* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Introduction to the Human Body
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
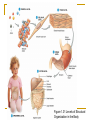
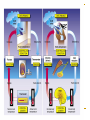
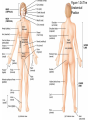
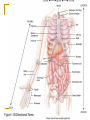
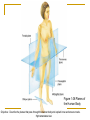
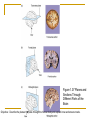
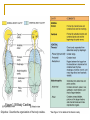
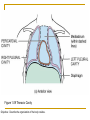
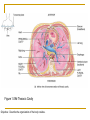
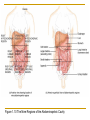
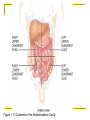
Introduction to the Human Body Chapter 1 Organization of the Human Body Warm Up Questions 1. 2. 3. Write a brief answer to these questions in your notebook. Try to answer the questions even if you are not sure. What is the difference between anatomy and physiology? What is a cell? What is an organ? Chapter Objectives Describe the levels of structural organization that compose the human body. Briefly explain how body systems relate to each other. Define the life processes of the human body. Define homeostasis and describe its importance in health and disease. Describe several planes that may be passed through the human body and explain how sections are made. What are we studying? I. What we are studying A. Anatomy—study of structure and relationships among structures. B. Physiology—study of body functions. C. “Form and Function” Organization II. Levels of Structural Organization A. B. C. D. E. F. Chemical level Cellular level Tissue level Organ level System level Organism level Figure 1.01 Levels of Structural Organization in the Body Organ Systems III. Organ Systems of the Human Body A. B. C. D. E. F. G. H. I. J. K. Integumentary system Skeletal system Muscular system Nervous system Endocrine system Cardiovascular system Lymphatic and Immune system Respiratory system Digestive system Urinary system Reproductive system How Body Systems Work Together Ex: The Integumentary system (skin, hair, and nails) is involved in the production of vitamin D, which the body needs in order to use calcium properly. The calcium is used for the growth and development of bones. Life Processes IV. Processes Essential to All Life A. B. C. D. E. F. G. Metabolism Responsiveness Movement Growth Differentiation Reproduction Homeostasis Warm Up #2 How are organs, cells, and tissues related? How is differentiation different from growth? Homeostasis V. Homeostasis A. The condition in which the body’s internal environment remains within certain physiological limits B. May be disturbed by any stimulus that creates an imbalance in the internal environment C. Related to health and disease Feedback Systems VI. Feedback system A. A cycle of events in which information about the status of body conditions is continually monitored and fed back to a central control region. B. Parts of feedback system: 1. 2. 3. Receptor Control center Effector Feedback Systems C. Types of feedback 1. Negative Feedback—reverses a change a. b. 2. Works towards homeostasis Ex: BP, temperature, glucose levels Positive Feedback—reinforces a change a. b. Works away from homeostasis Ex: Child birth and lactation Figure 1.03 Homeostasis of Blood Pressure Warm Up #3 Try to guess the anatomical/medical term for: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Nose Navel (bellybutton) Finger Hand Wrist Thigh Foot Buttock Anatomical Terms VII.Anatomical terminology A. Anatomical position B. 5 Body Regions 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Head Neck Trunk Upper Limb Lower Limb C. Many regional terms (Fig 1.04) Figure 1.04 The Anatomical Position Directional Terms D. Directional Terms 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Superior (cephalic) – Inferior (caudal) Anterior (ventral) – Posterior (dorsal) Medial – Lateral Proximal – Distal Superficial – Deep Intermediate Figure 1.05 Directional Terms Planes and Sections E. Planes / Sections 1. Sagittal a. Midsagittal b. Parasagittal 2. Frontal 3. Transverse 4. Oblique Objective: Describe the planes that pass through the human body and explain how sections are made. Figure 1.06 Planes of the Human Body Objective: Describe the planes that pass through the human body and explain how sections are made. Figure 1.07 Planes and Sections Through Different Parts of the Brain Objective: Describe the planes that pass through the human body and explain how sections are made. Cavities F. Body cavities 1. Dorsal a. b. Cranial Vertebral 2. Ventral – split by the diaphragm a. Thoracic i. ii. iii. b. Pleural Mediastinum Pericardial Abdominopelvic i. ii. Abdominal Pelvic Objective: Describe the organization of the body cavities. Figure 1.08 Body Cavities Objective: Describe the organization of the body cavities. Figure 1.09 Thoracic Cavity Objective: Describe the organization of the body cavities. Figure 1.09b Thoracic Cavity Objective: Describe the organization of the body cavities. Abdominopelvic Regions G. Regions of the abdominopelvic region 1. 9 region system a. Used by anatomists 2. 4 quadrant system a. Used in the medical field b. Divide cavity at the umbilicus Figure 1.10 The Nine Regions of the Abdominopelvic Cavity Figure 1.11 Quadrants of the Abdominopelvic Cavity