* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Network Topologies
Distributed firewall wikipedia , lookup
Computer security wikipedia , lookup
Wake-on-LAN wikipedia , lookup
Recursive InterNetwork Architecture (RINA) wikipedia , lookup
Zero-configuration networking wikipedia , lookup
Cracking of wireless networks wikipedia , lookup
Network tap wikipedia , lookup
Piggybacking (Internet access) wikipedia , lookup
Computer network wikipedia , lookup
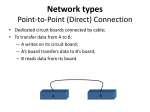
Data Communication & Computer Networks Lecture #5 Mrs. Vasanthi Muniasamy Department of Information System King Khalid university 1 Data Communication The transfer of data/messages from one point to another point. 2 Basic Elements of Communication System Three basic elements of communication system are:1. A sender (source) which creates the message to transmitted. 2. A medium which carries the message. 3. A receiver (destination) which receives the message. 3 Basic Elements of Communication System Sender (source) Medium Receiver (destination) 4 Data Transmission Modes There are three ways, modes for transmitting data from one point to another. These are simplex, halfduplex and full-duplex. 5 Data Transmission Modes Simplex: If transmission is simplex, communication can take place in only one direction. For example, radio & T.V. etc. Half-Duplex: A half-duplex system can transmit data in both directions, but only in one direction at a time. For example, wireless etc. Full-Duplex: A full-duplex system is used that allows information to flow simultaneously in both directions on the transmission path. For example, telephone etc. 6 Data Transmission Modes Sender Sender or Receiver Sender & Receiver Simplex Half-Duplex or Full-Duplex and Receiver Receiver or Sender Sender & Receiver 7 Digital & Analog Transmission Digital transmission sends data as distinct pulses, either on or off, in much the same way that data travels through the computer. Analog transmission, a continuous electrical signal in the form of a wave. 8 Digital & Analog Transmission 9 Digital & Analog Transmission Frequency: It is the rate (cycles/sec or HZ) at which the signals repeat. Bandwidth: It is the range of frequencies that is available for the transmission of data. Channel: A channel is a portion of the communications medium allocated to the sender and receiver for conveying information between them. Modems: A modem is a device that converts a digital signal to an analog signal and vice versa. 10 11 Transmission Media There are several types of physical channels (communication media) through which data can be transmitted from one point to another. Some of the most common data transmission medium are as under:- 12 Transmission Media Wire Pairs: It is also known as twisted pair. Wire pairs are wires twisted together to form a cable, which is thin insulated. Wire pairs are inexpensive. Application: Telephone networks, within buildings & LAN etc. Benefits & Drawbacks: Cheap Low data rate Short range Easy to work with 13 Transmission Media Coaxial Cable: are groups of specially wrapped and insulated wire lines that are able to transmit data at very high rates. These cables can transmit data much faster than wire pairs. Application: Long distance telephone transmission, Local Area Networks etc. 14 Transmission Media Fiber Optics: Instead of using electricity to send data, fiber optics uses light. Application: Long haul trunks, Metropolitan trunks, LAN & WAN etc. Benefits & Drawbacks: Greater capacity Smaller size & weight Lower attenuation 15 Protocol A protocol is a set of rules and procedures established to control transmission between two points. Some common protocols are: TCP/IP (Transmission Control Protocol/Internet protocol) IPX (Internet Packet Exchange) etc. 16 Computer Networks Network: A computer system that uses communications equipment to connect two or more computers and their resources. Network Interface Card (NIC): A circuit board that can be inserted into a slot inside a personal computer to allow it to send and receive messages on a LAN. Node: A device, usually a personal computer, that is connected to a computer. Topology: The physical layout of a network is called a topology. Some common network topologies are as under:- 17 Network Topologies Star Topology: A star network has a hub computer that is responsible for managing the network. All messages are routed through the central computer, which acts as a traffic cop to prevent collision. 18 Network Topologies Star Topology: Any connection failure between a node and the hub will not affect the overall system. However, if the hub computer fails, the network fails. 19 Network Topologies Ring Topology: A ring network links all nodes together in a circular chain. Data messages travel in only one direction around the ring. Any data passes by, is examined by the node to see if it is addressee; if not, the 20 Network Topologies Ring Topology: Data is passed on to the next node in the ring.. Since data travels in only one direction, there is no danger of data collision. However, if one node fails, the entire network fails. 21 Network Topologies Bus Topology: A bus network has a single line to which all the network nodes are attached. Computers on the network transmit data in the hope that it will not collide with data transmitted by other Nodes. If this happens, the sending node simply tries again. Furthermore, if one node fails, it does not affect the rest of the network. 22 Computer Networks There are two ways to organize the resources in networking, which are : Peer to Peer Networking Client/Server Networking 23 Computer Networks Peer to Peer Networking: In which, a group of computers communicate directly with each other, rather than through a central server. Client/Server Networking: A client/server arrangement involves a server, the computer that controls the networks. 24 Kinds of Networks There are different kinds of networks, for example, LAN (Local Area Networks) WAN (Wide Area Networks) MAN (Metropolitan Area Network) 25 Kinds of Networks Local Area Networks: A network which spreads over limited geographical area is called as LAN. Wide Area Networks: A WAN is a network of geographically distant computers. (e.g. Internet) 26 Local Area Networks LAN refers to a network with the following characteristics: The network is confined to a small area, typically a single building. The network consists of a shared transmission medium. The data rate on the network is high, anywhere from 1 Mbps to 100 Mbps. 27 Local Area Networks LAN Protocols: The two most common network protocols for LANs are Ethernet & Token Ring network. Ethernet – The network protocol which uses the high speed network cable. Ethernet uses a bus topology, inexpensive and relatively simple to set up. Since all the computers in a LAN use the same cable to transmit and receive data, they must follow a set of rules about when to communicate; otherwise two or more computers could transmit at the same time, 28 Local Area Networks Ethernet – Causing lost messages. So, if the cable is in use, the computer must wait. When the cable is free from other transmissions, the computer can begin transmitting immediately. This transmission method is called by the fancy name of carrier sense multiple access with collision detection (CSMA/CD). 29 Local Area Networks Token Ring – which is closely associated with IBM, works on the concept of a ring network topology, using a token, a kind of electronic signal. Only one token is available on the network. When a computer on a network wishes to transmit, it first captures the token; only then can it transmit data. When the computer has sent its message, it releases the token back to the network. Since only one token is circulating around the network, only one device is able to access the network at a time. 30 Network Applications Electronic Mail Voice Mail Facsimile Technology (FAX) Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) E–Commerce Instant Banking Video Conferencing etc. 31 Internet – & its use… ISP - An internet service provider provides the facility to connect the internet. Browser – is a software on the user’s computer that allows the user to access the internet, for example, Internet explorer & Netscape communicator etc. Domain Name – Which is the address of the specific web page. Search Engine – is a software that lets a user specify search terms; the search engine then finds sites that fit those terms. 32