 –9 –8 –7 –6 –5 –4 –3 –2 –1 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11