* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Sound Waves
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
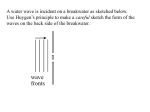
ICS Physics End of Physics Review 9-12 Science Std: Phys 3, 4, 5 Topic: The Right Tool You must choose the right equipment to get the best scientific readings To record sounds you would use a microphone To measure earthquake energy you would use a seismograph To measure electrical charge, current or voltage you would use a Electrometer, ammeter or Voltmeter To measure temperature you would use a thermometer Std I&E 1a Topic: The Right Tool Once you have your readings, you need to organize and compare your readings You can start by putting the data into a table You can take the data from the table and put it in a spreadsheet And once you put it into the spreadsheet, you can look at the data on a graph Std I&E 1a Topic: Entropy* Entropy is a physics term that describes: The amount of disorder is in a system Low Entropy means something is very organized, clean and everything is behaving nicely High Entropy means something is disorganized, messy and everything is behaving badly It is a fact that Entropy is always increasing And things will move to a less orderly state Std 3f Topic: Wave Types Waves have 2 different shapes The first type is a transverse wave EM Waves are transverse waves We made transverse waves when we were shaking a slinky The second type is a longitudinal wave Sound waves are longitudinal waves Std 4b Topic: Wave Motion As a wave moves through something it makes parts of the material move As a transverse wave moves by: It makes the material (or anything that is on it) move up and down Watch the little black dot as the transverse wave goes past it If you were on a surf board on the ocean The transverse wave would make you move up and down Std 4a Topic: Sound Waves Sound waves are longitudinal waves Sound waves need a material (medium) to travel through Sound waves move through the medium by having molecules bump into each other When the molecules bump into each other, they transfer the wave energy from one molecule to the next in a direction parallel to the direction of the sound Std 4b Topic: Speed of Sound Several things affect the speed of sound in materials Temperature: Higher temperature = sound moves faster Sound moves faster in the desert heat than the artic cold Density: Higher density = sound moves faster Sound moves faster in water or steel than in air Flexibility: Lower flexibility = sound moves faster Sound moves faster in a stiff plastic pole than a soft plastic toy Std 4d Topic: EM Wave Spectrum Electromagnetic Waves are a special kind of wave Depending on the frequency (and the wavelength) of the wave, we have special names for the waves Some of the special names are radio waves, microwaves, ultraviolet waves, x-rays and All of these waves are transverse waves and visible light can move without going through a material (medium) Std 4e Topic: EM Wave Speed Electromagnetic waves are special for many reasons They travel faster than anything else known today In a vacuum (out in space) they all travel at the same speed They go at the speed of light And the speed of light is: 3 x 108 meters per second Std 4e Topic: Refraction Refraction is a bending of waves caused by a change in the speed of the wave This can be caused by either: Going from one material into another material with a different wave speed Or a change in the material that causes a change in the speed of the wave Std 4f Topic: Index of Refraction You can measure how much a wave will bend using the Index of Refraction (n) The Index of Refraction is a measure of how much the velocity changes in a medium For light, the Index of Refraction is the speed of light in a vacuum (c) divided by the speed of light in the material (v) The bigger the Index of Refraction, the slower the wave speed in the material Std 4e Topic: Index of Refraction If you compare the Index of Refraction for 2 materials… You can tell how much the wave is going to bend If the indices of refraction are similar (numbers are close to each other) the wave will bend a little If the indices of refraction are not similar (numbers are far apart) the wave will bend a lot Std 4f Topic: Doppler Effect The Doppler Effect is an apparent change in the frequency of a wave The change is caused by relative motion between the source and the observer If a sound wave is coming towards the listener, the pitch goes up If the sound is going away from the listener, the pitch goes The bigger the difference in down speed between the sound If the sound is not getting closer and the listener, the or farther away from the bigger the change in pitch listener, the pitch doesn’t change Std 4f Topic: Sound Beats When sound waves add together it is called interference If two sound frequencies are close together, when they add you hear sound beats The number of beats you hear depends on the difference in the sound frequencies The smaller the difference, the smaller the beat frequency The larger the difference, the larger the beat frequency If there is no difference, you don’t hear any beats Std 4f Topic: Sound Limits We know that sound is a longitudinal wave And that all waves (except for EM waves) need to travel through something (a medium) So sound waves need a medium to travel through (air, water, etc.) If you don’t have a medium, sound waves can’t travel That is why sound won’t travel in a vacuum (in a place without any air) And in space, no one can hear you scream…… Std 4f Topic: Wave Energy All waves transfer energy when they move Some waves need a medium to move, some don’t If a wave needs a medium, the medium ends up in the same place where it started after the wave goes past We saw this when we did the lab with the string telephones The sound waves moved through the string but it didn’t move the string Std 4a Topic: Wave Energy So what happens to this energy? Sound waves can cause things to move And when things move they rub against each other When they rub against each other, friction causes them to heat up So if you had a loud enough sound wave, you could heat up water! Std 4d Topic: Electrostatic Force Electrically charged particles can be either positive (+) or negative (-) Charged particles can push or pull on each other (force) The amount of force depends on 2 things: The amount of charge (+) or (-) – more charge = more force The distance between the charges – more distance = less force If the distance gets big enough, the force goes to 0 (goes away) Std 5e Topic: Electrostatic Force When you have 2 charges, they can either pull or push on each other If the charges are the same (alike) they push against each other If the charges are opposite (different) they pull towards each other So remember that opposites attract and alike repel Std 5e Topic: Electrostatic Force When we draw Electrostatic Forces, we show the amount of force a special way If we draw a small number of lines we have a small force If we draw more lines we have a bigger force If we draw many lines we have a big force So more lines = more force And the closer the lines are to each other = the stronger the force is Std 5m Topic: Electrostatic Force How much does the force change? This is the equation for the amount of force between charges The amount of charge = q The distance between the charges = r 2x the charge = 2x the force 2x the distance = 1/4x the force 3x the charge = 3x the force 3x the distance = 1/9x the force A change in the distance between the charges has more affect because the distance is squared in this equation Std 5e Topic: Right Hand Rule When an electric current goes through a wire It makes a magnetic field around the wire The direction of the field depends on the Right Hand Rule Wrap your right hand around the wire Point your thumb in the direction of the current Your fingers wrap in the direction of the magnetic field You can see this if you put a compass next to the wire Std 5h Topic: Magnetic Induction When you move a magnet next to a wire… The magnet will induce (or make) a voltage in the wire When you have a voltage in a wire that is part of a electric circuit… Electric current will flow through the circuit So if you move a magnet next to wires in an electric circuit, you will cause electric current to flow Std 5h Topic: Transistors When transistors were invented in the 1940’s They made many changes in electronics They could be made cheaper They could be made smaller And they used less energy With all these changes they quickly replaced bigger vacuum tubes Std 5d Topic: Transistors Transistors are designed to do 2 things…. The 1st is to be a switch to turn on and off current The first function is used in a computer The 2nd is to add energy to a weak input signal The second function is used in an amplifier Std 5d Topic: Transistors Transistors have changed modern electronics because: They can amplify small inputs into larger output signals They don’t break easily like old vacuum tubes They are smaller than vacuum tubes So – the computers, radios and cell phones we use today are much smaller and tougher Std 5d Topic: Plasma Plasma is the 4th state of matter (solid, liquid, gas…) It happens when you take a gas and either heat it to a very hot temperature or put a large voltage on it You can find plasmas in the sun (very hot) or in a fluorescent light bulb (large voltage) A plasma is atoms of gas that have had their electrons pulled off so they are made of Plasma is like a positive ions and free electrons gas, but a gas Because they have ions and can’t conduct electrons they are good electricity electric conductors Std 5i