* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download PDF
History of geometry wikipedia , lookup
Surface (topology) wikipedia , lookup
Multilateration wikipedia , lookup
Tessellation wikipedia , lookup
Euler angles wikipedia , lookup
Line (geometry) wikipedia , lookup
Integer triangle wikipedia , lookup
Rational trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
History of trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Pythagorean theorem wikipedia , lookup
Trigonometric functions wikipedia , lookup
Perceived visual angle wikipedia , lookup
List of regular polytopes and compounds wikipedia , lookup
Approximations of π wikipedia , lookup
Euclidean geometry wikipedia , lookup
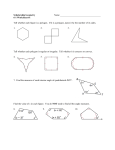
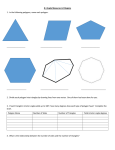
polygon∗ Wkbj79† 2013-03-21 23:55:37 A polygon is a simple, closed path that lies on a plane and is composed entirely of line segments. In other words, if someone were to walk on a polygon, then the person would end up back where he started; moreover, if a person walks on a polygon so that he travels exactly once around the polygon, then the path never crosses itself, and the person is either walking along a line or turning. Below are some examples of polygons: A side of a polygon is a line segment on the polygon that is of maximal length. In other words, any line segment that contains a side of a polygon and has a greater length than that side is not entirely on that polygon. A vertex of a polygon is an endpoint of a side of the polygon. Note that each vertex of a polygon is simultaneously the endpoint of exactly two adjacent sides of the polygon. A polygon with n sides is called an n-gon. For small n, there are more traditional names: ∗ hPolygon1i created: h2013-03-21i by: hWkbj79i version: h40006i Privacy setting: h1i hDefinitioni h51-00i † This text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share-Alike License 3.0. You can reuse this document or portions thereof only if you do so under terms that are compatible with the CC-BY-SA license. 1 number of sides 3 4 5 6 7 8 10 name of polygon triangle quadrilateral pentagon hexagon heptagon octagon decagon In spherical geometry, polygons with only two sides exist. They are called biangles. The perimeter of a polygon is the sum of the lengths of its sides. An interior angle of a polygon is the measure of an angle formed by two adjacent sides such that the angle is measured with respect to the interior of the polygon. For each polygon in the picture below, the interior angles are marked in blue: Note that the measure of any interior angle of a polygon is strictly between 0◦ and 360◦ and is not equal to 180◦ . We have the following criterion for a polygon to be convex: Theorem. A polygon is convex if and only if each of its interior angles has a measure that is strictly less than 180◦ . The angle sum of a polygon is the sum of the measures of its interior angles. In Euclidean geometry, the angle sum of an n-gon is exactly 180(n − 2)◦ . An exterior angle of a polygon is any angle that forms a linear pair with an interior angle of a polygon. In the picture below, all exterior angles of the triangle are marked in blue: 2 For a more rigorous treatment of polygons, see this entry. 3