* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download thinking like a geographer test review
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
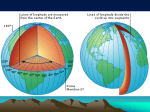
THINKING LIKE A GEOGRAPHER TEST REVIEW TEST IS ON FRIDAY, SEPT. 5!!!! STUDY STUDY STUDY! • 1. Geography is the study of….. The distribution and interaction of Earth’s physical and human features • 2. The most important question geographers ask is…… Where • 3. When something is transferred from one region to many other regions through space and time is known as…. Spatial Diffusion • 4. The fundamental element in the study of geography is identifying ….. Spatial Relationships • 5. The study of the impact of language, art, laws, and customs of people of the earth is known as….. Human Geography • 6. The study of the features of the earth and the changes in those features is known as…. Physical Geography Theme Description Examples 7. Location Relative and Absolute Where something is located on the Earth Near By = Relative 30N 120W = Absolute 8. Place Physical and Human Describing the Area Physical = Mountains 9. Movement Things moving through travel and communication Cars, Planes, Buses, Bikes, Facebook, MySpace, Phone 10. Region Grouping common places Gulf Coast, Asia, Midwest 11. Human Environment Interaction How people depend, modify, and adapt to the environment Depend for food and water, Have AC when it is hot, Dressing for the weather changes, Building Roads and Bridges Human = Dress • 12. Paris, France is located at 48N and 2E (exact global location). This is an example of …. Absolute Location • 13. The Midwest is known as America’s Bread Basket. This is an example of …. Region • 14. Using the internet to communicate with a friend in Portugal. This is an example of …. Movement • 15. This type of map show how humans have divided the surface of the earth into countries, states, etc…. Political Map • 16. This general reference map shows both natural and man-made features on the earth… Topographic Map • 17. This type of map shows how earth’s physical features such as mountains, rivers, plains, and lakes…. Physical • 18. This type of map shows the population density of an area… Special Purpose/Thematic Map • 19. This section on a map shows the meaning of the symbols… L- Legend • 20. The name of a map. T- Title • 21. The symbol that shows the direction on the map should be oriented in. O- Orientation • 22. Which set of imaginary lines goes around the earth over the poles? Longitude lines • 23. What geographic tool is a 3-D representation of the earth? Globe • 24. What is the name of the parallel lines on a map or glove that runs east and west; used to measure distances north or south of the equator? Latitude Lines • 25. What imaginary line divides the earth into eastern and western halves? (Hint: The line of longitude that runs through Greenwich, England at 0 degrees) Prime Meridian • 26. A person, who creates map projections, calculates latitude and longitude, calculates exact locations, and is known as a map maker is a…. Cartographer • 27. Spain and New York are both located in which Hemisphere? Northern • 28. Countries east of the Prime Meridian are in which Hemisphere? Eastern • 29. An image of Earth, taken from an orbiting camera or satellite. Remote sensor • 30. A visual representation of all or part of Earth’s surface, drawn to scale and made for a specific purpose. Map • 31. What term is used to name each half of the earth, divided either north and south or east and west? Hemisphere • 32. Which term is used to name a drawing of the earth’s surfaces that reduces distortions that are caused by converting 3-D to 2-D? Map Projections • 33. What imaginary line divides the earth into northern and southern halves? Equator • 34. What is a system that creates specialized maps from digital map information stored in a databank? GIS (Geographic Information Systems) • 35. What is a series of satellites that orbit the earth to pick up geographic data? Landsat