* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download document 8908090
Role of music in World War II wikipedia , lookup
Appeasement wikipedia , lookup
Consequences of the attack on Pearl Harbor wikipedia , lookup
British propaganda during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Allied Control Council wikipedia , lookup
Fascism in Europe wikipedia , lookup
Propaganda in Nazi Germany wikipedia , lookup
Western betrayal wikipedia , lookup
Collaboration with the Axis Powers wikipedia , lookup
World War II by country wikipedia , lookup
Pursuit of Nazi collaborators wikipedia , lookup
World War II and American animation wikipedia , lookup
Home front during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Consequences of Nazism wikipedia , lookup
Allies of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Nazi views on Catholicism wikipedia , lookup
Diplomatic history of World War II wikipedia , lookup
American Theater (World War II) wikipedia , lookup
Foreign relations of the Axis powers wikipedia , lookup
New Order (Nazism) wikipedia , lookup
Nazi Germany wikipedia , lookup
Economy of Nazi Germany wikipedia , lookup
End of World War II in Europe wikipedia , lookup
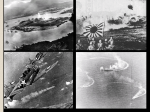
Every major European nation was near bankruptcy in 1918 Germany suffered most of all Germany blamed for WWI and forced to pay reparations of $33 billion Inflation skyrockets as German Government begins printing 400 quadrillion marks a day 1923 – 1,000,000 Marks equaled one US cent Daws Act – U.S. provided $200 million in relief to Germany to help stabilize the economy and lower reparation payments Mussolini & Italy Although Italy was victorious in WWI they didn’t reap many benefits Suffered high casualties during the war Did not get much land from Treaty of Versailles Unemployment, high prices, and food shortages after the war Fascism – interest of the state above that of the individual Power rested in a single person Mussolini – “I am Fascism” Wanted to restore the glory of ancient Rome Mussolini’s followers called “Squadristi” or “Black Shirts” 1922 – appointed dictator by King Italy invades and conquers Ethiopia in 1935 Adolph Hitler Corporal in WWI 1919 – joined National Socialist German Workers (Nazi) Party Hitler’s private Nazi army known as “Storm Troopers” or “Brown Shirts” Beer Hall Putsch – 1923, failed attempt by Hitler and the Nazis to overthrow the Bavarian Government Hitler arrested and imprisoned for 9 months Writes “Mein Kampf” or “My Struggle Nazi Party gains popularity Placed Jews as scapegoat for nations problems Played on peoples fears and promised to end the chaos in Germany Nazi Party went from 2.6 percent of the vote in 1928 to 37.3 percent in 1932 January 30, 1933 Hitler appointed Chancellor Hitler calls his new Government the Third Reich Axis Powers formed – military alliance between Italy and Germany in 1936 Kristallnacht – “Night of Broken Glass” Nov. 9, 1938 Nazi’s destroyed Jewish businesses and synagogues 1931 Japan invades Manchuria Looking to build an empire and gather natural resources The U.S. wished to remain isolated Disapproved of European and Japanese aggression Passed neutrality laws and placed embargoes on weapons trade to hostile nations 1938 – Hitler demanded that Czechoslovakia turn over the Sudetnland (home to many Germans), Czech’s refused and Hitler threatened war. Munich Conference – French and British leaders met with Hitler in Sept. 1938. Appeased Hitler by persuading the Czech’s to give up the Sudetenland to preserve peace. “The Government had to choose between shame and war, they have chosen shame but will get war” March 1939 Hitler seized the rest of Czechoslovakia. 1939 – Hitler demanded Poland return the City of Danzig which had belonged to Germany prior to WWI Britain and France pledged to defend Poland if Hitler attacked Non – aggression Pact - Aug 1939, Hitler and Stalin agreed not to attack each other and divide Poland WWII begins on September 1, 1939 when Germany invaded Poland Blitzkrieg – “lightning War” Germany attacked Poland from the west while the Soviet Union attacked from the east. Poland was overrun within a month. Allied Powers – Sept. 3, 1939 Britain and France declared war on Germany France moved it’s troops to the fortified wall built following WWI between France and Germany known as the Maginot Line. Immobile, stretched from Luxemburg to Switzerland Germany simply went around to the north. May 26 – June 3 Battle of Dunkirk trapped French troops had to be evacuated to Britain. June 22, 1940 France surrendered, and Germany took control of northern France With France defeated, Hitler prepared to invade Britain Before Hitler could launch an invasion (operation sealion), his Luftwaffe (German Air force) would need to gain control of the air by defeating the British Royal Air force (RAF) Radar helped RAF detect incoming aircraft Raids on London – Sept. 7 – hoped to break British moral By mid Sept. Hitler cancelled his plans for an invasion. 1st major setback for the 3rd Reich “Never was so much owed by so many to so few” Churchill Although Americans opposed Hitler, they didn’t want to get involved in a European conflict Neutrality laws prevented the U.S. from aiding the Allies Roosevelt persuaded Congress to change the laws 1939 – “cash and carry” allies could purchase U.S. weapons “We must be the great arsenal (arms supplier) of Democracy” 1941 – “Lend Lease Act” loaned $7 Billion in weapons and supplies to Britain. When Hitler broke the non-aggression in June 1941, Roosevelt extended the Lend Lease to the Soviets As U.S aid to Britain increased Germany used its U-Boats to stop the transportation of weapons and supplies, resulting in a long fight for control of the trade routes. U.S Navy began escorting and notifying the British of sub locations Oct 31, 1941 U.S.S. Ruben James was sunk by German sub, 115 American killed. Roosevelt ordered U.S. to shoot on site (war seemed certain) In July 1941 Japanese forces attacked French Indochina President Roosevelt froze Japanese funds in the U.S. and blocked the sale of oil to Japan (angered Japan) After failed attempts to negotiate with the U.S the Prime Minister General Tojo made preparations for war In Nov. 1941 Japanese aircraft carriers (General Yamamoto) left for Pearl Harbor Hawaii (home to the entire U.S. Naval Fleet) The attack began on Dec. 7, 1941 at about 7:30 am. The attack sunk or damaged 19 ship, destroyed 177 planes and killed 2335 people. The U.S.S. Arizona suffered the greatest losses (1177 killed) Dec. 8, 1941 Roosevelt asked Congress to declare war on Japan. Dec. 11, 1941 Germany declared war on the U.S. Americas involvement in WWII will help stimulate the economy helping to end the Great Depression. Production boomed – demand for war goods Earning rose and unemployment nearly vanished Farm production skyrocketed War Production Board – oversaw conversion of factories Increase armies – recruit and train millions of soldiers Increased Taxes – income tax on middle and lower class Women in workforce – replace men in factories and businesses, less pay. 300,000 in Armed Forces non - combat roles. In 1941 about 125,000 Japanese lived in the U.S. Issei – immigrants from Japan Nisei – Japanese born in the U.S Growing fear of sabotage and spying as well as possible violence against Japanese citizens 1942 forced into internment camps throughout western States 442nd Regiment – Japanese (Nisei) soldiers in U.S. Army, highly decorated combat team 18,000 individual medals 2 weeks after Pearl Harbor Roosevelt and Churchill agreed to focus on defeating Germany first. Allied Air Forced attempted to destroy German economic resources by targeting railroads, military centers and German cities Most bombing raids occurred during the daytime, this resulted in greater casualties General Rommel (Desert Fox) led Italian and German forces to gain control of the Suez Canal and oil field of Egypt. Battle of El Alamein – Allied forces under British commander General Montgomery stopped Rommel’s forces and drove the Axis Powers from Northern Africa. Allies invade Italy – July 1943, Allied forces attack Sicily and Italy (soft underbelly of Europe) Many Italians wanted peace (overthrew Mussolini) Hitler sent German troops to help Mussolini and to stop the Allied advance In April 1945, Allied forces drove German forces from Italy April 1945 Italian resistance fighter captured and executed Mussolini Turning point of the war between Axis powers and Soviet Union Operation Blue – Germany began its attack against the Soviet city of Stalingrad. Lasted 199 days from Aug 1942 – Feb 1943 Bloodiest battle in human history, 2 million casualties Stalin forbid civilians from leaving, put women and children to work building fortifications Germans bombed the city, reduced it to rubble, 80% of living spaces destroyed “Not a step back” Stalin ordered all those who retreated to be shot Bitter fighting for every street, factory, and house Harsh winter weather took its toll on Germany (low supplies) “Operation Uranus” – Soviet counter attack in Nov. 1942 to recapture the city. Surprisingly to Hitler dislike in Feb 1943 over 90,000 German soldiers surrendered “Operation Overlord” June 6 1944, allied invasion of the beaches of Normandy (northern France) Eisenhower’s Plan 150,000 allied soldiers largest land invasion in history Goal: to liberate western Europe from Nazi occupation Dec. 16, 1944 – Jan 28, 1945 Hitler made a desperate attempt to split advancing allied forces. Allied forces were outnumbered but fought to maintain the lines, allies retreated creating (The Bulge) 77,000 U.S. casualties Allied forces managed to launch a counterattack and began to drive back German lines Weakened German forces unable to wage offensive war Allies began advance towards Berlin while Soviet advanced from the east Following the attack on Pearl Harbor Japan seemed unstoppable Japan continue to strengthen their position by acquiring lands throughout southeast Asia Philippines – U.S. possession, U.S. and Filipino forces under the command of Douglas MacArthur March 1942 MacArthur order to evacuate “I Shall Return” Many U.S. and Filipino soldiers were trapped on the Island and surrendered 70,000 prisoners forced to march 65 miles (Bataan Death March) poorly treated 600 Americans and 10,000 Filipinos died To stop Japan, the allies had to defeat the Japanese Navy. Chester Nimitz – commander of U.S. Naval fleet in Pacific U.S.Navy had broken the Japanese code and could read secret messages. U.S learned of Japans plan to take Port Moresby in New Guinea U.S.fleet met the Japanese invasion force in the Coral Sea northeast of Australia Both fleets suffered losses (1 Carrier sunk, and 1 damaged) Allies able to stop Japanese advance for the first time Again Allies learn of Japans plan to capture the midway Islands Nimitz sent U.S. carriers to intercept the Japanese June 3-6 1942 - air battle, planes try to sink opposing Aircraft carriers Japans Navy crippled lost 4 carriers “Operation Watchtower” – Japanese occupied part of the Solomon Islands chain (wanted to use as an airbase) First offensive by U.S. land forces in the Pacific Allies plan to conquer 1 island at a time, gradually moving closer to Japan Hoped to gain bases from which they could bomb and later invade Japan When the U.S. evacuated the islands in 1942 Douglas MacArthur vowed “I shall return” Battle of Leyte Gulf – Oct 1944, largest naval engagement in history Kamikaze (divine wind) 1st battle that Japanese pilots used the suicide tactics Americans began bombing missions on Japanese cities (Tokyo) inflicting heavy damage. Despite the heavy losses Japan refused to surrender (fought even harder) rather die than surrender Iwo Jima (Feb. 1945) most of the 22,000 Japanese defenders fought to the death only 200 survivors Okinawa – (April 1945) used Kamikazes, killing nearly 5000 sailors. During 3 months of fighting Japanese suffered 110,000 casualties, and another 80,000 civilians As Allied and Soviet troops converged on Berlin Hitler retreated to his underground bunker where on April 30, 1945 he committed suicide On May 7th German authorities surrendered, the following day May 8th 1945 is celebrated as V-E Day (Victory in Europe) the official end of WWII in Europe Allied leaders feared an invasion of Japan would result in enormous losses (1 million) Manhattan Project – scientists had been secretly working on the development of the Atomic bomb (Robert Oppenheimer) since 1942 July 16, 1945 U.S tested the first atomic bomb in Alamogordo N.M When Japan refused to surrender President Harry Truman gave the order to drop the bomb on. August 6, 1945 the B29 bomber Enola Gay dropped the bomb (little boy) on the Japanese city of Hiroshima, killing nearly 80,000 people 3 days later on Aug. 9 a second bomb (fat man) was dropped on the city of Nagasaki Less than a month later on Sept. 2, 1945 Japan surrendered The use of this weapon changed the future of warfare The History of Nazi Anti-Semitism •Hostility toward or prejudice against Jews AntiSemitism Hitler’s Views History of Jews in Germany Told Germans that they came from a superior race – the Aryans Used the Jews as a scapegoat – someone to blame for Germany’s woes after World War I Jews lived in Germany for 1,600 years. Hostility toward Jews existed since the Middle Ages. Anti-Jewish Nazi laws mirrored medieval efforts to humiliate Jews. Anti-Semitism changed from prejudice based on religion to hatred based on ancestry. Nazi Anti-Semitism Hitler in Power Began campaign against Jews soon after becoming chancellor Established a series of anti-Semitic laws intended to drive Jews from Germany Laws stripped Jews of their citizenship and took away most civil and economic rights. Laws defined who was a Jew. Attacks on Jews Many Germans supported Hitler’s anti-Semitic ideas. Discrimination and violent attacks against Jews continued. Anti-Jewish riots broke out in an attack called Kristallnacht. Jews were sent to concentration camps, killed, and fined for the attack. Fleeing Germany Over 100,000 managed to leave Germany after Kristallnacht. Others found it difficult to leave the country as Nazi laws had left many without money or property. Many countries were unwilling to take in poor immigrants. The United States limited the number of Germans immigrants The Nazi Government’s Final Solution World War II brought many of Europe’s 9 million Jews under the control of the Nazi SS. Concentration camps were built in Germany and in other countries that the Germans occupied. The camps were prisons for Jews and others considered enemies of Hitler’s regime. Conditions in the camps were horrific. The Nazis also established ghettos to control and punish Jews. Ghettos are neighborhoods in a city to which a group of people are confined. Life in the Jewish ghettos was desperate. The worst ghetto was in Warsaw, Poland. In 1941 Hitler called for the total destruction of all of Europe’s Jews. At first mobile killing units—Einsatzgruppen—massacred Jews. Then, Nazi officials adopted a plan known as the Final Solution. Concentration Camps, Ghettos, and the Final Solution Camps Prisons for Jews, prisoners-of-war, and enemies of the Nazi regime Inmates received little food and were forced to labor. The combination of overwork and starvation was intended to kill. Punishment for minor offenses was swift, sure, and deadly. Ghettos Walls or fences kept the Jews inside and those trying to leave were shot. Food was scarce; starvation was rampant. Diseases spread rapidly. The worst ghetto was in Warsaw, Poland. Some Jews in the Warsaw ghetto—the Jewish Fighting Organization—fought back. The Final Solution Genocide – the killing of an entire people Involved building 6 new extermination camps for Jews Inmates were exposed to poison gas in specially built chambers. 3 million Jews died in extermination camps. 3 million Jews and 5 million others were killed by the Nazi using other means. The American response to the Holocaust Despite knowing about Hitler’s policies toward the Jews and events such as Kristallnacht, American immigration limited the number of Jews who could move to the United States. In 1942, Americans officials began to hear about what was happening to the Jews in Europe and specifically about Hitler’s Final Solution. The Americans were doubtful at first and thought the reports might just be war rumors. Finally in 1944, Roosevelt created the War Refugee Board. Through this board, the United States was able to help 200,000 Jews. The American Response Liberating the Nazi Camps In 1944, Soviet troops began to discover some of the Nazi death camps. By 1945 they reached the huge extermination camp at Auschwitz. Their reports gave proof of Hitler’s terrible plan. Also in 1945, American soldiers came upon concentration camps. Many camp inmates died after being rescued, but some were still strong enough to survive. The Nuremberg trials Many Nazis faced trial for their roles in the Holocaust. The court was located at Nuremberg, Germany. The court was called the International Military Tribunal. Twenty two Nazis were tried for war crimes, including Hermann Göering. Since Nuremberg, several Nazis have been captured and tried in different courts, including Israel.