* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download januarysciencetestnotes
Planet Nine wikipedia , lookup
Planets beyond Neptune wikipedia , lookup
Space: 1889 wikipedia , lookup
Dwarf planet wikipedia , lookup
Naming of moons wikipedia , lookup
Planets in astrology wikipedia , lookup
History of Solar System formation and evolution hypotheses wikipedia , lookup
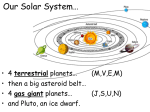
Canadian Contributions Canadarm-also known as the Shuttle Remote Manipulator System, the Canadarm is a well-known Canadian invention. It acts like a human arm. It is 15.2 metres long and weighs about 410 kilograms on Earth. It is used to grab and suppor t large objects in space. The Canadarm has special sensors and cameras to find damaged parts. Dextre-is used with the Canadarm and acts like a hand. It can do jobs usually done by astronauts and ones that require precise work. Microvariability and Osc illations of Stars telescope(MOST) -this is Canada's first telescope. It is the smallest telescope made yet, it can fit inside a suitcase. It is sometimes called the "Humble" telescope. Marc Garneau-the first Canadian astronaut in space. He worked in the Canadian Navy before becoming an astronaut. He went into space three times -1984, 1996 & 2000. Roberta Bondar-in 1992, she became the first Canadian astronaut to go into space. She is a neurologist and has several degrees. Benefits of Exploring Space Artificial satellites -artificial satellites are one of the greatest benefits which came about via space exploration. These communication satellites allow radio and television shows to be broadcast around the world. Other types of these satellites are weather satellites, GPS satellites, and map related satellites for land and ocean mapping. Costs of Exploring Space 1. Space exploration is dangerous as many people have died over the years. 2. Mission failure is a major concern since many instrumen ts have been damaged or don't perform as they should on space missions. 3.Exploring space is expensive as Canada spends $300,000,000 per year on space exploration. Members of the Solar System Solar System-the sun and all of the bodies that orbit it make up the solar system. This includes the planets and their moons, as well as comets, asteroids, meteoroids, and an y other bits of rock or dust. The main parts of our solar system are eight planets, an asteroid belt, and three dwarf planets. The Sun-the sun is one of millions of stars in Earth's galaxy. It is a relatively small star but it is still 109 times the size of the Earth. The sun's diameter is 1392000km and the temperature on the sun ranges ranges from 4000 to 9000 degrees Celsius. The Inner Planets-these are the four planets that are closest to the sun. They are: 1. Mercury-this is the smallest of the 8 planets and closest to the sun. It is a sm all rock y planet covered with craters. It has no atmosphere or moons. 2.-Venus-this is the s econd planet from the sun. It is a small rock y planet with no moons. This planet has a thick atmosphere of mainly carbon dioxide which also has miles of thick sulfuric acid clouds. It's the hottest planet in our solar system at 465 degrees Celsius. 3-Earth-this is the third planet from the sun. It is the only planet known to support life. One moon orbits the Earth. 4-Mars-this is the fourth planet from the sun. Mars has permanent ice caps on both of its poles. Mars is known for having dust storms and strong winds. Mars' surface is made up of iron-rich dust which gives it it's reddish appearance. Mars has two tiny moons. The Asteroid Belt-this lies between the Inner Planets and Outer Planets. It is made up of rocks, ice and metal. The Outer Planets -the next four planets in our solar system are referred to as the gas giants because they are mainly made up of gas and are much larger than the inner planets. The outer planets are: 1. Jupiter-this is the fifth planet from the sun and the largest of t he 8 planets. It is about 1000 times the size of Earth. Jupiter has 63 known moons. 2. Saturn-this is the sixth planet from the sun and the second largest of the 8 planets. Saturn's rings are mainly made up of water and it has 59 moons. 3. Uranus-this is the seventh planet from the sun and the third largest of the 8 planets. It is made of rock and ice and has 27 moons. 4. Neptune-it is the eighth planet from the sun. Neptune's winds are the fastest in our solar system, they can reach speeds of 2000 ki lometres per hour. Neptune has 13 moons. The Dwarf Planets-these are too small to be called planets but too large to be called asteroids. The three dwarf planets are: 1. Ceres-it is found in an asteroid belt in our solar s ystem. 2. Pluto-Pluto has 3 moons and is usually farther from the sun than Neptune. The orbit of Pluto and Neptune cross as certain points making Pluto closer to the sun than Neptune. 3. Eris-it is furthest away from the sun of the dwarf planets and has one moon. It is the largest of the dwarf planets. The Moons-moons are naturally occurring satellites that orbit the planets. Only Mercury and Venus don't have moons. Io, one of Jupiter's moons, is the most volcanically active bod y in our solar system. Asteroids and Meteoroids-these are too small to be called planets. Asteroids are large rocky fragments while Meteoroids are smaller fragments of rock. W hen a meteoroid hits the Earth's surface, it's called a meteorite. Manicougan crater, in Quebec, is the fifth largest crater in the w orld measuring 100 km across. Comets-consist mostly of gas, ice and dust. They orbit in large, oval orbits. As comets approach the sun, the ice melts creating the comet's tail. Objects that emit and reflect light in space Objects in space that emit light: Sun, Stars, Galaxies, Nebulae, and Meteors in the Earth's atmosphere. Objects in space that reflect light: Comets, Asteroids, Meteoroids in space, moons or natural satellites, and artificial satellites.