* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Slides for Smart Grid and Communication systems
Utility frequency wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
Public address system wikipedia , lookup
Distributed control system wikipedia , lookup
Electronic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Electric power system wikipedia , lookup
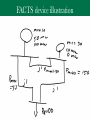
Wireless power transfer wikipedia , lookup
Control system wikipedia , lookup
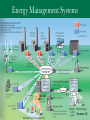
Distributed generation wikipedia , lookup
Fault tolerance wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Power over Ethernet wikipedia , lookup
Victor Bahl wikipedia , lookup
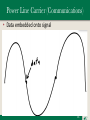
Immunity-aware programming wikipedia , lookup
Amtrak's 25 Hz traction power system wikipedia , lookup
Resilient control systems wikipedia , lookup
Electrical substation wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
Hendrik Wade Bode wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Power engineering wikipedia , lookup
EE 295 Smart Grid Communications Systems Dr. Paul Hines University of Vermont School of Engineering NY City, Nov. 9, 1965 © Bob Gomel, Life Back to what is smart grid • Coupling of informa?on networks (and semiconductors) with the power grid to make electricity work beHer 2 The OSI Model 3 The OSI Model 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Physical 1. 2. Method of encoding 1s and 0s Volts on a wire, shiOs in wireless frequency, op?cal signals 1. What system will we use to move the bits, and check them for errors. Bits are encoded into packets Data link 1. e.g, Ethernet. MAC addresses Network 1. Methods used to route packets between points. Router opera?ons. 1. 2. How do we get packets from source to des?na?on. TCP/IP (Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Prot) 1. How do we manage the opening/closing of source/des?na?on connec?ons. 1. How do the bits in the data translate into informa?on. For example ASCII, or UTF-‐16 1. 2. Applica?on-‐specific methods for moving end-‐to-‐end data HTTP, FTP, SMTP, SSH, etc. Transport layer Session Presenta?on Applica?on 4 Types of information/communication networks used in power systems • Applica?on(+) layer • Supervisory Control and Data Acquisi?on • Advanced Metering Infrastructure • Pilot relaying • Differen?al relaying • Physical layer • Microwave • Fiber-‐op?c • Wireless broadband • Middle layers • Mesh wireless networks • 3G/4G cellular systems • Proprietary vendor systems for RTU/EMS communica?ons 5 SCADA • Type of industrial control system • Purpose is to move sensor data to control center, and control data to devices 6 SCADA-connected sensors (representative) • Voltage transformers (magnitude and frequency) • Current transformers • Circuit breaker status indicators • BaHery status • Many alarms • Inter-‐area billing meters (an important one) • 1000s of Power plant sensors 7 SCADA-connected controls • Circuit breaker status!!! • Capacitors and synchronous condensers for reac?ve power (voltage control) • Some power plant controls (many have manual override, since plants have local operators) • FACTS devices 8 Flexible AC Transmission Systems • FACTS is defined by the IEEE as "a power electronic based system and other sta?c equipment that provide control of one or more AC transmission system parameters to enhance controllability and increase power transfer capability.” • Primarily: • High Voltage power electronic systems to dynamically control power flow on a transmission line, or voltage at a bus (or both) 9 FACTS device illustration 10 Energy Management Systems Siemens AG 11 barco.com 12 Distribution system communications • Automa?on/SCADA: • Typically using SCADA-‐like systems. Communica?ons are typically wireless and/or fiber 13 Billing system communications • Electromechanical meters + readers • Smart grid <1.0 (1970s) • 2-‐register EM meters for TOU rates • Direct communica?on with some devices (water heaters) • Automated Meter Reading • Near-‐distance communica?ons • Advanced Metering Infrastructure • 2-‐way, near real-‐?me communica?ons 14 2 most common AMI communications • Mesh wireless networks 15 Power Line Carrier (Communications) • Data embedded onto signal 16 Project discussion • Choose one area: • Genera?on/Transmission/Distribu?on/Demand • Choose a problem within this area • Do some reading. • Find a few recent (>2010) papers that look at this par?cular problem. Review them in some detail. (Like a page each) • Gather some data • EIA, IEA, ISO-‐NE, PJM, ERCOT, NREL EWITS/WWSIS, local u?li?es. • Do something interes?ng with the data, related to your area of interest (overlap with your primary research is high recommended) • Explain what you did, and what it means. • Quan?ty of wri?ng is not important. Evidence that you thought deeply about your problem is. 17