* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Exploring Earth`s Surface
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
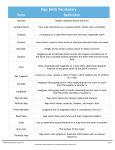
Mapping Earth’s Surface Table of Contents Exploring Earth’s Surface Models of Earth Topographic Maps 8.1 Vocabulary •Topography •Elevation •Relief •Landform •Plain •Mountain •Mountain range •Plateau •Landform region What does the topography of an area include? •The topography of an area includes the area’s elevation, relief, and landform. •Elevation is the height above sea level at a specific point on the Earth’s surface. •Relief is the difference between the highest point and lowest point of a region. •Landform is created by the processes that shape the Earth’s surface. Exploring Earth’s Surface Lewis & Clark’s Journey The route of the Lewis and Clark expedition crossed regions that differed greatly in elevation and relief. Which are the highest and lowest points on their route? Exploring Earth’s Surface What are the main types of landforms? Landforms Plains, mountains, and plateaus are three of the many landforms that make up the topography of Earth’s surface. Plains •A plain that lies along a seacoast is called a coastal plain, with low elevation and low relief and extends around the eastern and southeastern shores. •A plain that lies away from the coast is called an interior plain, with varying elevations. The broad interior plains are called the Great Plains. Mountains •Mountains have high elevation and high relief. •Mountain ranges and mountain systems in a long, connected chain form a larger unit called a mountain belt. •The Rocky Mountains stretch down the western side of North and South America. Plateaus •A plateau will have high elevation with a more or less level surface. •A plateau is rarely perfectly smooth on top. Streams and rivers may cut into the surface creating varied elevation. Exploring Earth’s Surface Landform Regions All of the land in one major landform region tends to have much in common. Highest elevation in US is Mt. McKinley (6,194m) and lowest elevation Death Valley (-86m). Models of Earth Measuring Earth What science skills did Eratosthenes use to estimate the Earth's circumference? 8.2 Vocabulary •Globe •Map •Map projection •Symbol •Key •Scale •Degree •Equator •Hemisphere •Prime meridian •Latitude •Longitude How do maps & globes represent Earth? •Both maps and globes show the shape, size, and position of features on Earth’s surface. •Maps are 2-D representations while globes are 3-D representations and always represent the whole Earth. •Maps and globes are drawn to scale and use symbols to represent features on Earth’s surface. •To show Earth’s curved surface on a flat map, cartographers use map projection. Map projection •While trying to portrait Earth’s features on to a map, continents, oceans, & islands may have distorted shapes and sizes depending upon the type of projection used. •A Mercator projection is based on Earth’s features projected onto a cylinder that encircles the Earth at the equator. •The size and shape of landmasses at the poles are more distorted, but are more accurate near the equator.. Models of Earth Mercator Projection A Mercator projection is based on a cylinder with grid lines that has been flattened. What’s in a map? •A map may show the whole Earth or just part of the earth. •A map uses symbols explained in a key, and usually has a compass rose to show direction. Often north is shown at the top of the map. •A scale is often given as a ratio showing the relationship between the distance on the map to the distance on the Earth’s surface. Models of Earth What’s in a Map? A map uses symbols explained in a key, and usually has a compass rose to show direction. A scale is often given as a ratio showing the relationship between the distance on the map to the distance on the Earth’s surface. Google Maps How is distance measured in degrees? • To help find places on the Earth’s surface, a grid is created that curves to cover the entire planet. • Distances on Earth are measured in degrees from the equator and the prime meridian. • On Earth’s surface, degrees are a measure of an angle formed by lines drawn from the center of Earth to points on the surface. • To locate points precisely, degrees are further divided into smaller units called minutes and seconds. • There are 360º in a circle, 60’ (minutes) in a degree, 60” (seconds)in a minute Models of Earth Degrees Around Distances around a circle are measured in degrees, minutes, and seconds. Equator •Half way between the north pole and south pole is the imaginary line that circles the Earth at the widest part. •It divides the Earth into the Northern and Southern hemispheres. Prime Meridian •Another imaginary line that makes a half circle from the North Pole to the South Pole through Greenwich, England is the Prime Meridian. •Places west of the Prime Meridian are in the Western Hemisphere while to the east is the Eastern Hemisphere. •On the other “side” of the Prime Meridian is the International Date Line. Models of Earth Equator and Prime Meridian The equator and prime meridian divide Earth’s surface into hemispheres. What are latitude and longitude? •The grid on the Earth is created by lines of latitude and longitude. •The equator is the starting line for measuring latitude, 0° and measures to each pole, 90°N at the North Pole, 90°S at the South Pole. •Each line of latitude is parallel to one another, about 111km apart. •There are 360° of longitude that run from north to south meeting at the poles. •Each line is about 111km apart at the equator, but at the poles, the lines come together to 0km. •The Prime Meridian, which is the starting point, is at 0° and numbered to 180° at the International Date Line. Models of Earth Latitude and Longitude Points on Earth’s surface can be located using the grid of latitude and longitude lines. •The location of any point on Earth’s surface can be expressed in terms of the latitude and longitude lines that cross a that point. •Each longitude line crosses the latitude lines, including the equator, at a right angle. •Lines of latitude (N-S) are given first, then lines of longitude (E-W). Models of Earth Interpret Maps Every point on Earth’s surface has a particular latitude and longitude. 8.3 Vocabulary •Contour line How do maps who topography? •Topographic maps portray the land as if you were looking down on it from above. •Contour lines connect points of equal elevation and show the relief and slope of the ground. •The change between contour lines is the contour interval and given in the map key. •Every fifth contour line is an index contour, a darker line to help read the elevation. Topographic Maps To read a topographical map, begin at the labeled index contour. Then count the number of contour lines up or down to the feature. Closely spaced lines indicate steep slope, a change of height over a short distance. Widely spaced lines indicate gentle slopes. A closed loop indicates a hilltop, but with dashes inside, indicates a depression in the ground. Vshaped lines pointing downhill indicate a ridge line while pointing uphill indicate a valley. A stream may flow toward the open end of the V. Topographic Maps Mapping a Mountain How is a map a model of Earth? Topographic Maps Topographic Map What feature is shown by this map?