* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Regions - Grand Saline ISD
Human ecology wikipedia , lookup
Geopolitics wikipedia , lookup
Biogeography wikipedia , lookup
Geomorphology wikipedia , lookup
Environmental determinism wikipedia , lookup
Royal Geographical Society wikipedia , lookup
Department of Geography, University of Kentucky wikipedia , lookup
Children's geographies wikipedia , lookup
Military geography wikipedia , lookup
{
World
Geo
Unit 1Lesson 1
Ms. Crone
2012
Think About the Local Geography:
Write the answer to each question on a sticky note.
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
11.
12.
Describe the landscape.
What is the weather like?
What language do most people speak? What other languages are
spoken?
Does the town grow crops to export to other parts of the state,
country, or world?
Where does our water source come from?
What is the history of our place? When was it founded?
What county does our place belong to?
What country does our place belong to?
In what continent is it located?
In what hemisphere is it located?
What is the relative location of our town/city?
How can we find out what the absolute location of our city is?
If we were to categorize
these questions into two
categories, what two
categories might we choose?
Physical Geography and
Human Geography
Physical
Geography
Human
Geography
Physical v. Cultural Geography
Physical Geography
Cultural Geography
Rocks/Minerals
Population/Settlements/Urbanization
Landforms
Economic and Political Systems
Animal and Plant Life
Transportation
Soils
Human Migration
Atmosphere/Climate/Weather
Social Systems
Environment
Recreation
Rivers/Oceans/Other bodies of
Water
Religion/Belief System
Physical Geography is the study of the Natural Landscape of the
Earth while Cultural Geography is the study of the Human
Landscape of the Earth.
©2012, TESCCC
So, What is Geography?
• Geography is the study of the physical and cultural
landscapes of Earth.
• The study of the physical and human landscape of the
Earth and the interaction between the two.
• It is the study of place and space.
• It is a science that deals with the description,
distribution, and interaction of the diverse physical,
biological, and cultural features of the earth's surface.
• Physical Geography, a subset of geography, is the study
of natural features and phenomena of the earth’s surface.
Human Geography is the study of the world, its people,
communities, and cultures.
Assignment:
Frayer Model:
Physical and Human
Geography
Get out a piece of paper and make
3 columns labeled:
Geography
Terminology
Tools
Regions
Geography
By the end of our lesson you will be able
to: Create a diagram about geography in
order to identify what geographers study,
what tools geographers use, and geography
terminology.
©2012, TESCCC
Geography Terminology (Vocabulary)
• Geography: The study of the physical and human
landscapes of Earth and the interaction between the two
(human-environment interactions).
• Physical Geography: study of processes and patterns (the
natural environment of the Earth)
• Human Geography: studies culture, population, economy,
etc.
• Geographers use many tools to study the Earth: Examples
maps, aerial photos, observation, surveys, satellites,
organize information into charts and graphs.
• Geographers also study location, place, region, movement
and the human-environment interactions.
• 3 types of Regions: formal, functional, perceptual
• Why is geography important in our everyday lives?
©2012, TESCCC
Geographers use tools to study the
interactions between the physical
and human landscapes of Earth.
CONCEPTS/BIG IDEAS: GEOGRAPHIC TOOLS,
GEOGRAPHY TERMINOLOGY (VOCABULARY),
PHYSICAL GEOGRAPHY, HUMAN GEOGRAPHY AND
REGIONS
©2012, TESCCC
GEOGRAPHIC REGIONS:
• Change over time.
• Do not have definite borders
– Are separated from or blend with other regions
by transition zones.
• Transition Zone: Gradual shift (not a sharp break) to
neighboring regions.
• Properties of Regions
– Area
– Boundaries
– Location
©2012, TESCCC
3 Types of Regions
• Formal Region: Counties, States, Countries
(political divisions); based on facts
(population/demographics, income, climate,
etc.)
• Example: Latin America, Europe
©2012, TESCCC
• Functional Region:
Metropolitan area; places
connected by transportation
or other means
• Organized around a set of
interactions and
connections between
places.
©2012, TESCCC
• Perceptual Region: Based on
human attitudes about a place
• Region in which people perceive
the characteristics of the region
in the same way.
• Example: American Midwest,
The South
©2012, TESCCC
Tools: Satellite Images
©2012, TESCCC
Tools: Using Twitter, this individual
created a map of people reporting
where their planes were landing
©2012, TESCCC
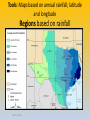
Tools: Maps based on annual rainfall; latitude
and longitude
Regions based on rainfall
©2012, TESCCC
Tools: observation and survey the land
Regions: West Texas: Cotton (trade)
©2012, TESCCC
Tools: data to determine population density
Regions based on Population
©2012, TESCCC
Tools: data collected based on imports and
exports
Regions for Trade
©2012, TESCCC
Regions based on physical features:
River Valley and Hill Country
©2012, TESCCC
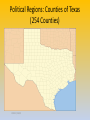
Political Regions: Counties of Texas
(254 Counties)
©2012, TESCCC
Regions: Physical Features
©2012, TESCCC
Regions: Religion
©2012, TESCCC
Now…
• Complete the diagram • On the back, write & answer
about geography in
these questions:
order to identify what
1. What is the study of
geographers study,
geography?
what tools geographers
2. What tools do geographers
use, and geography
use?
terminology.
3. What is a region?
4. What are the four
important types of regions?
5. How do physical
characteristics of places
affect people’s lives?
©2012, TESCCC