* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Circulatory System PP
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
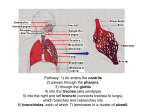
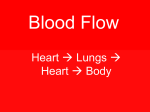
CIRCULATORY SYSTEM CARDIOVASCULAR/CARDIAC NATURAL AGING CHANGES Heart muscle weakens: heart pumps with less force 2. Blood flow decreases (reduced cardiac output/volume): Older people tire easily 3. Heart size increases: Heart has to work harder 4. Blood vessels harden and lose elasticity with age; they become more narrow with fatty deposits: diminished blood flow/higher BP 1. HEART Muscle that pumps blood and O2 to cells. Located L of sternum between 2nd and 5th ribs. 3 Layers Endocardium Myocardium Pericardium HEART IS REALLY “2” HEARTS IN ONE…. LEFT SIDE- PUMPS OXYGENATED BLOOD TO BODY RIGHT SIDE – PUMPS UNOXYGENATED BLOOD TO LUNGS 4 CHAMBERS Heart Diagram Handout What separates the sides and the chambers??? SEPTUM VALVES “Gates” that control the flow of blood in 1 direction: Mitral Valve- LA and LV Aortic Valve- LV and aorta Pulmonary Valve- pulmonary artery and RV Tricuspid Valve- RA and RV BLOOD VESSELS Arteries- largest blood vessels that carry blood AWAY from heart and carry only oxygenated blood Veins- Smaller blood vessels that carry blood TO the heart and carry only unoxygenated blood. Capillaries- microscopic blood vessels that have mixed blood and help exchanges gases, nutrients and waste products. They connect arteries and veins. MAIN VESSELS OF THE HEART 1. Aorta- largest artery, sends blood from heart to rest of body. 2. Coronary Arteries- arteries that surround heart and carry O2 to heart muscle and tissues. AORTA MAIN VESSELS OF THE HEART 3. Superior/Inferior Vena Cavas- 2 large veins that bring unoxygenated blood from body to R side of heart 4. Pulmonary Artery- carries unoxygenated blood to lungs from RV 5. Pulmonary Veins- carries oxygenated blood from lungs to heart These are the exceptions to the artery/vein rule in terms of oxygenated and unoxygenated blood. WHY??? SUPERIOR/INFERIOR VENA CAVAS These are the exceptions to the artery/vein rule…WHY??? 4. Pulmonary Artery- carries unoxygenated blood to lungs from RV 5. Pulmonary Veins- carries oxygenated blood from lungs to heart These are the exceptions to the artery/vein rule in terms of oxygenated and unoxygenated blood. WHY??? Physiology: How blood flows through the heart Pulmonary Circulation Right sided blood flow: R side of heart pumps blood to lungs Pulmonary Circulation Systemic Circulation Left sided blood flow: L side of heart pumps blood to the body systems Systemic Circulation How Does the Heart Beat?? Cardiac Cycle: Mechanical and electrical events that occur between 1 heart contraction and the next. Mechanical- the actual relaxation and contractions of the heart chambers Electrical- the conduction system that involves special neuromuscular tissue that sends out electrical impulses within the heart to “tell” the heart cells to contract. Mechanical Events 1. 2. 3. Atria relax and fill with blood as ventricles contract, forcing blood out of the heart and through the aorta. Ventricles relax allowing blood to flow into them. Cycle repeats itself Electrical Events/Conduction System How Does This Happen? The rate and rhythm of the cardiac cycle is controlled by the conduction system. This system is made up of special neuromuscular tissue that sends out electrical impulses that “tell” the heart muscle cells to contract using a complex set of electrical events. Electrical Events/Conduction System 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. RA has special area in upper part of chamber called S-A node. (“Natural Pacemaker”) Atria contract S-A node impulses spread to bottom of RA to the A-V node A-V node spreads to septum to the Bundle of His Bundle of His spreads to Purkinje Fibers which reach deep into the ventricle walls. Ventricles contract http://highered.mcgr awhill.com/sites/007249 5855/student_view0/ chapter22/animation __conducting_syste m_of_the_heart.htm l What happen when a person’s “natural pacemaker” doesn’t work?? EKG (electrocardiogram) BLOOD Blood carries nutrients and O2 to cells. Red Blood Cells (RBC) Formed in bone marrow and carries O2 Erythrocytes b. White Blood Cells (WBC) Defends body against infection Leukocytes c. Platelets- in charge of blood clotting Thrombocytes d. Plasma- liquid portion of blood. Antibodies, nutrients, gases and waste products. a. Functions of Blood 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Carries O2 from lungs to cells Carries CO2 from cells to lungs Absorbs nutrients Carries waste products from cells to kidneys Helps regulate body temperature through: constriction/dilation Maintains fluid balance