* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download AHM 244 PowerPoint
Industrial radiography wikipedia , lookup
History of radiation therapy wikipedia , lookup
Radiosurgery wikipedia , lookup
Positron emission tomography wikipedia , lookup
Medical imaging wikipedia , lookup
Technetium-99m wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear medicine wikipedia , lookup
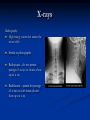
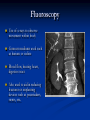
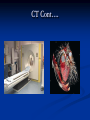
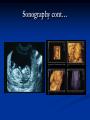
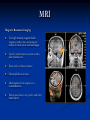
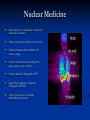
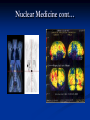
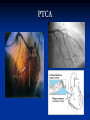
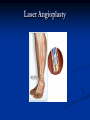
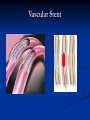
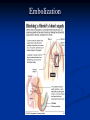
AHM 244 Introduction to Imaging Principles of Radiology X-rays (discovered late 19th century) Computed Tomography (CT scan) Sonography (ultrasound) Fluoroscopy Nuclear Medicine – used for diagnostic and therapeutic procedures Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) Positron Emission Tomography (PET) X-rays Radiography High energy waves that cannot be seen or felt Similar to photographs Radiopaque – do not permit passage of x-rays i.e. bones; show up on x-ray Radiolucent – permit the passage of x-rays i.e. soft tissue; do not show up on x-ray X-rays Patient Positioning Radiation Safety Can cause cellular or genetic damage 2-dimensional Minimize exposure Requires 2 exposures 90 degrees to each other Avoid unnecessary exams May require multiple positions and views Limit area of body exposed Review standard positions in handouts and in text Shield sensitive body parts Review exam sequencing in text Pregnancy status http://www.rtstudents.com/radiologypositions.htm Workers: Use shielding Wear dosimeter Diagnostic Procedures Mammography – x-ray examination of the breast Vital adjunct to biopsy Performed yearly after age 40 or sooner with history or suspicion Diagnostics cont… Contrast Studies Used to differentiate structures Introduced via IV, catheter, orally Iodine – blood vessels; if allergic to shellfish, do not use iodine! Barium – intestines and stomach Air - Joints Fluoroscopy Use of x-rays to observe movement within body Contrast mediums used such as barium or iodine Blood flow, beating heart, digestive tract Also used to aid in reducing fractures or implanting devices such as pacemakers, stents, etc.. Computed Tomography Cross-sectional group of xrays that target a specific site Tube circles the patient, computer analyzes to create the cross-sectional views Done with and without contrast Organs can be viewed from all angles CT Cont…. Sonography Ultrasound Non-invasive Uses high-frequency sound waves Creates cross-sectional still views or views in real time movement with help of a computer Used for heart function, abdominal and pelvic structure views and fetal visualization Sonography cont… MRI Magnetic Resonance Imaging Uses high-intensity magnetic fields (magnets), radio waves and computer analysis to create cross-sectional images Used for central nervous system studies, joint structure, etc. Done with or without contrast Claustrophobia is an issue Metal implants from surgeries is a contraindication Patient must remove any jewelry and other metal objects MRI cont… Nuclear Medicine Small amounts of radionuclides (radioactive materials) are injected These concentrate in specific areas of body Computer cameras detect particles and create an image Used to study thyroid, brain, lungs, liver, spleen, kidney, bone and breast Positron Emission Tomography (PET) Single Photon Emission Computed Tomography (SPECT) Assists with diagnosis of cellular abnormalities esp. cancer Nuclear Medicine cont… Interventional Radiologic Procedures Designed to treat specific disease conditions – helps patients avoid surgeries, lifesaving Percutaneous Transluminal Coronary Angioplasty (PTCA) – balloon angioplasty; used to enlarge lumen of blocked artery Laser Angioplasties – use lasers to remove deposits in vessels Vascular Stents – plastic or wire tubes inserted into a constricted vessel to open it; this procedure is guided by fluoroscopy Embolizations – artificially stop bleeding from a blood vessel or reduce blood flow to a diseased area of an organ PTCA Laser Angioplasty Vascular Stent Embolization Radiation Therapy Major force in fight against cancer Uses high-energy radiation to kill cancer cells Used in conjunction with surgery and chemotherapy (drug therapy) Precise and carefully planned by radiation oncologist (MD specializing in radiology) Each treatment must be identical to a specifically defined area of the body Side effects: weight loss, hair loss, loss of appetite, skin changes, digestive system disturbances Patient Education & Preparation Help alleviate anxiety Calm fears Explain procedures Explain preparation – different for each test from no prep to liquid diet and laxatives Assist as needed Post procedure education Handling and Storage of Radiographic Films Protect unexposed films from extremes of temperature and light Exposed films kept in protective sleeves Maintain patient confidentiality per HIPAA Correct labeling of patient films Films obtained on site remain part of patient record – films belong to the site that performed the procedure; can be signed out by patient or sent by courier to specialist or PCP Digital films can be kept in the EMR Written summary sent to providers of patient care Teleradiology – computed imaging and information systems; many places use (PACS) Picture Archiving and Communication System to store films on computers Can outsource films this way to other countries even for a radiologist to read films; consults with specialists from around the world is possible with this system and in rural areas