* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Download
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
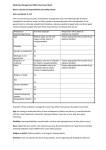
Regulation of prices or reimbursement prices of medicines, a) 2013 Scope of price regulation Method(s) Belgium Maximum ex-factory price is set for listed medicines. Prices of innovative drugs set with a premium over comparators. Prices of less innovative drugs set using international benchmarking and therapeutic referencing. Denmark No price regulation at market entry, but periodically price cap agreements between the Ministry of Health and the association of pharmaceutical companies. International benchmarking for hospital drugs (Commitment of the industry). France Maximum statutory price for medicines listed for outpatient care and for a list of expensive hospital medicines, set at the time of listing. International benchmarking for most innovative drugs; Internal/therapeutic referencing for less innovative ones. Germany Since 2011: Statutory price negotiated after market entry RP for clusters of equivalent products ( ATC 4, 5). Therapeutic referencing (and international benchmarking). Italy Maximum statutory ex-factory price for outpatient reimbursed medicines and for expensive hospital medicines, set at the time of listing. Therapeutic referencing. Netherlands Maximum wholesale price for outpatient prescription-only medicines (listed or not) and expensive hospital drugs. RP for groups of interchangeable products (ATC 4 & 5). International benchmarking. Spain Maximum ex-factory prices for reimbursed medicines. International benchmarking and therapeutic referencing. Sweden In order to be reimbursed, the manufacturer must propose a price at which the drug will be considered cost-effective. Purchase and retail prices are regulated. United Kingdom No direct price control, but possible price agreement following NICE negative recommendation based on economic assessment. In case of price negotiation, the ICER is used to determine the acceptable price. Norway Maximum pharmacy purchase price set for all prescriptiononly medicines, at the time of market entry. International benchmarking and therapeutic referencing for reimbursement price. Australia Maximum ex-factory price is set for listed medicines. RP for classes of interchangeable products. Therapeutic referencing and cost plus. Canada At Federal level: Maximum ex-factory price for all patented Medicines. Provinces and Territories level: Maximum prices set for drugs covered by public drug plans. Federal level: International benchmarking for most innovative drugs and therapeutic referencing for less innovative ones. Japan Reimbursement price for medicines included in the positive list. Therapeutic referencing. Korea Maximum reimbursement price. Assessment of the reimbursement committee, international benchmarking; Budget impact; R&D costs for drugs launched first in Korea. Drug plan level: Therapeutic referencing. (a) This table refers to price regulation potentially applicable to on-patent products. It only refers to Reference Prices (RP) policies when they have the potential to influence the price of new products (i.e. when RP are not limited to clusters of generic equivalents but can include patented products). Source: Value in Pharmaceutical Pricing, OECD Health Working Papers No. 63, 2013, p. 21. Page 1 of 1


![My_Body[1] - Junior2TopicWiki](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008060165_1-be31cd2568d5e2c9fee6ce67732b07b4-150x150.png)