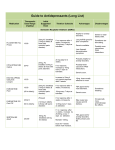
* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Click here for handout
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
Onuma, Kalu MD
PGY 4
CASE PRESENTATION
IDENTIFYING PROFILE.
25 years old married Caucasian female who lives with
her husband and their 5 years old son and 3 years old
daughter in Kingsport, TN
CLINICAL PRESENTATION
Sustained upward deviation of eyes.
Mutism
Restlessness
Agitation
Behavioral disturbance.
Pupil dilation
Backward flexion of neck.
HPI
Patient had been in apparent good health until the
death of her father in law, from which time she
became increasingly depressed, not eating and
sleeping well.
Was subsequently admitted to psych hospital to
address worsening psychosis and mood symptoms.
Was rushed to the ER for evaluation and treatment of
sudden onset of AMS after 48 hours of hospitalization
in the psych facility for Psychosis NOS.
MEDICATION HISTORY.
Ambien orally 10mg QHS, Ativan taper.
Abilify PO 5mg x 1
Geodon IM 10mg bid(
Haldol IM 5mg q8hours prn(
Thorazine IM 25mg x 1
PAST PSYCHIATRY HISTORY.
Significant for polysubstance abuse.(THC, Opiates, Benzos)
Nil previous psych hospitalization.
PAST MEDICAL HISTORY.
None
LABS/IMAGING STUDIES.
CMP, CBC, CT, MRI, HIV, CRP, Ammonia levels
Vit B12, Ceruloplasmin, EEG.
DIAGNOSIS/TREATMENT
OCULOGYRIC CRISIS
IM Benadryl.
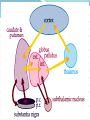
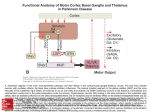
PATHOGENESIS
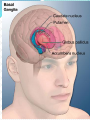
MIDBRAIN PATHWAYS
-Substantia nigra pars reticula---Superior Colliculi
-Substantia nigra pars compacta--Reticular formation
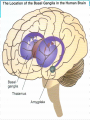
BASAL GANGLIA
-subcortical component
of family of circuits{Oculomotor, Limbic, Prefrontal
Skeletal motor circuits}
CAUSES
MEDICATIONS
-Neuroleptics, Metoclopramide.
-Carbamazepine, lithium, PCP
-Levodopa, Amantadine, Chloroquine
BRAIN STEM LESION
-Ischemic, Neoplastic, or Inflammatory.
HEAD TRAUMA
INFECTIONS
-Neurosyphylis, and Herpes Encephalitis.
OTHERS.
-Alcohol, Emotional stress, and fatigue
-Inherited errors of metabolism
CLINICAL FEATURES
Involuntary, sustained deviation of the eyes.
CLINICAL FEATURES
Involuntary, sustained deviation of the eyes.
Mutism, eye blinking, and pupil dilation.
Flexion of the neck.
Restlessness, Agitation, and Behavioral disturbances.
Transient psychotic episodes.
-Visual hallucination.
-Auditory hallucination.
Autonomic dysfunction.
RISK FACTORS
Male gender
Young age.
High doses
High-potency antipsychotics
History of substance abuse(alcohol, and or cocaine)
Genetic susceptibility(Slow metabolizers)
Comorbid conditions(Tourette & Parkinsonism)
PATIENT ASSESSMENT
Physical status.
-safety of patient and staff.
-history/collateral information.
-careful review of medications .
-review of medical records.
-physical and neurological examination.
Mental status examination.
DIAGNOSTIC STUDIES
CBC
CMP
UDS
VDRL
CT
MRI
EEG
EKG
URINALYSIS
DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS
Seizure Disorder.
Delirium.
Other EPS.
-Tardive, Parkinsonism, Akathisia
CNS lesion(focal basal ganglia or Thalamus).
Postencephalic parkinsonism.
Tyrosine hydroxylase deficiency.
TREATMENT/MANAGEMENT
Pharmacologic Intervention
-Anticholinergic medication
(Benadryl or Cogentin)
Environmental manipulation.
-Place patient in a room near nursing station.
-Orient patient repetitively.
-Use sitter.
- Use restraints when less restrictive measures have failed.
-
COURSE(PROGNOSIS)
Typical course usually ranges from 24-48 hours.
-upon medication withdrawal or reduction.
Symptom relief within minutes with anticholinergics.
Recurrent crisis maybe observed on med re-exposure.
Excellent prognosis.
THANK YOU!
Questions ?
Contributions……
References will be made available on request.
Contact: [email protected]