* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Transformations That Produce Equivalent Inequalities
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
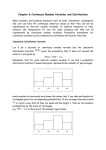
ABSOLUTE VALUE a = a if a ≥ 0 a = −a if a < 0 1. If a < b, then -b < a < b 2. If a > b, then -b > a > b 3. If a = b , then a = ± b Open Interval: a<x<b denoted: (a,b) Closed Interval: a≤ x≤b denoted: [a,b] Half-Opened interval: a≤ x<b denoted: [a,b) On a number line, the distance between the graphs of two numbers a and b ( |a – b| or |b – a|) is the absolute value of the difference of a and b. Example #2: Solve for x in the equality |x - 2| = 5 (Equivalent to the disjunction: x – 2 = 5 or x – 2 = -5) x= 7 or x = -3 Example #3: Solve for x in the inequality |x + 5 | < 6 (Note: |x – (-5)| < 6 (Equivalent to the conjunction: -6 < x + 5 and x + 5 < 6). Note: Less Thand. -11 < x < 1 or x ∈ (−11,1) Example 4: Solve for x in the inequality | 2 x − 3 |≥ 6 (Equivalent to the disjunction: 2 x − 3 ≤ −6 or 2 x − 3 ≥ 6 ) Note: Greator 2 x − 3 ≤ −6 or 2 x − 3 ≥ 6 2 x ≤ −3 or 2x ≥ 9 −3 9 x≤ or x ≥ 2 2