* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download SO FAR:
Modified Newtonian dynamics wikipedia , lookup
History of astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Hubble Deep Field wikipedia , lookup
Rare Earth hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Perseus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Geocentric model wikipedia , lookup
International Ultraviolet Explorer wikipedia , lookup
History of Solar System formation and evolution hypotheses wikipedia , lookup
Formation and evolution of the Solar System wikipedia , lookup
Solar System wikipedia , lookup
Malmquist bias wikipedia , lookup
Dialogue Concerning the Two Chief World Systems wikipedia , lookup
Open cluster wikipedia , lookup
Tropical year wikipedia , lookup
H II region wikipedia , lookup
Aquarius (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Observational astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Corvus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Star formation wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical unit wikipedia , lookup
Timeline of astronomy wikipedia , lookup
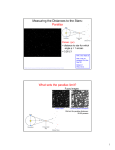
SO FAR: • Galaxy types • Ancient history • Properties of Interstellar Dust • Milky Way and spiral galaxy morphology • Nuclear bulge • Disk • Stellar halo • Dark matter halo • Chemical enrichment • Measuring chemical abundances – Absorption lines (stars) – Continuum energy distributions (stars) – Emission lines (H II regions) • Star-forming regions NOW… Kinematics of spiral galaxies • Rotation curves Î mass distribution • Spiral structure (includes sidetrack about measuring distances) • General properties of S, E, Irr galaxies • Midterm Kinematics of the Milky Way • From [CO] 24.3, especially pp 901-14. • Coordinate systems • Spherical coordinates centered on Sun: Galactic latitude (lII) , longitude (bII) • Π, Θ, Z • Velocity components in cylindrical coordinate system centered on Galactic Center w u v • Peculiar velocities u, v, w • Π, Θ, Z velocities but relative to Local Standard of Rest • LSR is point instantaneously centered on Sun, but moving in a perfectly circular orbit. • Solar motion: motion of sun relative to LSR 1 • Star density is higher towards GC. • LSR’s orbit Those stars are on orbits that Sun overtakes. • Velocity ellipsoids and asymmetrical drift. • Sun’s orbital velocity V ~ 220 km s-1 • Sun’s orbital period R P = 0 ~ 230 million yrs. V • Approx. mass interior to Sun’s orbit F =F centrifugal Fig 24.20 grav 2 mV GmM = 2 R0 R0 M= V 2 R0 ~ 9x1010 M☼ G Differential Rotation Fig 24.21 (see [CO pp. 909-911) = G.C. • From the figure: vr • Angular rotation velocity: • + some geometry Î vt = SUN [Fig 24.22] • Taylor expansion: Oort’s Constants: 2 Oort’s Constants vr vt • Easily (?) evaluated from the observations: • contain important information about Galactic rotation curve. • Angular velocity for circular motion at Ro: Θ(R) Ro Ωo = A – B R Θ • Gradient of rotation curve at Ro: Ω( R ) = dΘ = −(A + B) dR Ro Θ( R ) R R G.C. Observed MW rotation curve • In principle, for stars, clusters, etc: • measure distance d and vr • assume circular orbit • For H I 21cm, CO, etc. radio emission: • Only can measure vr • Use tangent point method + d d Sun For objects at A: get distance from star clusters, or from H I disk thickness. 3 Observed MW rotation curve • In principle, for stars, clusters, etc: • measure distance d and vr • assume circular orbit + • For H I 21cm, CO, etc. radio emission: d d • Only can measure vr • Use tangent point method Sun Radio data Tangent point method Young star clusters For objects at A: get distance from star clusters, or from H I disk thickness. Measuring the Distances to the Stars: Parallax Parsec (pc) = distance to star for which angle p = 1 arcsec = 3.26 LY http://sci2.esa.int/interactive/media/html/sec23p1.htm 4 Measuring Distances inside the MW • Parallax • Pulsating variables • Main sequence fitting for clusters • Calibrate with Hyades (moving cluster method = pp. 919-922) vt = vr tan φ µ= d= vt d vr tan φ µ What sets the parallax limit? Fuzzy images A field of stars …blurred by Earth’s atmosphere. Old limit for parallax distances: 20-50 parsecs 5 What sets the parallax limit? Fuzzy images Our Galaxy A field of stars 50 pc around Sun …blurred by Earth’s atmosphere. Old limit for parallax distances: 20-50 parsecs 30,000 pc Sharp Images from Space Our Galaxy A field of stars 50 pc around Sun Hipparcos Old limit for parallax distances: 20-50 parsecs 30,000 pc Hipparcos (1989-1993): 100-200 parsecs (1σ =1 milliarcsec = 1kpc) 6 Coming Attraction Our Galaxy A field of stars 50 pc around Sun 10 kpc around Sun GAIA spacecraft: Dec 2011 launch Old limit for parallax distances: 20-50 parsecs 30,000 pc Hipparcos (1989-1993): 100-200 parsecs (1σ =1 milliarcsec = 1kpc) GAIA: 10 kpc 7