* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Geographer`s World
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
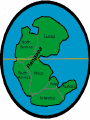
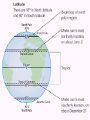
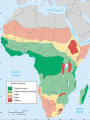
Geographer’s World Chapter 2 A. One World • Pangaea (Alfred Wegener) – Super continent where all the continents were connected • Tectonic Plates – Caused the continents to move and drift apart • Creates earthquakes and volcanoes B. Five Themes • 1) Location • Absolute Location – Exact spot on earth where a place is found • Also known as site • Latitude – Lines that run parallel to the equator • Show distant north and south of the equator • Longitude – Lines that run between the North and South Pole • Show the distance east and west of the prime meridian Where in the World? Australia • Relative Location – Location in relation to other places • Also known as situation • Question: Why is Stanton located where it is today? • 2) Place • What a place is like • Type of climate, landform, and body of waters, and animals of a place Rio de Janeiro, Brazil • 3) Region – Places that have physical and human characteristics in common • Geographers divide the world into regions to make studying it easier • Natural Regions – Region determined by plant, animal, and climate • Cultural Regions – Region determined by language, custom, and traditions • 4) Movement • Migrate – To move from one country to another • When people move to new places they bring their culture with them • Change the place they move into Push and Pull Factors • Push Factors – Problems in one place to force people out – Poverty, overcrowding, lack of jobs, prejudice, war • Pull Factors – Advantages in one place that cause people to move there – Education, freedom, rights, and safety Passenger Train in Germany • 5) Human-Environment Interaction • People often adapted their way of life to the natural resources and local environment • People also change their surroundings in order to suit their needs • Examples include building a dam, driving a car or turning on an air conditioner Eskimo Igloo