* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 1 Looking at the Earth
Early world maps wikipedia , lookup
Iberian cartography, 1400–1600 wikipedia , lookup
History of cartography wikipedia , lookup
History of navigation wikipedia , lookup
Cartographic propaganda wikipedia , lookup
Location-based service wikipedia , lookup
Map database management wikipedia , lookup
Map projection wikipedia , lookup
Military geography wikipedia , lookup
History of longitude wikipedia , lookup
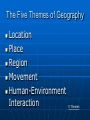
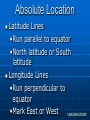
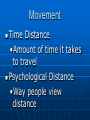
Chapter 1 Looking at the Earth The Five Themes of Geography Geography: the study of the distribution and interaction of physical and human features on the earth Why Study Geography The Five Themes of Geography Location Place Region Movement Human-Environment Interaction 5 Themes Location Where is it? Absolute Location •Exact place on earth where a geographic feature is found •Hemispheres: North, South, East, West •Equator •Prime Meridian Absolute Location Latitude Lines •Run parallel to equator •North latitude or South latitude Longitude Lines •Run perpendicular to equator •Mark East or West Longitude/Latitude Location Relative Location •Describes how a place is related to its surrounding environment Place What is it like? Includes physical features and cultural characteristics Description of a place may change over time Region How are places similar or different? Formal Regions •Defined by limited number of related characteristics U.S.A and Canada, Latin America, South Asia Region Functional Regions •Organized around set of interactions and connections between places City and its suburbs Region How are places similar or different? Perceptual Regions •People perceive the characteristics of region in the same way -American Midwest Human-Environment Interaction How do people relate to physical world? Learn to use what environment offers them Change environment to meet their needs Human-Environment Interaction Learn to live with certain aspects of environment People respond to same environment in different ways Movement How do people, goods and ideas move from one location to the other? Linear Distance •How far across the earth something travels Movement Time Distance •Amount of time it takes to travel Psychological Distance •Way people view distance The Geographer’s Tools Maps, globes, and data 3 kinds of maps •General reference map •Thematic map •Navigation map Countries of the World