* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Presentation
Transformation optics wikipedia , lookup
Mathematical descriptions of the electromagnetic field wikipedia , lookup
Maxwell's equations wikipedia , lookup
Metamaterial antenna wikipedia , lookup
Lorentz force wikipedia , lookup
Metamaterial wikipedia , lookup
Negative-index metamaterial wikipedia , lookup
Magnetotellurics wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnetic field wikipedia , lookup
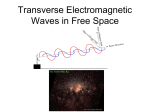
Electromagnetic Waves Electromagnetic Waves • Electromagnetic Waves – Made by vibrating electric charges – Can travel through space where matter is not present – We cannot hear them, but can feel and experience their effects • Vibrations of Electric Charges Electromagnetic Waves • Electromagnetic Waves – Travel by transferring energy between vibrating electric and magnetic fields – Like some mechanical waves, electromagnetic waves are considered transverse Electric and Magnetic Fields • Electric Fields – Electric field surrounds all electric charges – Electric Field Lines • Magnetic Fields – Magnetic field surrounds all magnets – Magnetic Field Lines Electric and Magnetic Fields Making Electromagnetic Waves • Electric charges vibrate • Electric field around it changes • The magnetic field around the charge changes • Both fields change continuously creating the wave Making Electromagnetic Waves • Electromagnetic Waves • Making of Electromagnetic Wave Properties of Electromagnetic Waves • All objects contain charged particles • All objects emit electromagnetic waves • Radiant Energy – Energy carried by EM waves Properties of Electromagnetic Waves • Wave speed – Travel at 300,000 km/s in the vacuum of space – Called “speed of light” – Usually travel slowest in solids – Travel fastest in gases Properties of Electromagnetic Waves • Wavelength and Frequency – Crest to crest – As frequency increases, wavelength decreases Waves and Particles • Em waves – Can behave like particles – This is why energy depends on frequency, not amplitude • Photons – Particles of electromagnetic waves – Carrier of electromagnetic radiation Electromagnetic Spectrum • Frequency range – Wide variety of frequencies – Entire range is known as the electromagnetic spectrum Radio Waves • Lowest frequency on the spectrum • Can’t see or hear • Functions: – Carry radio waves – Used by some cell phone towers – RADARs (Radio Detecting and Ranging) – MRIs Microwaves • Little shorter wavelengths than radio waves • Functions – Cell phone towers – Satellite signals – Microwave ovens Infrared Waves • Shorter wavelengths than radio or microwaves • Functions – Transmits thermal energy – Remote controls – CD-ROMs are read by infrared waves – Infrared imagery Visible Light • Only part of the spectrum we can see • ROY G BIV Ultraviolet Waves • Can enter skin cells • Overexposure can cause skin damage and cancer • UVA and UVB waves • Functions – Kills bacteria on objects such as food or medical supplies – Make some materials fluoresce (CSI) X-Rays • Can penetrate skin • Functions – X-rays of bones and teeth – At airport to screen luggage and other devices Gamma Rays • Shortest wavelength of the spectrum • Functions – Radiation therapy in which gamma rays kill diseased or cancerous cells Radio Communication • Radio Transmission – Each station assigned a certain frequency – Carrier Wave • Specific frequency of the electromagnetic wave assigned to a station AM Radio • AM Radio – AM = amplitude modulation – Broadcasts by varying the amplitude of the carrier wave – AM carrier range from frequencies of 540,000 to 1,600,000 HZ FM Radio • FM Radio – FM = Frequency Modulation – FM broadcasts by changing the frequency of the carrier wave – Frequencies range from 88 million to 108 million Hz