* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Q2. What Are the Components of a LAN?
Internet protocol suite wikipedia , lookup
Deep packet inspection wikipedia , lookup
Computer security wikipedia , lookup
Net neutrality law wikipedia , lookup
Recursive InterNetwork Architecture (RINA) wikipedia , lookup
Wireless security wikipedia , lookup
Wake-on-LAN wikipedia , lookup
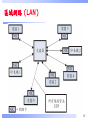
Network tap wikipedia , lookup
Computer network wikipedia , lookup
Airborne Networking wikipedia , lookup
Distributed firewall wikipedia , lookup
Zero-configuration networking wikipedia , lookup
Management Information Systems Chapter 6 Data Communications This Could Happen to You Dee needs to decide where she will run the blog It needs to be private to maintain a competitive advantage Sales people need to have easy access Passwords may be needed to restrict access Emerson has a private network Protected by firewall Employees access through VPN (Virtual Private Network) Can be protected from unauthorized access Sales people can access with same password they already use 2 Study Questions Q1. What is a computer network? Q2. What are the components of a LAN? Q3. What are the alternatives for a WAN? Q4. How does encryption work? Q5. What is the purpose of a firewall? Q6. What is a VPN and why is it important? 3 Q1. What Is a Computer Network? Network Collection of computers Communicate with one another over transmission line Three basic types Local area network (LAN) Wide area network (WAN) Internet 4 主要的網路類型 5 LAN Connects computers residing in single location 2 to several hundred computers One geographic area Communication lines can be placed where the organization wants 6 WAN Connect computers in different geographical areas Two or more cities Uses communication networks from vendors Licensed by government 7 Internet Network of networks Connect LANs, WANs, and other internets Private networks of networks Use a variety of communication methods and conventions Seamless flow of data provided by layered protocol Set of rules that communicating devices follow 8 Q2. What Are the Components of a LAN? Local area network Computers connected on single company site Usually located within half mile area Property controlled by company operating network Company can run cabling as necessary Components Switch Special purpose computer that receives and transmits messages Network Interface Card (NIC) Hardware that connects each device’s circuitry to the cable Onboard NIC or card that fits into an expansion slot 9 區域網路(LAN) 10 NIC Devices MAC address Unique identifier Media connections Unshielded twisted pair (UTP) cable RJ-45 connector Optical fiber cables Light rays reflected inside glass core surrounded by cladding Uses ST and SC connectors 11 網路卡 圖6-3 12 無遮蔽式雙絞線電纜 13 光纖電纜 14 IEEE 802.3 Protocol Ethernet protocol standard Specifies hardware characteristics Describes how messages are packages Determines how messages are processed Operates at Layers 1 and 2 of TCP/IP-OSI architecture Personal computers usually support 10/100/1000 Ethernet 15 LANs with Wireless Connections Wireless NIC (WNIC) LAN operation NICs operate on 802.3 protocol WNICs operate on 802.11 protocol WNICS connect to Access Point (AP) AP processes both standards 16 無線區域網路 17 LAN 和 WAN 18 Q3. What Are the Alternatives for a WAN? WANs connect computers at separate sites No cabling between sites Cable connections made through licensed communications companies Internet service provider (ISP) Provides legitimate Internet address Serves as gateway to Internet Pay for Internet 19 Connecting to the ISP Connections made through: Regular telephone lines Use of DSL line Cable TV lines All require digital data to be converted to analog Modem makes conversion 20 類比與數位訊號 21 個人電腦的網際網路管道 22 MIS In Use: Larry Jones (Student) Network Services Larry set up LAN networks Realized that he had to offer support Customers had problems Customers needed to add more devices Coupled installation with support package Extra charges for support beyond normal wear and tear 23 Dial-Up Modems Handles conversion between analog and digital Connection made by dialing ISP Maximum transmission speed of 56 kbps Modulation governed by V.34, V.90. or V.92 standards PPP (Point-to-Point Protocol) controls message packaging and handling 24 DSL Modems Operates over telephone lines Do not interfere with voice telephone service Faster data transmission than dial-up Connection always maintained Use their own Layer 1 and 2 protocols Download and upload speeds vary Asymmetric digital subscriber lines (ADSL) Symmetrical digital subscriber lines (SDSL) 25 Cable Modems (1) Provide high-speed data transmission Use cable television lines High-capacity optical fiber cable run to neighborhood distribution center Television cables connect at distribution center and runs to subscribers Does not interfere with television transmission Up to 500 subscribers connected at each center Performance varies based on number connected 26 Cable Modems (2) Download speed up to 10Mbps, upload up to 256 kbps Operate with Layer 1 and 2 protocols Speeds Narrowband Transmission speeds less then 56 kbps Broadband Transmission speeds in excess of 256 kbps 27 Networks of Leased Lines WAN connects computers located at geographically distributed sites Access devices connect sites to transmission Switch Router Alternative is leasing lines T1, T3 Set up as a point-to-point line Only predefined sites can use leased lines Provide low cost per bit transmitted 28 使用租用線路的 WAN 29 Transmission Line Types, Uses and Speeds Figure 6-11 30 Problem Solving Guide: Thinking Exponentially Is Not Possible, but… Nathan Myhrvoid claimed that: Humans cannot think exponentially Think of fastest linear change and extrapolate from there Was writing about growth of magnetic storage Also applies to growth of computer network phenomena Ubiquitous and cheap connectivity is growing exponentially What are the threats and opportunities? 31 Exponential Phenomena Brings Changes Technology doesn’t drive people to do new things Social progress occurs in small, evolutionary, adaptive steps Technology may enable a capability, but people may not want it People want to do what they are doing more easily They want to solve existing problems Respond by hedging your bets The more time involved, the more potential for error 32 Public Switched Data Network (PSDN) Network of computers and leased lines Developed and maintained by vendor Time leased on network Utility that supplies network for other companies to lease Each site leases line to connect to PSDN network at access point Point of presence (POP) Saves setup and maintenance activities 33 PSDN Protocols Frame relay Process traffic at 56 kbps to 40 Mbps Simplest and easiest to support Asynchronous transfer mode (ATM) Process speeds from 1 to 156 Mbps Ethernet Operates at speeds of 10 to 40 Gpbs 34 使用 PSDN 的廣域網路 35 Criteria for Comparing WANs (1) Costs Setup costs Examples: costs of acquiring lines and equipment Operational costs Examples: lease fees, ISP charges, training Maintenance costs Examples: periodic maintenance, repair, upgrades 36 Criteria for Comparing WANs (2) Performance Speed Latency Availability Loss rate Transparency Performance guarantees Growth potential Length of contract commitment 37 比 較 網 路 的 考 量 點 38 Q4. Security Guide: How Does Encryption Work? (1) Encryption Process of transforming clear text into coded text Used for secure storage or communication Uses algorithms DES, 3DES, AES Key Used to encrypt data Algorithm applies key to produce coded message Symmetric encryption Asymmetric encryption 39 Security Guide: How Does Encryption Work? (2) Public key / Private key Public key used to encrypt messages Public key sent to other party to encode messages to be sent back Decoded with private key Complex and slow HTTPS Secure communication over Internet Encrypted using SSL (Secure Socket Layer) / TLS (Transport Layer Security) protocol Encodes messages using Web site’s public key, decoded with private key 40 Q5. What Is the Purpose of a Firewall? Computer device that prevents unauthorized network access May be special-purpose computer or program Organizations may have multiple firewalls Perimeter firewalls sit outside organizational network Internal firewalls are inside network Packet-filtering firewalls examine source address, destination address, and other data before allowing message to pass May filter both incoming and outgoing messages Access control list (ACL) encodes rules stating what packets are allowed or prohibited 41 多重防火牆的使用 42 Q6. What Is a VPN and Why Are VPNs Important? Virtual private network Uses Internet or private network to create appearance of point-to-point connections Uses public Internet to create appearance of private network Client and server have point-to-point connection called tunnel Private pathway over shared network Secure, encrypted communications 43 以 VPN 做遠距連結:實際、實體連結 44 以 VPN 做遠距連結:表面上的連結 45 使用 VPN 的廣域網路 46 Ethics Guide: Human Networks Matter More Six degrees of separation Often unaware of those in the chain Build personal human networks for success Someone, somewhere that you need to know or will need to know Meet people at professional and social situations Pass out and collect cards Converse to expand network Look for new channels Social network theory Weak and strong ties 47 How Does the Knowledge in This Chapter Help Dee? (1) Dee and salespeople use thin client computers Dee creates blog entries on Web pages using Moveable Type Salespeople use pages served by Moveable Type Client computers contain VPN client software Interacts with VPN server via Internet Secure, private connections Firewalls stop traffic not addressed to VPN server Salespeople know how to use VPN 48 How Does the Knowledge in This Chapter Help Dee? (2) IT department cannot schedule resources to setup blog server in timely fashion Will not allow outside person to do setup Would then have access to system Consultant can create server on unprotected test server Can be copied onto network server after acceptance Requires some internal IT labor Consultant could include Trojan horse virus or malware Install only software from known sources Code should not reside on production server 49 How Does the Knowledge in This Chapter Help Dee? (3) Dee negotiates with IT department Threatens to set up own system of user Ids and passwords Says she will set up blog on public server Would cause confusion that would add to IT department’s work Her proposal is the lesser of two evils 50 在網誌使用防火牆和 VPN 51