* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Dizziness
Lip reading wikipedia , lookup
Auditory brainstem response wikipedia , lookup
Management of multiple sclerosis wikipedia , lookup
Hearing loss wikipedia , lookup
Hemiparesis wikipedia , lookup
Werner syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Otitis media wikipedia , lookup
Audiology and hearing health professionals in developed and developing countries wikipedia , lookup
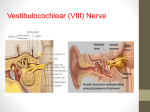
A practical approach to dizziness Michael Gilchrist, MD MPH 8/17/09 Case 71 year old female with hypertension present to clinic with “dizziness”. What questions would you ask? Dizziness Common primary care complaint Vertigo, presyncope, disequilibrium, other Outline Presyncope Vertigo Causes Characteristics of different causes History and physical Warning signs How to approach the patient? “I’m dizzy” Non-specific term Vertigo and psychiatric causes make up the majority of cases seen in clinic setting (55-70%) Multicausal, presyncope, unknown, hyperventilation Presyncope Prodromal symptom of fainting Usually occurs when patient is standing or upright, not supine Orthostatic hypotension, cardiac arrhythmias, vasovagal attacks most common Other causes Parkinson’s disease Peripheral neuropathy Hyperventilation Medications Hypoglycemia Psychiatric disorders Vertigo vs. presyncope Positional vertigo and postural presyncope often confused Both can occur when someone goes from sitting to standing Vertigo (especially BPPV) can be provoked with maneuvers that move the head without changing BP Vertigo Dysfunction of vestibular system (central vs. peripheral) Vertigo Illusion of motion Self-motion Motion of the surrouding environment “spinning”, “tilting”, “moving” All vertigo is made worse by moving the head. The history… Patient description (“spinning” sensation, however is non-specific) Time course Vertigo is rarely described as continuous. Hearing loss? If so, duration and progression, unilateral vs. bilateral, tinnitus, sx of otitis Causes of Vertigo Peripheral Benign positional vertigo Vestibular neuritis Herpes zoster oticus Meniere’s disease Labyrinthine concussion Cogan’s syndrome Acoustic neuroma Aminoglycoside toxicity Otitis media Central Migrainous vertigo Brainstem TIA Wallenberg’s syndrome Cerebellar infarcation or hemorrhage Chiari malformation MS BPV Most commonly recognized form of vertigo Attributed to calcium debris within the semicircular canal (canalithiasis) “I feel like the room is spinning when I turn my head” Lasts seconds, but pt may feel destabilized for hours after an attack No ear pain, tinnitus, or hearing loss BPV (cont.) Diagnosis usually made by history Dix Hallpike maneuver Positive in 50-80% of patients Canalith repositioning maneuvers Medical therapy usually not helpful due to transient symptoms Vestibular neuritis Viral or postviral inflammatory disorder Rapid onset of severe persistent vertigo with nausea, vomiting, ataxia Sometimes combined with unilateral hearing loss (labyrinthitis) Steroid taper. Dramamine, meclizine (H1 blockers), benzodiazapines Herpes zoster oticus AKA Ramsay Hunt syndrome Activation of latent herpes zoster infection Vertigo + hearing loss, ipsilateral facial paralysis, ear pain, vesicles Antiviral therapy Meniere’s disease Excess endolymphatic fluid pressure Episodic, acute vertigo, lasts minutes to hours Unilateral tinnitus, hearing loss, ear fullness Treatment Salt, caffeine, tobacco restriction Diuretics Surgical Labryinthine concussion Traumatic vestibular injury following head trauma Transverse fractures of the temporal bone Cogan’s syndrome Autoimmune Similar to Meniere’s: veritgo, ataxia, nausea, vomiting, tinnitus, hearing loss “oscillopsia”: perception of objects jiggling after abruptly turning the head Acoustic neuroma Slow growing tumor Patients often experience mild vertigo or no vertiginous symptoms at all Unilateral tinnitus and hearing loss MRI brain Otitis media Fever, hearing loss, nausea, vomiting If pt has pain with tragal stimulation, consider CT scan of face to evaluate for labryinthine fistula in the temporal bone Peripheral causes Benign positional vertigo - most common, no hearing loss Vestibular neuritis - sometimes hearing loss Herpes zoster oticus (Ramsay-Hunt) Meniere’s disease - unilateral hearing loss Labyrinthine concussion Cogan’s syndrome - autoimmune Acoustic neuroma - often minimal vertigo Aminoglycoside toxicity Otitis media Central causes… Migrainous vertigo Can have central and peripheral manifestations Diagnosis made by history (aura, headache Sometimes associated with migraine headaches Brainstem ischemia Vertebrobasilar arterial system Rarely the sole manifestion, however MRI brain Wallenberg’s syndrome Lateral medullary infarction Posterior inferior cerebellar artery Oftentimes concurrent Ocular movements Ipsilateral Horner’s syndrome Ipsilateral limb ataxia Sensory loss Hoarseness, dyphagia (CN IX) Cerebellar infarction/hemorrhage Sudden intense persistent vertigo with nausea and vomiting. Pronounced gait abnormalities Pt falls toward the side of the lesion Typically older pts (>60 y/o) with CV risk factors Warning signs Suggestions of central vestibular disease or brainstem lesions Persistent vertigo Ataxia Nausea/vomiting Headache Vision loss, diplopia Slurred speech Vertigo, physical exam findings Nystagmus Hallpike maneuver Move patient rapidly from sitting to lying position, head tilted downward of facing you The Dix-Hallpike Test of a Patient with Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo Affecting the Right Ear Furman J and Cass S. N Engl J Med 1999;341:1590-1596 Central vs. Peripheral Vertigo Peripheral Nystagmus unidirectional, horizontal with a torsional component Other neurologic signs absent Deafness or tinnitus may be present Central Nystagmus can be in any direction Other neurological signs often present Gait instability Deafness or tinnitus typically absent Often less severe More likely to be chronic, not episodic High yield historical questions Subjective description, avoid leading questions Duration/frequency of symptoms Triggering factors Associated nausea/vomiting? Hearing loss or tinnitus? Any other neurological complaints Recent viral illness, fever, systemic symptoms? New medications? Physical exam Neurological exam Check for nystagmus with and without Dix-Hallpike Ear exam Gait Cardiovascular exam